Mar 4, 2016
Goodyear Thinks Tires Of The Future Will Be 3D-Printed Spheres
Posted by Shailesh Prasad in categories: 3D printing, transportation
These #3Dprinted sphere-shaped tires could be the future of automobiles thanks to Goodyear.
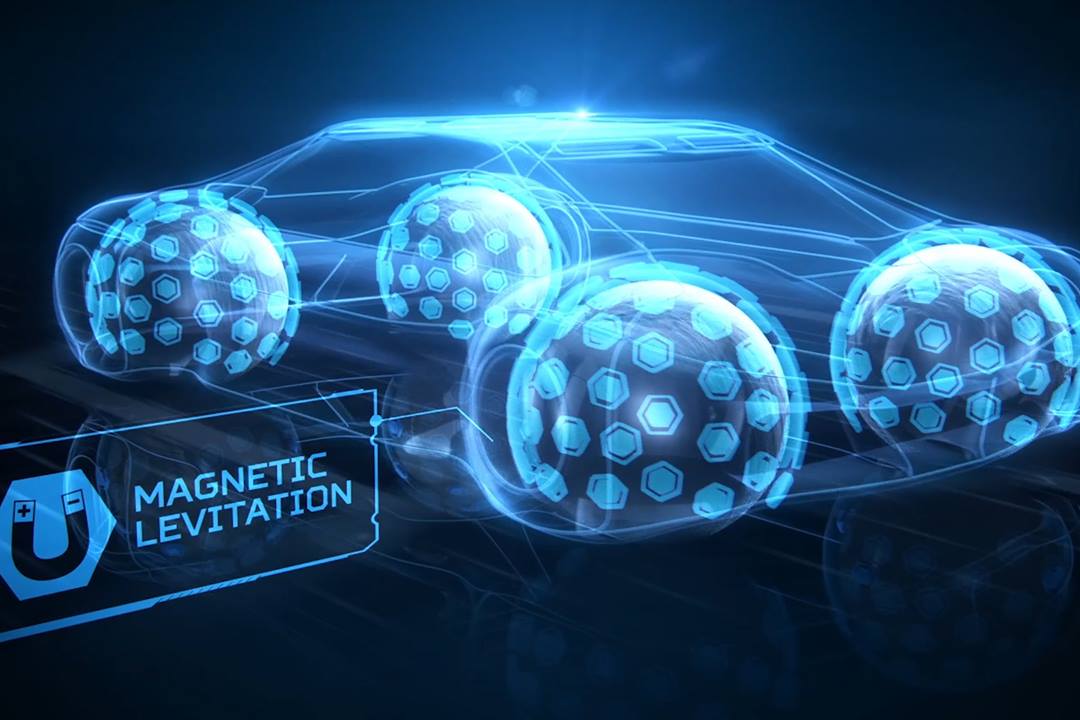
These #3Dprinted sphere-shaped tires could be the future of automobiles thanks to Goodyear.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ySPvBbfY2Fc
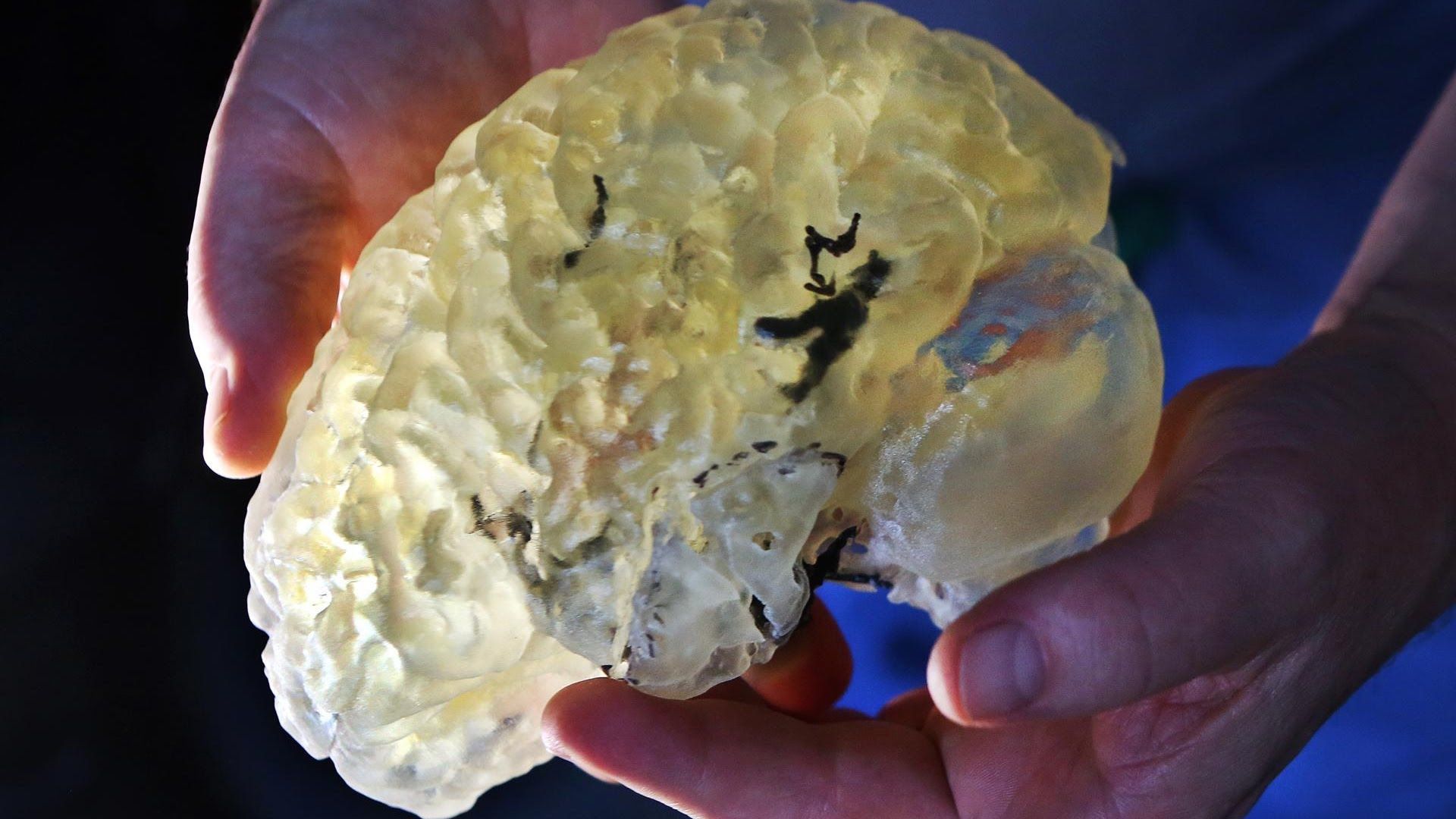
A 3D-printed layered structure that incorporates neural cells to mimic the structure of brain tissue has been created by researchers at the ARC Centre of Excellence for Electromaterials Science (ACES) in Australia, and it could have major consequences in studying and treating conditions such as schizophrenia and Alzheimer’s. The three-dimensional structure will allow scientists to better understand the complex nature of the brain and its 86 billion nerve cells. We look at the benefits and risks of this scientific breakthrough on the Lip News with Jose Marcelino Ortiz and Jo Ankier.
