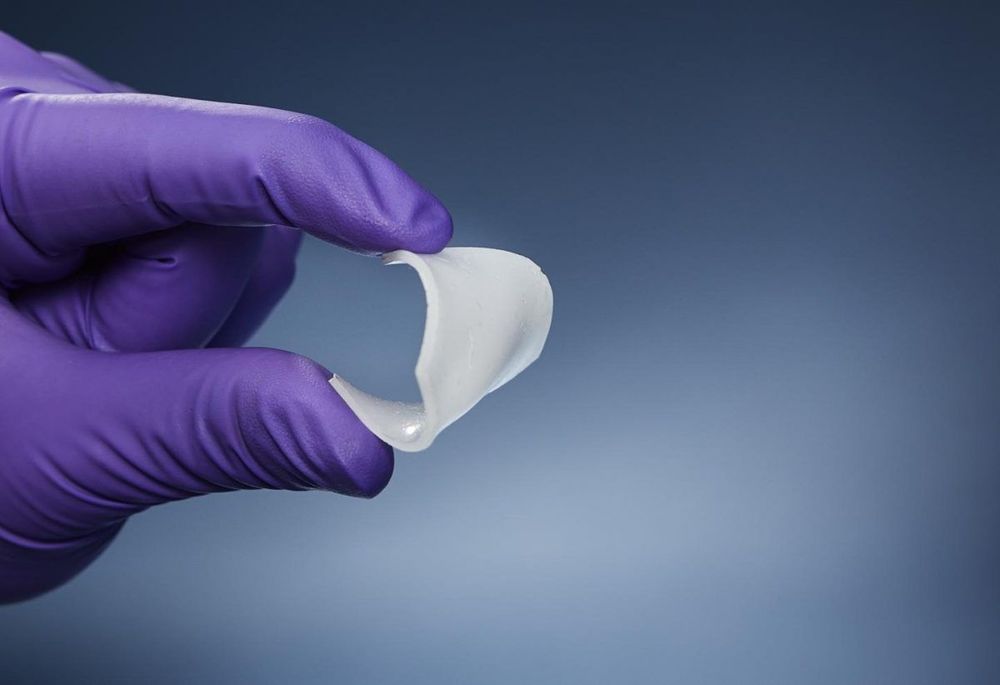
Researchers from Chalmers University of Technology, Sweden, have created a new, rubber-like material with a unique set of properties, which could act as a replacement for human tissue in medical procedures.

Dr. Ezekiel Emanuel, an American oncologist and bioethicist who is senior fellow at the Center for American Progress as well as Vice Provost for Global Initiatives at the University of Pennsylvania and chair of the Department of Medical Ethics and Health Policy, said on MSNBC on Friday, March 20, that Tesla and SpaceX CEO Elon Musk told him it would probably take 8–10 weeks to get ventilator production started at his factories (he’s working on this at Tesla and SpaceX).
I reached out to Musk for clarification on that topic and he replied that, “We have 250k N95 masks. Aiming to start distributing those to hospitals tomorrow night. Should have over 1000 ventilators by next week.” With medical supplies such as these being one of the biggest bottlenecks and challenges at the moment in the COVID-19 response in the United States (as well as elsewhere) — something that is already having a very real effect on medical professionals and patient care — the support will surely be received with much gratitude. That said, while there has been much attention put on the expected future need for ventilators, very few places reportedly have a shortage of them right now. In much greater need at the moment are simpler supplies like N95 masks, which must be why Tesla/SpaceX is providing 250,000 of them.
Dr. Emanuel also said in the segment of MSNBC’s “Morning Joe” he was on that we probably need 8–12 weeks (2–3 months) of social distancing in the US in order to deal with COVID-19 as a society. However, he also expects that the virus will come back and we’ll basically have a roller coaster of “social restrictions, easing up, social restrictions, easing up … to try to smooth out the demand on the health care system.”
“Infusions of antibody-laden blood have been used with reported success in prior outbreaks, including the SARS epidemic and the 1918 flu pandemic.”
John Hopkins University
With a vaccine for COVID-19 still a long way from being realized, Johns Hopkins immunologist Arturo Casadevall is working to revive a century-old blood-derived treatment for use in the United States in hopes of slowing the spread of the disease.
With the right pieces in place, the treatment could be set up at Johns Hopkins University in Baltimore within a matter of weeks, Casadevall says.
The technique uses antibodies from the blood plasma or serum of people who have recovered from COVID-19 infection to boost the immunity of newly infected patients and those at risk of contracting the disease. These antibodies contained in the blood’s serum have the ability to bind to and neutralize SARS-CoV-2, the virus that causes COVID-19. Casadevall—a Bloomberg Distinguished Professor of molecular microbiology and immunology and infectious diseases at the Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health and School of Medicine—published a paper on the proposal today in The Journal of Clinical Investigation.
Good Science here. A Covid-19 Primer.
Wash your hands.
Ninja Nerds.
What is Corona virus? What is COVID-19? Coronaviruses (CoV) are a large family of viruses that cause illness ranging from the common cold to more severe diseases such as Middle East Respiratory Syndrome (MERS-CoV) and Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome (SARS-CoV). Coronavirus disease (COVID-19) caused by SARS-COV2 is a new strain that was discovered in 2019 and has not been previously identified in humans.
Coronaviruses are zoonotic, meaning they are transmitted between animals and people. Detailed investigations found that SARS-CoV was transmitted from civet cats to humans and MERS-CoV from camels to humans. Several known coronaviruses are circulating in animals that have not yet infected humans. It is believed that COVID-19 was transmitted from pangolin to humans (current theory).
Common signs of infection include respiratory symptoms, fever, cough, shortness of breath and breathing difficulties. In more severe cases, infection can cause pneumonia, severe acute respiratory syndrome, kidney failure and even death (WHO, 2020).
Ninja Nerd Lectures has compiled the most up to date and recent data on COVID-19 as of March 15, 2020. Please follow along with this lecture to understand the origin and zoonosis of COVID-19, the routes of transmission, epidemiology (current as of 3/15/2020), pathophysiology, and diagnostic tests used to identify COVID-19.
As new information and research is published we will continue to provide updates on COVID-19 and ensure all of our viewers are kept up to date on the most recent data.
SUPPORT US! paypal.me/ninjanerdscience
REFERENCES: World Health Organization (WHO), Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC).

