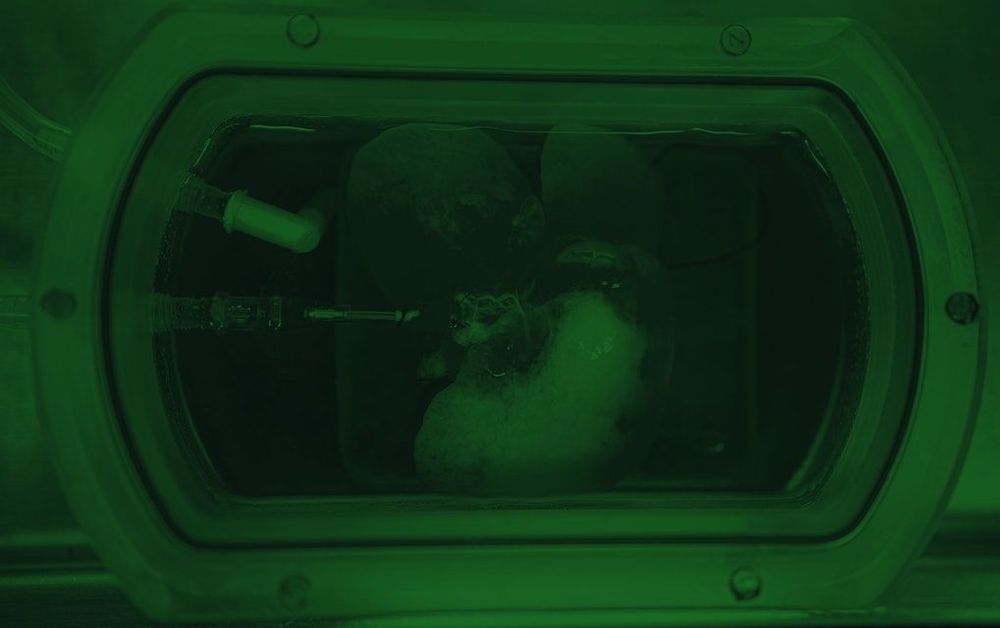
Scientists have successfully transplanted functional miniature livers into rats, after growing the bioengineered organs in the lab from reprogrammed human skin cells.
The experiment, which gave the animals working liver organs, could lay the groundwork for future treatments to address terminal liver failure – a disease that claims the lives of over 40,000 people in the US every year.
While there’s still a lot of work to be done before the technique can directly aid human patients, the researchers say their proof of concept may help underpin a future alternative to liver transplants, which are often incredibly expensive procedures to perform, in addition to being strictly limited by donor supply.