Archive for the ‘biotech/medical’ category: Page 1850
Nov 5, 2019
Forget Growing Weed—Make Yeast Spit Out CBD and THC Instead
Posted by Omuterema Akhahenda in category: biotech/medical
Now researchers have turned to yeast to do something more improbable: manufacturing the cannabis compounds CBD and THC. By loading brewer’s yeast with genes from the cannabis plant, they’ve turned the miracle microbes into cannabinoid factories. It’s a clever scheme in a larger movement to methodically pick apart and recreate marijuana’s many compounds, to better understand the plant’s true potential.
Yeast gives us beer and bread. Now researchers have engineered it to do something more improbable: manufacturing the cannabis compounds CBD and THC.
Nov 5, 2019
Israeli team develops novel therapy to target advanced cancerous tumors
Posted by Omuterema Akhahenda in categories: biotech/medical, innovation
Holon-based cancer immunotherapy company Compugen disclosed encouraging preliminary results on Tuesday from its Phase 1 clinical trial for an antibody acting against a novel cancer drug target (PVRIG) in patients with advanced solid tumors.
The Nasdaq and Tel Aviv-listed company, a pioneer in predictive drug target discovery, has developed innovative computational discovery platforms to identify new drug targets and subsequently produce first-in-class therapeutics. The clinical trial of the anti-PVRIG antibody, called COM701, aimed to assess the safety of escalating doses of the therapy in patients with advanced solid tumors, but also demonstrated initial signals of anti-tumor activity in the heavily pre-treated patient population enrolled in the study.
“We are encouraged by the emerging safety profile and initial signals of anti-tumor activity of COM701,” said Compugen president and CEO Dr. Anat Cohen-Dayan.
Nov 5, 2019
David Pearce — Experience Machines and Hedonic Treadmills
Posted by Mark Larkento in categories: biotech/medical, ethics, virtual reality

“…consider Robert Nozick’s thought-experiment in conjunction with Felipe De Brigard’s inverse experience machine argument: “If you like it, does it matter if it’s real?”
Does Nozick’s experience machine prove anything?
Continue reading “David Pearce — Experience Machines and Hedonic Treadmills” »
Nov 4, 2019
Scientists 3D-Printed Living Skin, Complete With Blood Vessels
Posted by Omuterema Akhahenda in categories: 3D printing, biotech/medical
Researchers claim to have 3D-printed skin that’s alive and has blood vessels. The new technique could greatly accelerate the healing process for patients who require skin grafts, such as burn victims. In an animal trial phase, the printed skin even connected to a mouse’s own blood vessels.
This could be a game changer for burn victims.
Nov 4, 2019
Drug combination preserves cognitive function in mice with Alzheimer’s disease
Posted by Paul Battista in categories: biotech/medical, life extension, neuroscience
A new study from the Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine shows that selectively removing senescent cells—cells that no longer divide—from brains with a form of Alzheimer’s disease can reduce brain damage and inflammation and slow the pace of cognitive decline. These findings, say researchers, add to evidence that senescent cells contribute to the damage caused by Alzheimer’s disease.
“Our results show that eliminating these cells may be a viable route to treat Alzheimer’s disease in humans,” says Mark Mattson, a professor of neuroscience at the School of Medicine and a senior investigator in the Laboratory of Neurosciences at the National Institute on Aging.
A report on the work was published April 1 in Nature Neuroscience.
Nov 4, 2019
Blood–brain barrier best breached by small molecules
Posted by Paul Battista in categories: biotech/medical, neuroscience
Focused ultrasound (FUS) can be used to help drugs pass from the bloodstream into the brain, but the technique’s effectiveness depends on the ultrasound pressure and the size of the drug molecules. Michael Valdez and colleagues at the University of Arizona measured how thoroughly differently sized molecules diffused into mouse brains under a range of ultrasound intensities, and found that the largest molecules could not be delivered under any safe FUS regime. The results set a limit on the types of drugs that might one day be used to treat neurological conditions like Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s disease (Ultrasound Med. Biol. 10.1016/j.ultrasmedbio.2019.08.024).
Usually, the brain is isolated from substances circulating in the bloodstream by the blood–brain barrier (BBB), a semipermeable layer of cells that permits only certain molecules to pass. This restricts the range of drugs that can be used in the brain to small, hydrophobic molecules (such as alcohol and caffeine), other small drugs like psychotropics and some antibiotics. Extending that range would open the door to new therapeutic possibilities, says Theodore Trouard, who led the team. “The ability to temporarily and safely open the BBB to allow drugs into the brain would help address a number of neurological diseases for which there is currently no effective treatment.”
