Feb 11, 2018
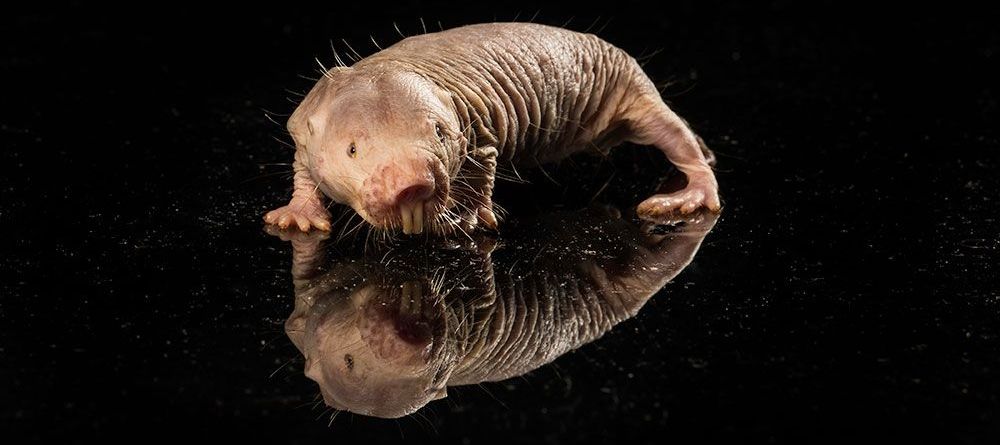
The key to a naked mole rat’s cancer-free life?
Posted by Brady Hartman in categories: biotech/medical, life extension
Summary: Clues to the naked mole rat’s remarkable cancer-fighting abilities have been uncovered by researchers at the University of Rochester in a new study. [This article first appeared on LongevityFacts. Author: Brady Hartman. ]
With their wrinkled, hairless bodies, naked mole rats won’t be winning any beauty contests.
However, they do win longevity contests.
Continue reading “The key to a naked mole rat’s cancer-free life?” »