Sep 18, 2017
Hospital Captures First Commercial Volta GPU Based DGX-1 Systems
Posted by Roman Mednitzer in categories: biotech/medical, robotics/AI
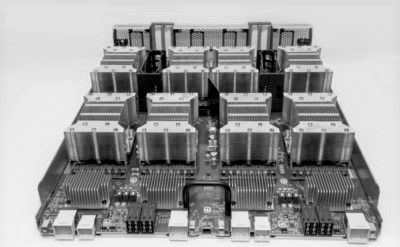
At well over $150,000 per appliance, the Volta GPU based DGX appliances from Nvidia, which take aim at deep learning with framework integration and 8 Volta-accelerated nodes linked with NVlink, is set to appeal to the most bleeding edge of machine learning shops.
Nvidia has built its own clusters by stringing several of these together, just as researchers at Tokyo Tech have done with the Pascal generation systems. But one of the first commercial customers for the Volta based boxes is the Center for Clinical Data Science, which is part of the first wave of hospitals set to use deep learning for MR and CT image analysis.
The center, which is based in Cambridge, Massachusetts, has secured a whopping four DGX-1 Volta appliances, which sport the latest GPUs with eight per node with the NVlink interconnect. The Next Platform talked with Neil Tenenholtz, senior data scientist at the center, about where deep learning will yield results for hospitals and medical research and about their early experiences with the four machines.
Continue reading “Hospital Captures First Commercial Volta GPU Based DGX-1 Systems” »