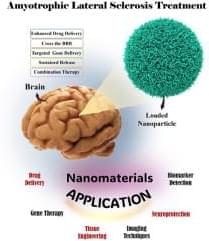
This review explores the transformative potential of nanotechnology in the treatment and diagnosis of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), a progressive neurodegenerative disorder characterized by motor neuron degeneration, muscle weakness, and eventual paralysis. Nanotechnology offers innovative solutions across various domains, including targeted drug delivery, neuroprotection, gene therapy and editing, biomarker detection, advanced imaging techniques, and tissue engineering. By enhancing the precision and efficacy of therapeutic interventions, nanotechnology facilitates key advancements such as crossing the blood-brain barrier, targeting specific cell types, achieving sustained therapeutic release, and enabling combination therapies tailored to the complex pathophysiology of ALS.
Promising breakthroughs in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis treatment through nanotechnology’s unexplored frontier
Posted in bioengineering, biotech/medical, nanotechnology, neuroscience | Leave a Comment on Promising breakthroughs in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis treatment through nanotechnology’s unexplored frontier