http://motherboard.vice.com/read/researchers-are-getting-clo…ing-brains
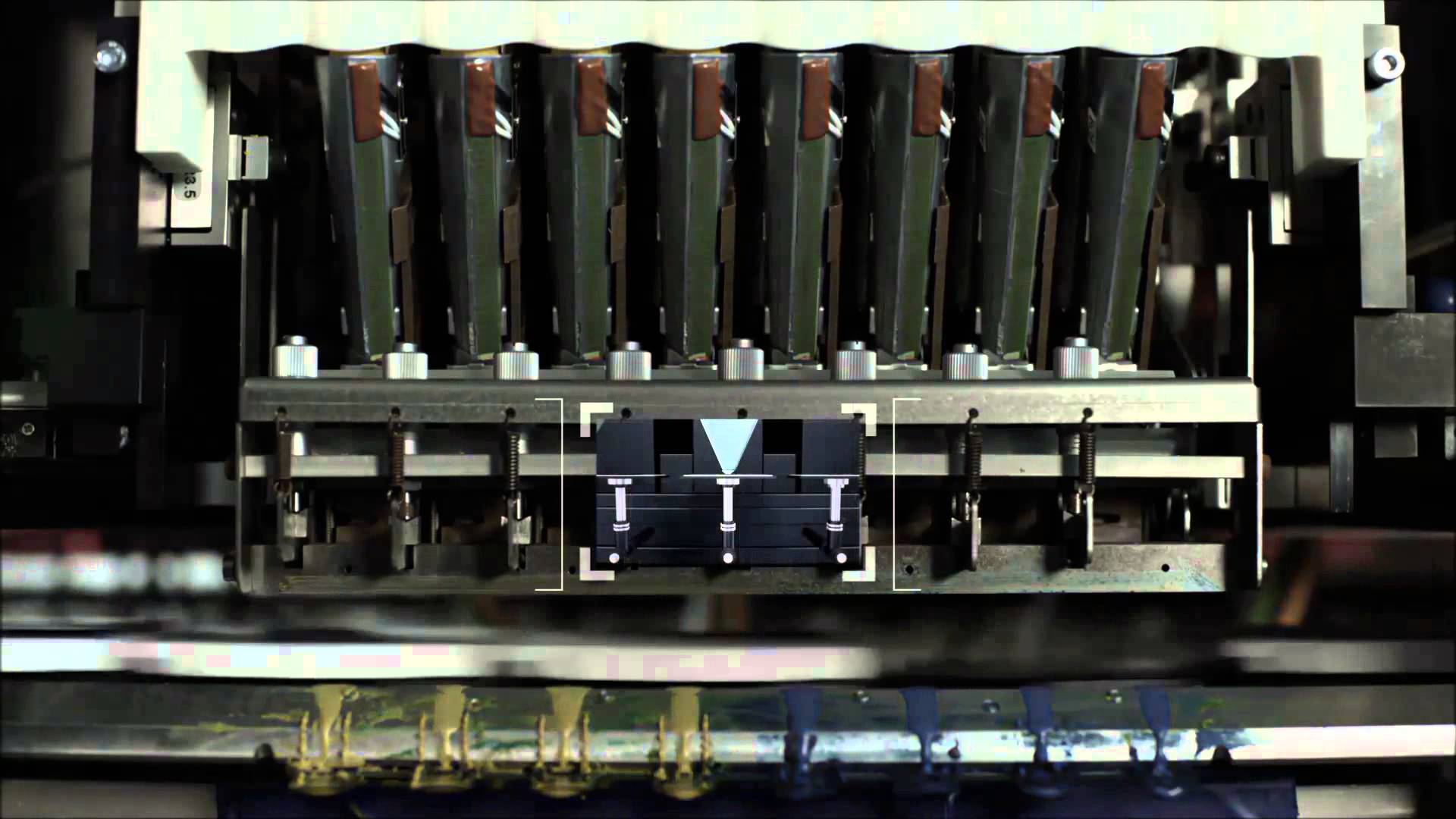
At the end of last year, Davide Sher predicted that 2016 would see metal 3D printing move from a technology capable of producing small batches to a fully-automated method for serial manufacturing. Davide cited a number of machines in development that herald the age of serial metal 3D printing, but he may have left one system out: the Hyproline platform.

