Archive for the ‘biotech/medical’ category: Page 2457
Feb 9, 2017
Wave of the future: Terahertz chips a new way of seeing through matter
Posted by Carse Peel in categories: biotech/medical, computing
Electromagnetic pulses lasting one millionth of a millionth of a second may hold the key to advances in medical imaging, communications and drug development. But the pulses, called terahertz waves, have long required elaborate and expensive equipment to use.
Now, researchers at Princeton University have drastically shrunk much of that equipment: moving from a tabletop setup with lasers and mirrors to a pair of microchips small enough to fit on a fingertip.
In two articles recently published in the IEEE Journal of Solid State Circuits, the researchers describe one microchip that can generate terahertz waves, and a second chip that can capture and read intricate details of these waves.
Feb 9, 2017
Could Predictive Policing Lead to a Real-Life Minority Report?
Posted by Carse Peel in categories: biotech/medical, information science, law enforcement, robotics/AI
Everyone knows prevention is better than a cure, and that’s as true for law enforcement as it is for medicine. But there’s little evidence that a growing trend towards “predictive policing” is the answer, and it could even bake in racial bias.
Police departments faced with tight budgets are increasingly turning to machine learning-enabled software that can sift through crime data to help predict where crimes are likely to occur and who might commit them.
Using statistics in law enforcement is nothing new. A statistical system for tracking crime called Compstat was pioneered in New York in 1994 and quickly became popular elsewhere. Since then, crime has fallen 75 percent in New York, which has been credited by some to the technology. But while Compstat simply helped identify historical hotspots, “predictive policing” uses intelligent algorithms to forecast tomorrow’s hotspots and offenders.
Continue reading “Could Predictive Policing Lead to a Real-Life Minority Report?” »
Feb 8, 2017
Marina Biotech Announces a License Agreement to SMARTICLES
Posted by Carse Peel in categories: biotech/medical, nanotechnology
A biopharmaceutical company focused on the development and commercialization of innovative therapeutics for disease intersections of arthritis, hypertension, and cancer, today announced that they have entered into a license agreement regarding the Company’s SMARTICLES platform for the delivery of nanoparticles including small molecules, peptides, proteins and biologics…
Marina Biotech, Inc. a biopharmaceutical company focused on the development and commercialization of innovative therapeutics for disease intersections of arthritis, hypertension, and cancer, today announced that they have entered into a license agreement regarding the Company’s SMARTICLES platform for the delivery of nanoparticles including small molecules, peptides, proteins and biologics. This represents the first time that the Company’s SMARTICLES technologies have been licensed in connection with nanoparticles delivering small molecules, peptides, proteins and biologics. Under terms of the agreement, Marina could receive up to $90MM in success based milestones. Further details of the agreement were not disclosed.
Feb 8, 2017
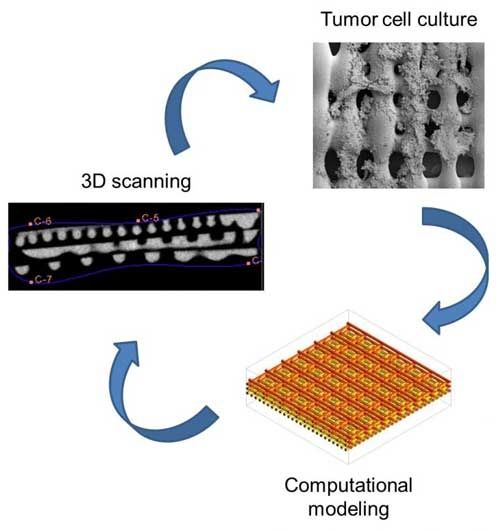
Better 3D-printed scaffolds help scientists study cancer
Posted by Karen Hurst in categories: 3D printing, bioengineering, biotech/medical
Nice.
Testing treatments for bone cancer tumors may get easier with new enhancements to sophisticated support structures that mimic their biological environment, according to Rice University scientists.
A team led by Rice bioengineer Antonios Mikos has enhanced its three-dimensional printed scaffold to see how Ewing’s sarcoma (bone cancer) cells respond to stimuli, especially shear stress, the force experienced by tumors as viscous fluid such as blood flows through bone. The researchers determined the structure of a scaffold, natural or not, has a very real effect on how cells express signaling proteins that help cancer grow.
