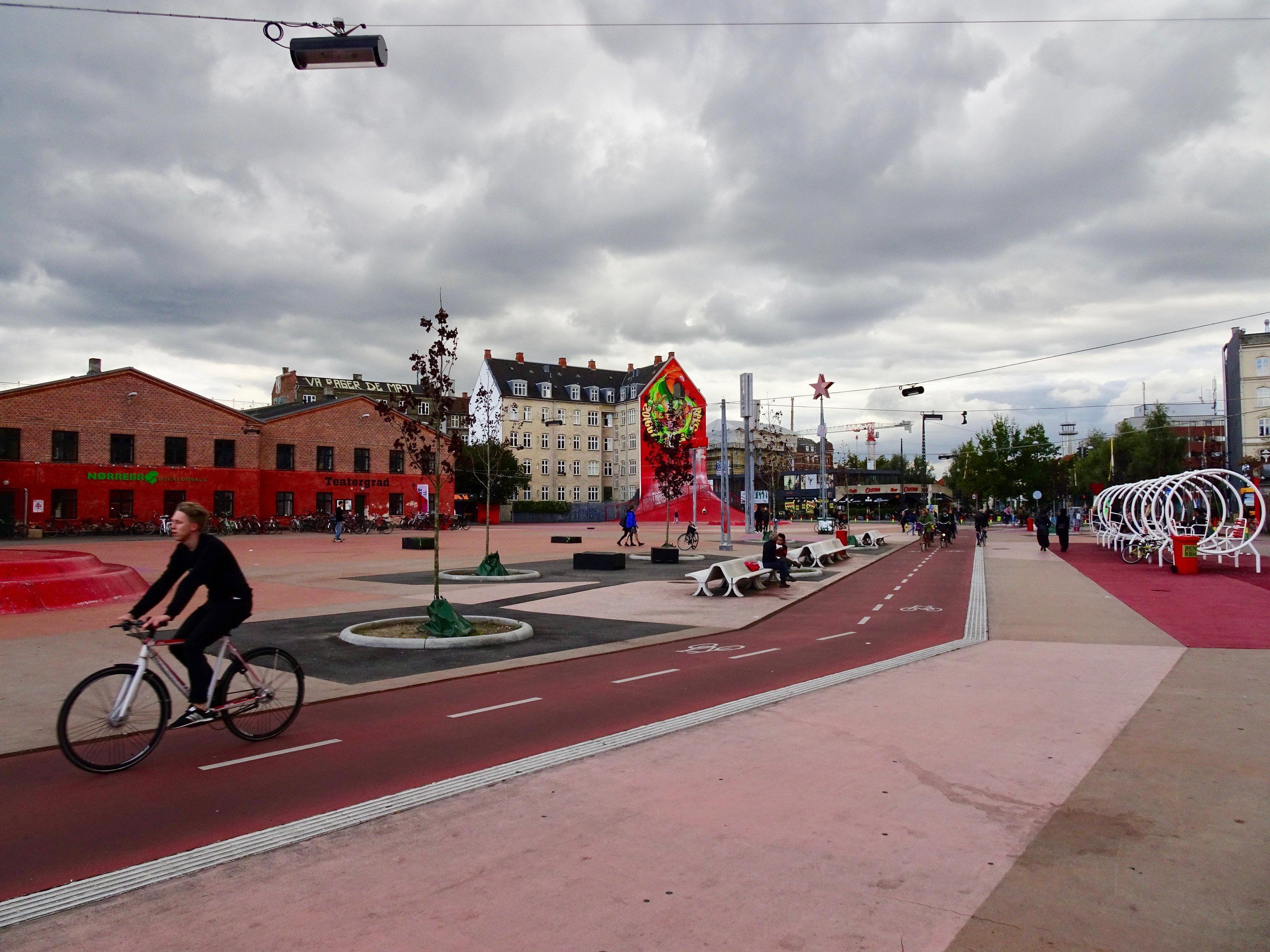
European public spaces are becoming more original, but also more homogeneous. The author of an architecture thesis, written at EPFL, explains this paradox and calls on critics and public authorities to do something about it.
For almost two decades, designers of public spaces throughout Europe have been striving to give passers-by unique experiences. Using a multitude of materials, shapes, interactive street furniture and sensory effects, these squares, streets and walkways are becoming genuine tourist attractions for their cities. The problem is that, rather than integrating with the existing urban environment, the public spaces of the 21st century are tending to diverge from it intentionally and, most importantly, to look alike.
This is one of the findings in Sonia Curnier’s thesis, which she researched at EPFL’s Theory and History of Architecture Laboratory (LTH2), supervised by Bruno Marchand. Until now, academic research has mainly focused on the use of public spaces, for example observing whether or not passers-by really connect with them, but spent very little time looking at their design. This is the novel approach taken by Curnier’s thesis, which offers the first comprehensive overview of the subject. The public defense of his Ph.D. will take place on 2 May at EPFL.