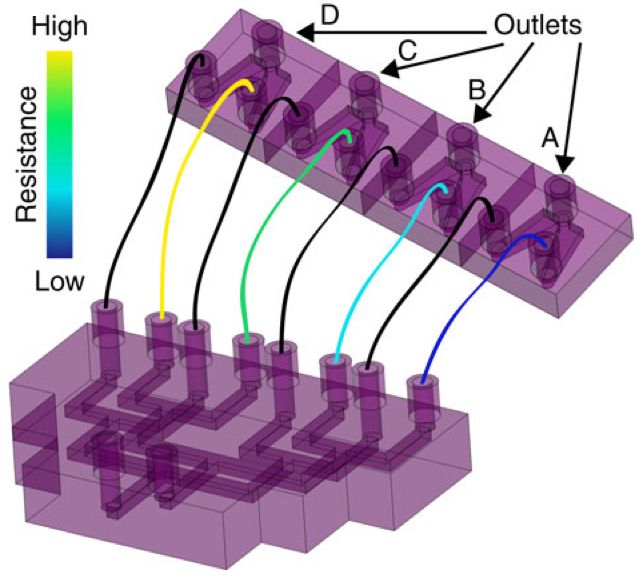
Nanoparticles form in a 3-D-printed microfluidic channel. Each droplet shown here is about 250 micrometers in diameter, and contains billions of platinum nanoparticles. (credit: Richard Brutchey and Noah Malmstadt/USC)
USC researchers have created an automated method of manufacturing nanoparticles that may transform the process from an expensive, painstaking, batch-by-batch process by a technician in a chemistry lab, mixing up a batch of chemicals by hand in traditional lab flasks and beakers.
Continue reading “A practical solution to mass-producing low-cost nanoparticles” »
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=deCY0_Zveeg&feature=youtu.be
An Australian neurosurgeon has completed a world-first marathon surgery removing cancer-riddled vertebrae and successfully replacing them with a 3D-printed body part.
Just Amazing
Ralph Mobbs, a neurosurgeon at the Prince of Wales Hospital in Sydney, made medical history in late 2015 when he successfully replaced two vertebrae with custom made prosthesis. The patient, in his 60s, suffered from Chordoma, a particularly nasty form of cancer that had formed on his top two vertebrae and threatened to cinch off his spinal cord as it grew. That would have left him a quadriplegic. Complicating matters, those top two vertebrae are what allow you to turn and tilt your head, so it’s not like doctors can easily fashion a replacement out of bone grafted from another part of the patient’s body. They have to fit perfectly and that’s where the 3D printers come in.
Mobbs worked with Anatomics, an Australian medical device manufacturer, to craft perfect replicas of the patient’s top two vertebrae out of titanium. This is the first time that these two particular neck bones have been printed and installed. “To be able to get the printed implant that you know will fit perfectly because you’ve already done the operation on a model … It was just a pure delight,” Mobbs told Mashable Australia. “It was as if someone had switched on a light and said ‘crikey, if this isn’t the future, well then I don’t know what is’.”
Continue reading “Doctors implant 3D-printed vertebrae in ‘world’s first’ surgery” »
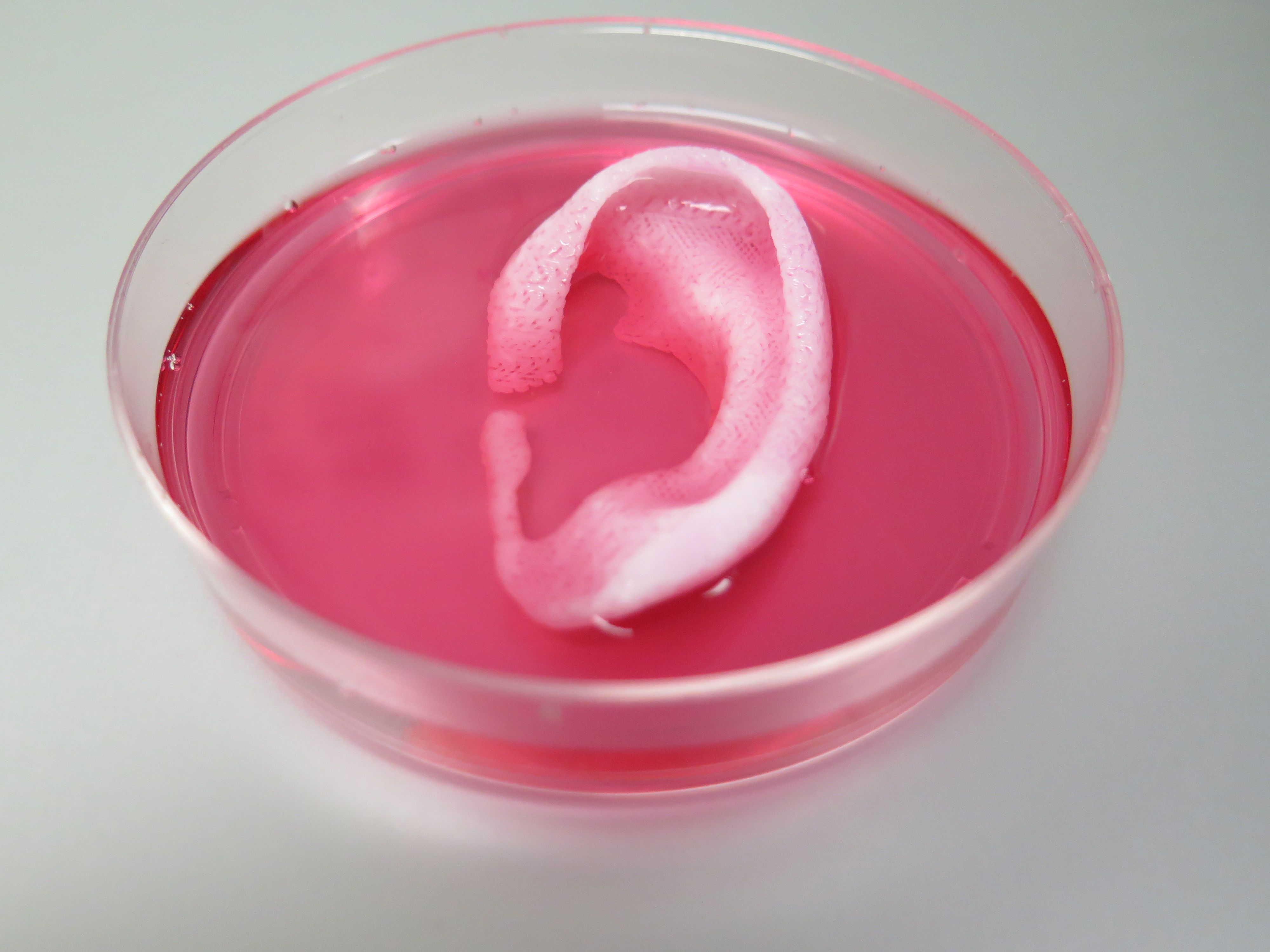
