May 14, 2019
LATE: A Disease That Mimicks Alzheimer’s Disease
Posted by Steve Hill in categories: biotech/medical, life extension, neuroscience
A recent article, published in the Oxford journal Brain, categorizes and draws attention to an age-related disease that impacts the brain yet is widely unknown, even among scientists: limbic-predominant age-related TDP-43 encephalopathy (LATE) [1].
The symptoms of this disease are similar to those of Alzheimer’s disease. It causes cognitive impairment and, when presenting alongside Alzheimer’s disease, can lead to even faster degeneration along with heightened agitation and aggression.
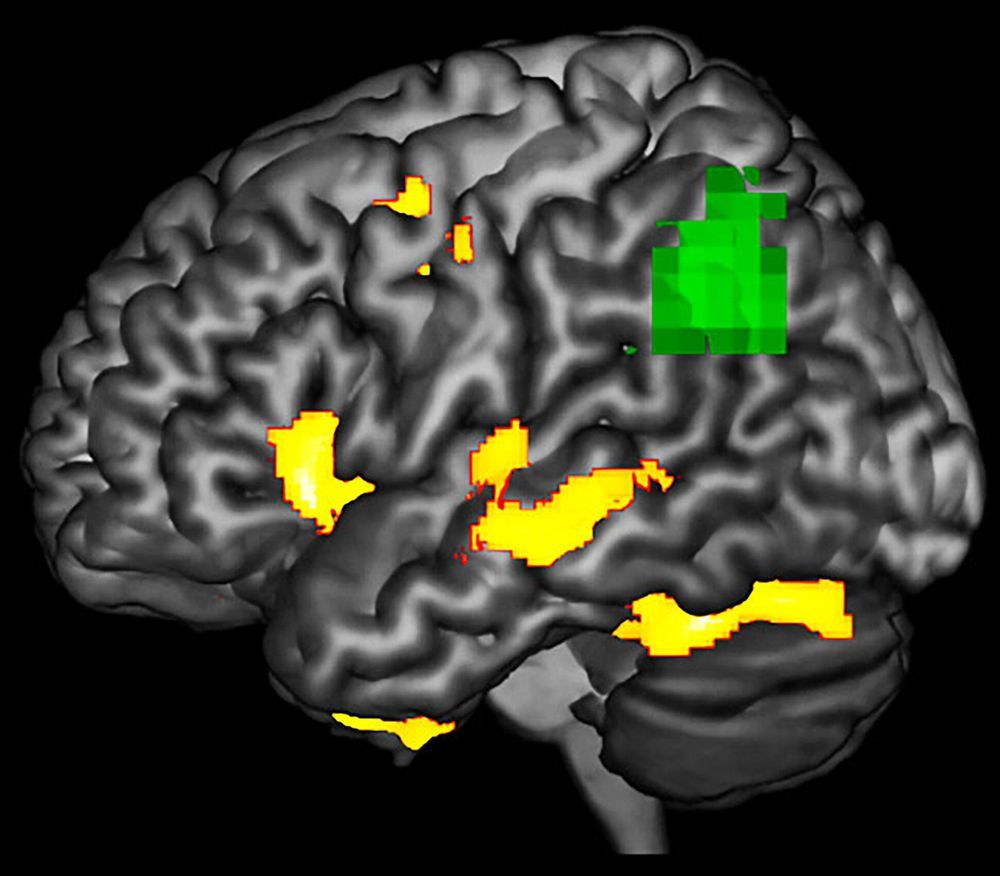
This new disease has been found to impact very specific areas of the brain – generally traveling vertically through the brain, it degenerates areas partly responsible for emotions, memory, and language, influencing different areas depending on its stage.
Continue reading “LATE: A Disease That Mimicks Alzheimer’s Disease” »