Continue reading “Better 3D-printed scaffolds help scientists study cancer” »
Feb 8, 2017
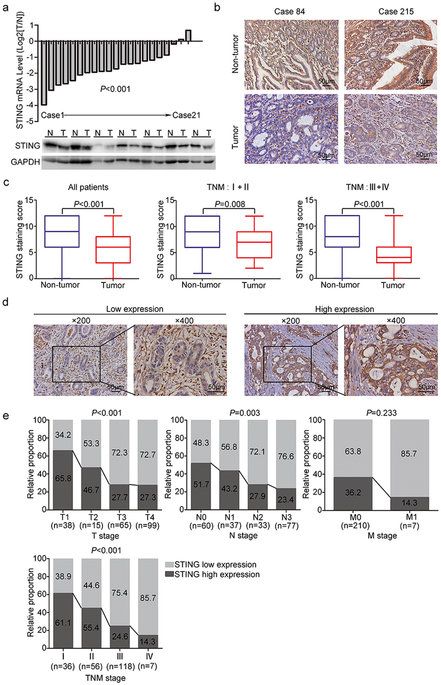
Decreased expression of STING predicts poor prognosis in patients with gastric cancer
Posted by Karen Hurst in categories: biotech/medical, chemistry, food
Interesting read on recent Gastric Cancer research. I do a lot of work with the National Esophageal Cancer (EC) Awareness Association; I can tell you that this disease is truly a killer as gastric related cancers are horrible to detect early enough and have a horrible record of reoccurring. Survival rates are some of the worst and today the rates of EC have skyrocketed especially in the younger age groups such as 25 to 35 year olds.
When you work for these foundations, read the stories from patients and their families looking for answers and help with everything from help on what types of food can their love eat and hopefully keep down for nutrition, to how can they get help with transportation to simply go to work or the doctor as meds restrictions on driving, to knowing the end is near and how to prepare, etc. The worst ones are the 27 to 36 yr old fathers and mothers whose love one is saying good bye to the person they married only recently married the year before or spent 7 years with. This is why I work for my foundations as every small step does in the end create a larger impact in the end and hopefully helps us finally beat this disease.
STING (stimulator of interferon genes) has recently been found to play an important role in host defenses against virus and intracellular bacteria via the regulation of type-I IFN signaling and innate immunity. Chronic infection with Helicobacter pylori is identified as the strongest risk factor for gastric cancer. Thus, we aim to explore the function of STING signaling in the development of gastric cancer. Immunohistochemistry was used to detect STING expression in 217 gastric cancer patients who underwent surgical resection. STING protein expression was remarkably decreased in tumor tissues compared to non-tumor tissues, and low STING staining intensity was positively correlated with tumor size, tumor invasion depth, lymph mode metastasis, TNM stage, and reduced patients’ survival. Multivariate analysis identified STING as an independent prognostic factor, which could improve the predictive accuracy for overall survival when incorporated into TNM staging system. In vitro studies revealed that knock-down of STING promoted colony formation, viability, migration and invasion of gastric cancer cells, and also led to a defect in cytosolic DNA sensing. Besides, chronic H. pylori infection up-regulated STING expression and activated STING signaling in mice. In conclusion, STING was proposed as a novel independent prognostic factor and potential immunotherapeutic target for gastric cancer.
Feb 8, 2017
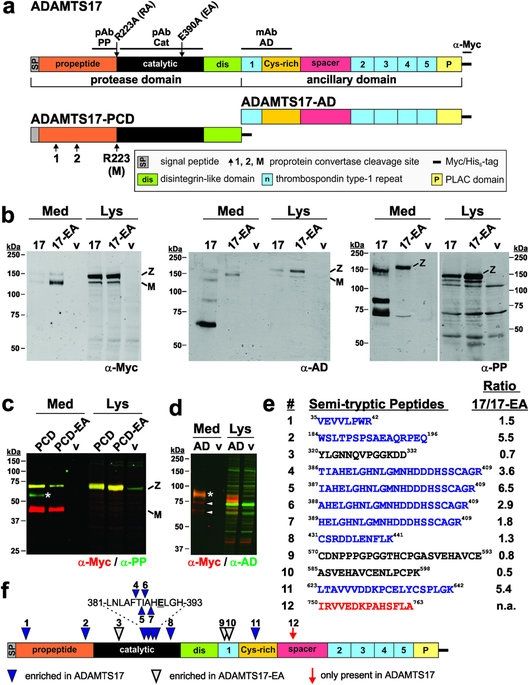
Unusual life cycle and impact on microfibril assembly of ADAMTS17, a secreted metalloprotease mutated in genetic eye disease
Posted by Karen Hurst in categories: biotech/medical, genetics
Need to share this with a few folks researching glaucoma disease and treatment/ mutation reversal.