Using a sophisticated, custom-designed 3D printer, regenerative medicine scientists at Wake Forest Baptist Medical Center have proved that it is feasible to print living tissue structures to replace injured or diseased tissue in patients.
Reporting in Nature Biotechnology, the scientists said they printed ear, bone and muscle structures. When implanted in animals, the structures matured into functional tissue and developed a system of blood vessels. Most importantly, these early results indicate that the structures have the right size, strength and function for use in humans.
Continue reading “Regenerative medicine scientists ‘print’ replacement tissue” »
MOFFETT FIELD, California — Within five years, companies could begin in-orbit manufacturing and assembly of communications satellite reflectors or other large structures, according to Made in Space, the Silicon Valley startup that sent the first 3D printer to the International Space Station in 2014.
As Made in Space prepares to send a second 3D printer into orbit, the company is beginning work with Northrop Grumman and Oceaneering Space Systems on Archinaut, an ambitious effort to build a 3D printer equipped with a robotic arm that the team plans to install in an external space station pod, under a two-year, $20 million NASA contract. The project will culminate in 2018 with an on-orbit demonstration of Archinaut’s ability to additively manufacture and assemble a large, complex structure, said Andrew Rush, Made in Space president.
NASA’s selected the Archinaut project, officially known as Versatile In-Space Robotic Precision Manufacturing and Assembly System, as part of its Tipping Points campaign, which funds demonstrations of space-related technologies on the verge of offering significant payoffs for government and commercial applications. Archinaut was one of three projects NASA selected in November that focus on robotic manufacturing and assembly of spacecraft and structures in orbit.
3D Printing hazardous to the environment due to toxins.
Three-dimensional (3D) printing, also known as additive manufacturing, refers to those technologies capable of developing 3D objects from raw materials, like metals and polymers based on computerized 3D parametric models.
