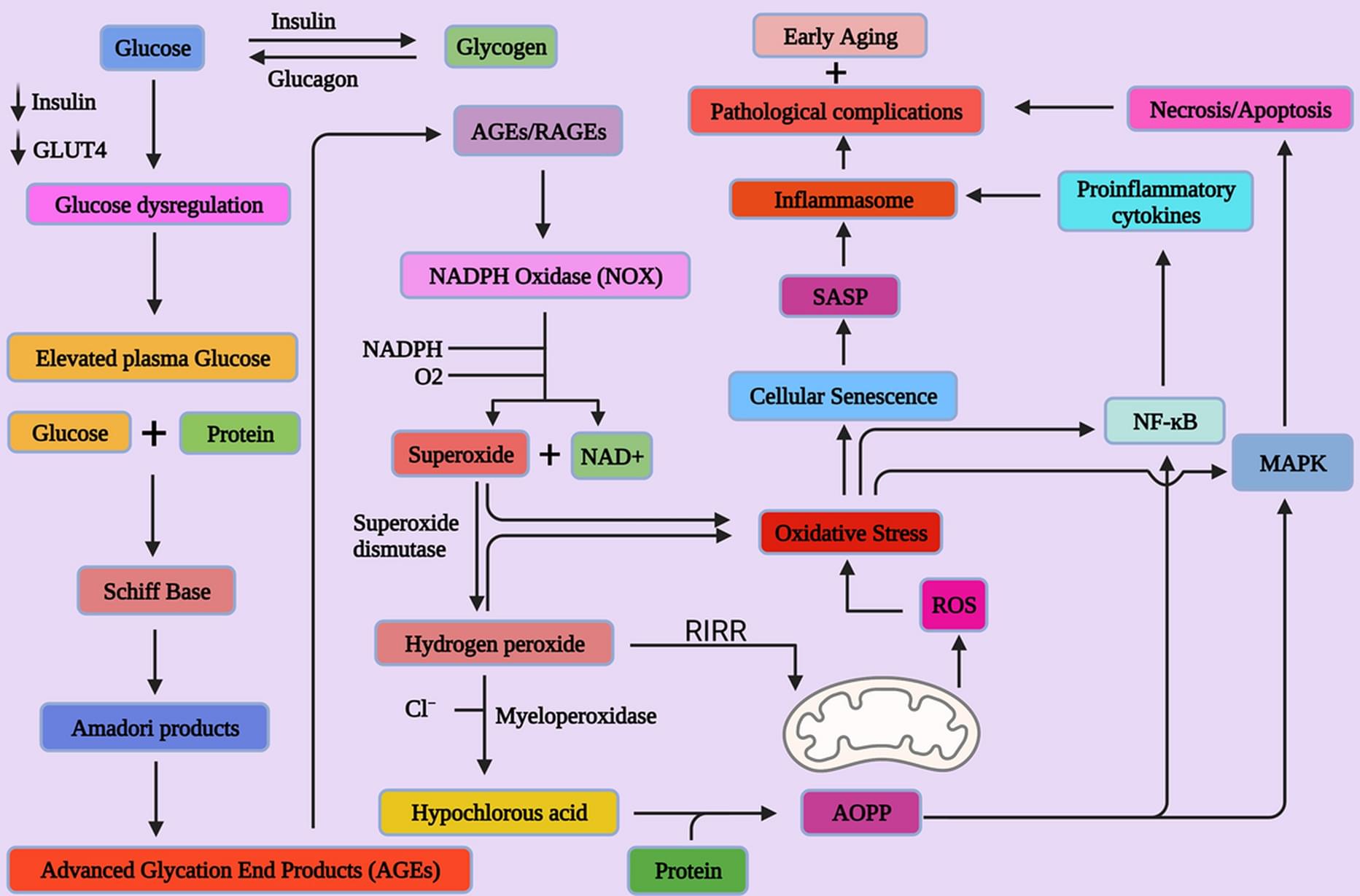
Geroprotectors, a class of compounds that ameliorate molecular, cellular, or physiological aging-related alterations, have garnered significant attention in the quest to promote healthy aging and extend the human health span. Among these, Calorie Restriction Mimetics (CRMs) have emerged as promising candidates due to their potential to mimic the benefits of calorie restriction, a dietary approach involving reduced calorie intake without malnutrition. Prospective CRMs may include biguanides (metformin and aminoguanidine), which exert effects on the insulin signaling pathway; rapamycin, which interacts with mTOR signaling pathways; and stilbenes (resveratrol), which influences stress signaling pathways and promotes the activation of AMPK, impacting mitochondrial metabolism in addition to the activity of FOXO and sirtuin.