Previous research has shown that such opening can be achieved by focusing an ultrasound beam in the brain while gas microbubbles circulate in the blood. The microbubbles – perfluorocarbon-filled lipid shells about 1 µm across – are inert while they move around the body, but rapidly expand and contract in the local pressure fluctuations caused by the ultrasound field. Mechanical forces exerted by this phenomenon create temporary gaps in the layer of cells that make up the BBB, giving larger molecules a chance to breach the brain’s defences.
Nov 4, 2019
China approves seaweed-based Alzheimer’s drug. It’s the first new one in 17 years
Posted by Paul Battista in categories: biotech/medical, neuroscience
Authorities in China have approved a drug for the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease, the first new medicine with the potential to treat the cognitive disorder in 17 years.
The seaweed-based drug, called Oligomannate, can be used for the treatment of mild to moderate Alzheimer’s, according to a statement from China’s drug safety agency. The approval is conditional however, meaning that while it can go on sale during additional clinical trials, it will be strictly monitored and could be withdrawn should any safety issues arise.
In September, the team behind the new drug, led by Geng Meiyu at the Shanghai Institute of Materia Medica under the Chinese Academy of Sciences, said they were inspired to look into seaweed due to the relatively low incidence of Alzheimer’s among people who consume it regularly.
Nov 4, 2019
How we Benefit from Getting our Genomes Sequenced
Posted by Paul Battista in categories: biotech/medical, finance, food, genetics, habitats, health, internet, mobile phones

When the first smartphones arrived, few people understood how they would change our reality. Today, our internet-connected mobile device maps our travel, manages our finances, delivers our dinner, and connects us to every corner of human knowledge. In less than a generation, it has become almost an extension of our central nervous system — so indispensable that we can’t imagine leaving home without it to guide us.
We are about to embark on another journey even more important to every individual and to human society. We are entering the age of genomics, an amazing future that will dramatically improve the health outcomes of people across the planet. Soon, we won’t be able to imagine a time when we left home without knowledge of our genome to guide us.
Continue reading “How we Benefit from Getting our Genomes Sequenced” »
Nov 4, 2019
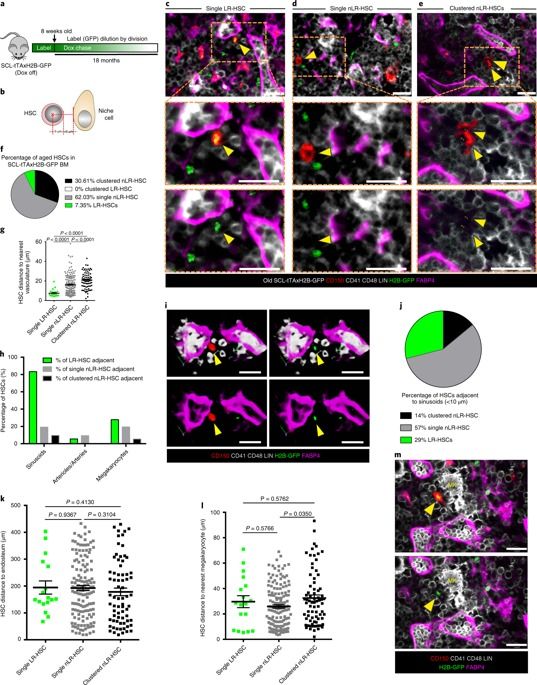
Haematopoietic stem cells in perisinusoidal niches are protected from ageing
Posted by Genevieve Klien in categories: biotech/medical, life extension
With ageing, intrinsic haematopoietic stem cell (HSC) activity decreases, resulting in impaired tissue homeostasis, reduced engraftment following transplantation and increased susceptibility to diseases. However, whether ageing also affects the HSC niche, and thereby impairs its capacity to support HSC function, is still widely debated. Here, by using in-vivo long-term label-retention assays we demonstrate that aged label-retaining HSCs, which are, in old mice, the most quiescent HSC subpopulation with the highest regenerative capacity and cellular polarity, reside predominantly in perisinusoidal niches. Furthermore, we demonstrate that sinusoidal niches are uniquely preserved in shape, morphology and number on ageing. Finally, we show that myeloablative chemotherapy can selectively disrupt aged sinusoidal niches in the long term, which is linked to the lack of recovery of endothelial Jag2 at sinusoids. Overall, our data characterize the functional alterations of the aged HSC niche and unveil that perisinusoidal niches are uniquely preserved and thereby protect HSCs from ageing.