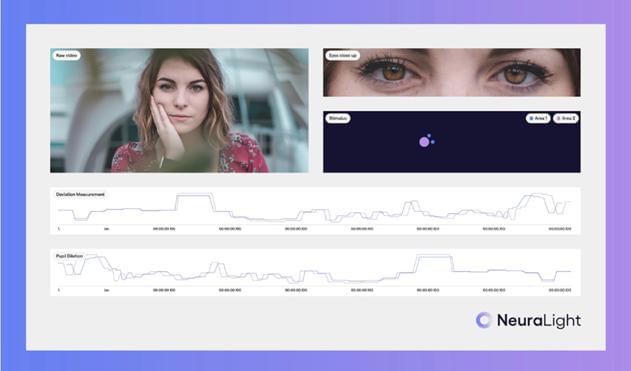
“The eyes are the windows to the soul.” It’s an ancient saying, and it illustrates what we know intuitively to be true — you can understand so much about a person by looking them deep in the eye. But how? And can we use this fact to understand disease?
One company is making big strides in this direction. Israel’s NeuraLight, which just won the Health and Medtech Innovation award at SXSW, was founded to bring science and AI to understanding the brain through the eyes.
A focal disease for NeuraLight is ALS, which is currently diagnosed through a subjective survey of about a dozen questions, followed by tests such as an EEG and MRI.
The patient’s eyes follow dots on a screen, and the AI system measures 106 parameters such as dilation and blink rate in less than 10 minutes. In other words, this will be an AI-enabled digital biomarker.