Elderly are frequently hospitalized due to their age-associated organ degeneration, the presence of co-morbidities, and their susceptibility to adverse insults. Alterations in functional status often occur during hospitalization, and the degree of functional decline can parallel the severity of illnesses. For older persons, gauging their pre-morbid and in-hospital functional status facilitates treatment planning and potentially functional restoration1,2,3. While the identification of risk factors or markers of poor pre-morbid and in-hospital functional status may help facilitate this process, this area remains under-researched to date. Factors associated with functional decline in the hospitalized elderly include the types of morbidities and the reasons for their admission. Indeed, elderly with chronic kidney disease (CKD) are more likely to exhibit functional decline, beginning from the earlier stage of CKD to end-stage renal disease (ESRD)4,5; functional dependency also predisposes individuals with CKD and ESRD to recurrent hospitalization and higher mortality.
Albuminuria and proteinuria, as the staging criteria for CKD in the most recent version of Kidney Disease Improving Global Outcomes (KDIGO) CKD guidelines, are both well-established predictors of subsequent renal function decline. There is increasing awareness that albuminuria and proteinuria have an independent role in the prediction of adverse outcomes apart from the baseline renal function. As explained above, although CKD is associated with poor functional status, it is still unclear whether proteinuria alone exhibits similar association with functional status regardless of CKD. No reports focus on this association using the severity of proteinuria among geriatric patients with acute medical illnesses.
Feb 8, 2017
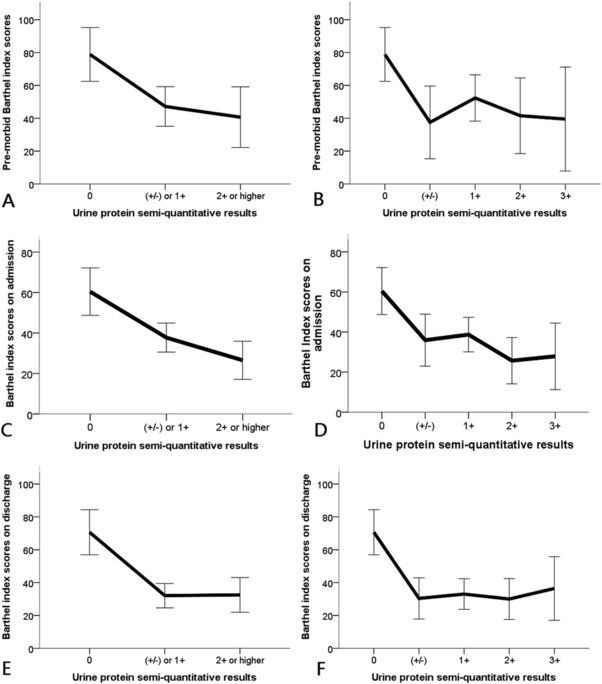
Dipstick proteinuria level is significantly associated with pre-morbid and in-hospital functional status among hospitalized older adults: a preliminary study
Posted by Karen Hurst in category: biotech/medical
Latest study on chronic kidney disease (CKD) as it relates to the elderly patients and the relationship to the elderly’s organ decline over time. I can most certainly attest that I have seen many patients in their final days/ hours seeing their kidneys shutdown as a final state of life. Key is hopefully what doctors find in this research will enable us to prevent kidney failure or even improve the synbio kidney product that is being experimented on today for dialysis patients who badly need transplants and have a hard time finding donors.
Elderly are frequently hospitalized due to their age-associated organ degeneration, the presence of co-morbidities, and their susceptibility to adverse insults. Alterations in functional status often occur during hospitalization, and the degree of functional decline can parallel the severity of illnesses. For older persons, gauging their pre-morbid and in-hospital functional status facilitates treatment planning and potentially functional restoration1,2,3. While the identification of risk factors or markers of poor pre-morbid and in-hospital functional status may help facilitate this process, this area remains under-researched to date. Factors associated with functional decline in the hospitalized elderly include the types of morbidities and the reasons for their admission. Indeed, elderly with chronic kidney disease (CKD) are more likely to exhibit functional decline, beginning from the earlier stage of CKD to end-stage renal disease (ESRD)4,5; functional dependency also predisposes individuals with CKD and ESRD to recurrent hospitalization and higher mortality.
Albuminuria and proteinuria, as the staging criteria for CKD in the most recent version of Kidney Disease Improving Global Outcomes (KDIGO) CKD guidelines, are both well-established predictors of subsequent renal function decline. There is increasing awareness that albuminuria and proteinuria have an independent role in the prediction of adverse outcomes apart from the baseline renal function. As explained above, although CKD is associated with poor functional status, it is still unclear whether proteinuria alone exhibits similar association with functional status regardless of CKD. No reports focus on this association using the severity of proteinuria among geriatric patients with acute medical illnesses.