As they increasingly log on from home, Americans are having to meld their personal technology with professional tools at unprecedented scale. For employers, the concern isn’t just about capacity, but also about workers introducing new potential vulnerabilities into their routine — whether that’s weak passwords on personal computers, poorly secured home WiFi routers, or a family member’s device passing along a computer virus.
The dramatic expansion of teleworking by US schools, businesses and government agencies in response to the coronavirus is raising fresh questions about the capacity and security of the tools many Americans use to connect to vital workplace systems and data.
At one major US agency, some officials have resorted to holding meetings on iPhone group calls because the regular conference bridges haven’t always been working, according to one federal employee. But the workaround has its limits: The group calls support only five participants at a time, the employee noted.
“Things have worked better than I anticipated, but there are lots of hiccups still,” said the employee, who spoke on condition of anonymity because he is not authorized to speak on the record.


Andrew Sinclair does not have anything to lose. He takes a number of drugs including the anti-diabetic medication metformin, given to him by his son David, the renowned Australian biologist and professor of genetics at Harvard Medical School, to combat the ill-effects of ageing.
David Sinclair says his father remains in good health, travelling, socialising and exercising with the energy of a man far younger than his 80 years.
David Sinclair will discuss why ageing should be classified as a disease at the Festival of Dangerous Ideas.
Renowned Australian scientist David Sinclair says we have all the information to be young again, “if we can just flip the switch”.
How did Viruses evolve?
The evolutionary history of viruses remains unclear. Some researchers hypothesize that viruses evolved from mobile genetic elements that gained the ability to move between cells. Other researchers postulate that viruses evolved from more complex organisms that lost the ability to replicate independently. Still others hypothesize that DNA viruses gave rise to the eukaryotic nucleus or that viruses predate all cellular life-forms. Reasonable arguments can be made for all of these hypotheses. It may be that viruses arose multiple times, via each of these mechanisms. It may be that viruses arose from a mechanism yet to be described. Continuing studies of viruses and their hosts may provide us with clearer answers.
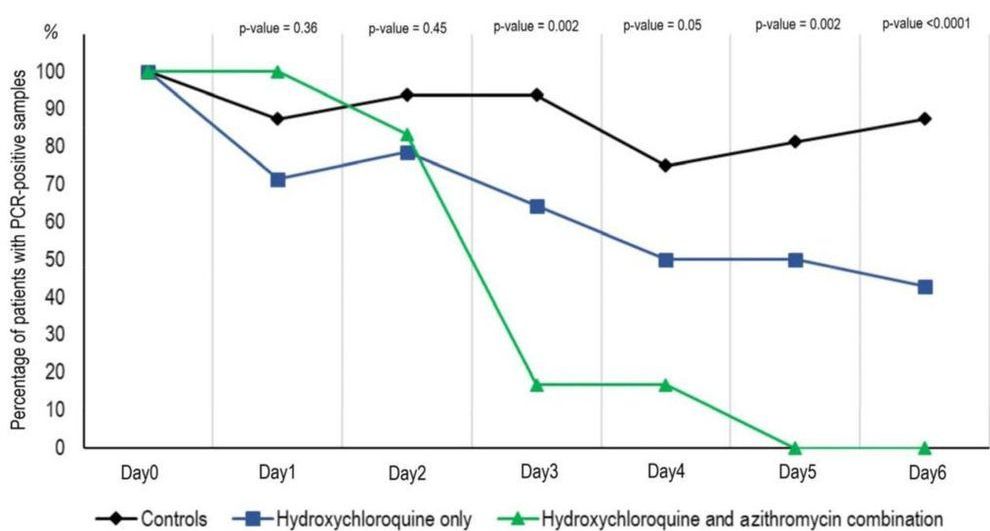
You can access information for this clinical trial in the links pdf.
Percentage of patients with PCR-positive nasopharyngeal samples from inclusion to day6 post-inclusion in COVID-19 patients treated with hydroxychloroquine only, in COVID-19 patients treated with hydroxychloroquine and azithomycin combination, and in COVID-19 control patients.