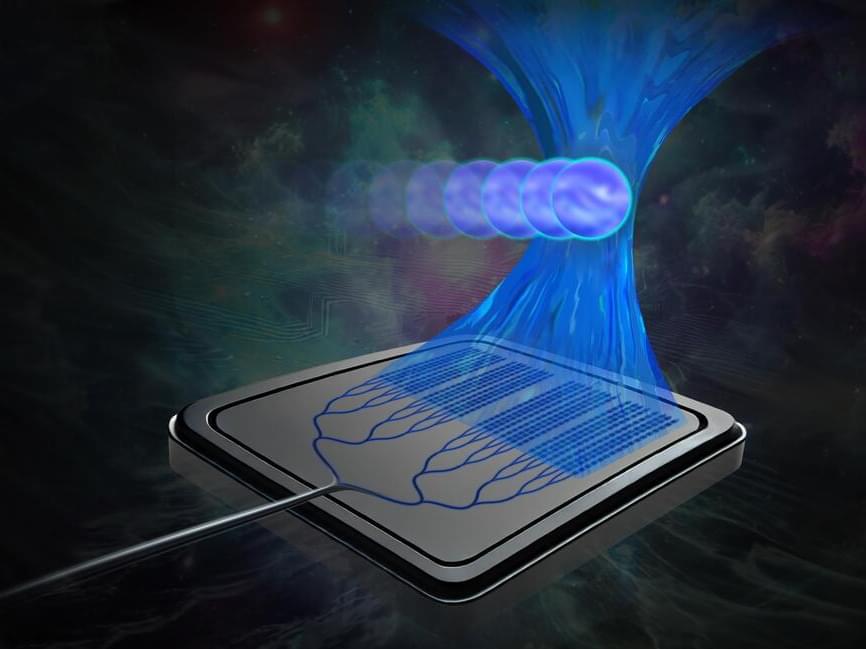
MIT researchers have developed a miniature, chip-based “tractor beam,” like the one that captures the Millennium Falcon in the film “Star Wars,” that could someday help biologists and clinicians study DNA, classify cells, and investigate the mechanisms of disease.
Small enough to fit in the palm of your hand, the device uses a beam of light emitted by a silicon-photonics chip to manipulate particles millimeters away from the chip surface. The light can penetrate the glass cover slips that protect samples used in biological experiments, enabling cells to remain in a sterile environment.
Traditional optical tweezers, which trap and manipulate particles using light, usually require bulky microscope setups, but chip-based optical tweezers could offer a more compact, mass manufacturable, broadly accessible, and high-throughput solution for optical manipulation in biological experiments.