Feb 8, 2017
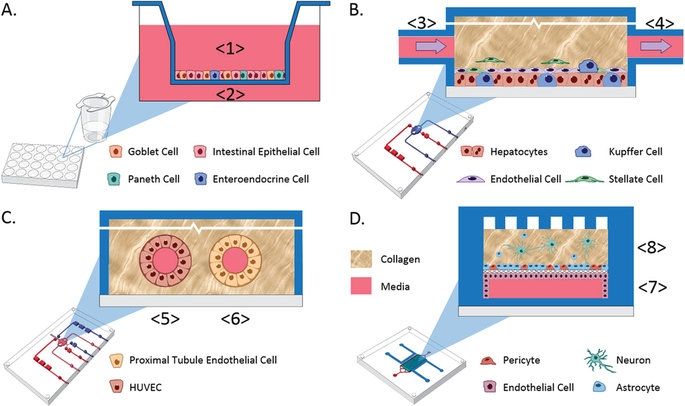
Intestine, Liver, Kidney Proximal Tubule, Blood-Brain Barrier and Skeletal Muscle
Posted by Karen Hurst in categories: bioengineering, biotech/medical, life extension, neuroscience, quantum physics
This is definitely a share that is interesting to many studying synthetic organs and their acceptance into the human body as well as the work occurring on Quantum biology as well.
The goal of in vitro and in vivo toxicity testing is to identify compounds that would predict adverse reactions in humans. Olson et al. found that only 70% of human toxicity was predicted from animal testing. Currently we rely on traditional toxicity testing in animals, a 1930’s methodology that is now challenged due to questionable relevance to human risk, high cost, ethical concerns, and throughput that is too limited for the nearly 80,000 industrial chemicals not yet tested for safety. Additionally, testing usually extrapolates acute, high dose animal results to chronic, low dose human exposures, thereby risking rejection or limiting the use of drugs, industrial chemicals or consumer products. Moreover, the ability of lab animal target organ toxicity to predict dose-limiting toxicity in the corresponding human organ varies widely, from a low of 30% for human cutaneous toxicity, to 50–60% for human hepatotoxicity, to a high of 90% for hematological drug toxicity. Animal drug efficacy models are also notoriously discordant. In an analysis of six drugs to treat head injury, hemorrhage, acute ischemic stroke, neonatal respiratory distress syndrome, and osteoporosis, it was found that efficacy was similar in animals and humans for three drugs but was dissimilar for another three. In oncology drug development, animal models often over-predict anti-tumor efficacy in humans3,4. Examples such as these highlight the need to continue research into methods that reduce the dependence on laboratory animals for toxicity testing of environmental chemicals, determine efficacy and toxicity in drug development, serve as a mimic of human diseases, and provide patient-specific guidance in the emerging field of precision medicine.
Recent advances in bioengineered materials, microfluidic technology, and the availability of human primary, immortalized, and induced pluripotent stem cell (iPSC)-derived cells are enabling development of human microphysiological systems (MPS), sometimes called “organs-on-a-chip” or “human-on-a-chip,” that use multiple organ-specific human cells to recapitulate many functional and structural properties of a human organ. It is now generally accepted and supported by data that cellular responses to drugs in most human organs are more accurately approximated in 3D cell cultures than in traditional static 2D cell cultures5,6. Microfluidic perfusion further improves model performance by providing a flow of nutrients and oxygen and the removal of waste products from the cell cultures. Physiologically relevant flow increases oxygen consumption, Krebs cycle activity and secretion of synthesized proteins, and decreases expression of the hypoxia HIF1 gene. Flow also improves the absorption and metabolism of compounds like benzo[a]pyrene6,8,9. The large number of recent publications reviewing organ MPS models indicates a high degree of interest by industrial and academic researchers, granting agencies and other stakeholders10,11,12,13. In addition to the stand-alone MPS, investigators are linking MPS to study organ-organ functional interactions, efficacy, PK and toxicology14,15,16,17,18.
Feb 8, 2017
Faraday Rotation Spectroscopy for Speedy Medical Testing
Posted by Karen Hurst in categories: biotech/medical, computing, engineering, nanotechnology
Nice.
Researchers at the University of Central Florida (UCF) in the US are combining nanoscience with the principle of Faraday rotation, a magnetic phenomenon discovered in 1845, in a new method for speedy medical tests.
The team applied the magneto-optical technique, called frequency-domain Faraday rotation spectroscopy—or fd-FRS, to characterize proteins, using antibody-functionalized magnetic nanoparticles (MNPs).
Continue reading “Faraday Rotation Spectroscopy for Speedy Medical Testing” »