Scientists say new early diagnosis method could improve research into treatments that slow or prevent the disease.
Ian Sample Science editor.

Scientists say new early diagnosis method could improve research into treatments that slow or prevent the disease.
Ian Sample Science editor.
Our willingness to help others is governed by a specific brain region pinpointed by researchers in a study of patients with brain damage to that region.
Learning about where in the brain “helping” decisions are made is important for understanding how people might be motivated to tackle large global challenges, such as climate change, infectious disease and international conflict. It is also essential for finding new approaches to treating disorders of social interactions.
The study, published in Nature Human Behaviour, was carried out by researchers at the University of Birmingham and the University of Oxford, and shows for the first time how a region called the ventromedial prefrontal cortex (vmPFC) has a critical role in helping, or “prosocial” behaviors.

In the future, getting help for depression might involve a quick brain scan to find the most effective treatment for you.
An analysis of brain activity during rest and while undertaking specific tasks among a large group of people with depression and anxiety has identified six distinct types of brain activity patterns, symptoms, and responses to treatment.
The team from the US and Australia who conducted the study also determined treatments that are more likely to work for some of these categories. This means doctors could potentially match patients with the best therapies based on how their brains function.

Johnson’s latest foray into anti-aging science took him to the Roatan, an island off the coast of Honduras, where he received follistatin gene therapy in the form of two injections. The entrepreneur says that he spent $20,000 on reversible gene therapy developed by the method development company Minicircle.
Over the past decade, immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICI) have revolutionized the cancer treatment area. These drugs block the interaction between proteins known as immune checkpoints and immune cells within our bodies. At times, immune checkpoints play a vital role in immune regulation, preventing unnecessary responses. However, tumors can upregulate proteins, thus evading an immune response, and in a tumor setting, this response is indeed necessary. ICIs interfere with checkpoint pathways and allow active immunity against cancer.
In 2011, the United States Foor and Drug Administration (FDA) approved the first ICI, ipilimumab, a CTLA-4 blocker, for treating advanced melanoma. Subsequently, ICIs targeting PD1 (pembrolizumab and nivolumab) and PDL1 (atezolizumab and durvalumab) received approval for treating various malignancies. Many clinical trials test the efficacy of novel ICIs in different settings.
A recent study published in Science Immunology unveiled a promising new avenue for cancer immunotherapy and ICIs. The study evaluated a drug targeting an immune checkpoint molecule called VISTA (V-domain immunoglobulin suppressor of T cell activation), shedding light on its potential as an effective immunotherapy target.
The cost of new gene-based sickle cell treatments isn’t the only barrier to access. Coming up with new ways to treat the whole disease—and person—could make treatment more equitable.
Last fall, to great fanfare, US regulators approved two gene therapies for sickle cell disease, and the European Union and UK soon followed. Many people hope that these treatments will provide a “functional cure” for the genetic condition, which causes rigid, misshapen red blood cells that lead to anemia, episodes of extreme pain, blood vessel and organ damage, stroke risk and lower life expectancy. These sickle cell therapies also bring us closer to an age of “CRISPR medicine” in which new gene-editing tools could be used to fix a range of debilitating genetic diseases, including Duchenne muscular dystrophy and cancer.
“There is an urgent need for new methods for antibiotic discovery,” Dr. Luis Pedro Coelho, a computational biologist and author of a new study on the topic, said in a press release.
Coelho and team tapped into AI to speed up the whole process. Analyzing huge databases of genetic material from the environment, they uncovered nearly one million potential antibiotics.
The team synthesized 100 of these AI-discovered antibiotics in the lab. When tested against bacteria known to resist current drugs, they found 63 readily fought off infections inside a test tube. One worked especially well in a mouse model of skin disease, destroying a bacterial infection and allowing the skin to heal.

This ambitious initiative aims to significantly extend human lifespan, targeting a 130-year life expectancy through cutting-edge mitochondrial transplantation techniques.
Star Trek star boldly joins Biotech Explorers longevity project to extend human lifespan and explore the final frontier of aging.
Organoids are an improved model for the study human biology and disease, because they are miniaturized versions of human organs and tissues. | Cell And Molecular Biology.
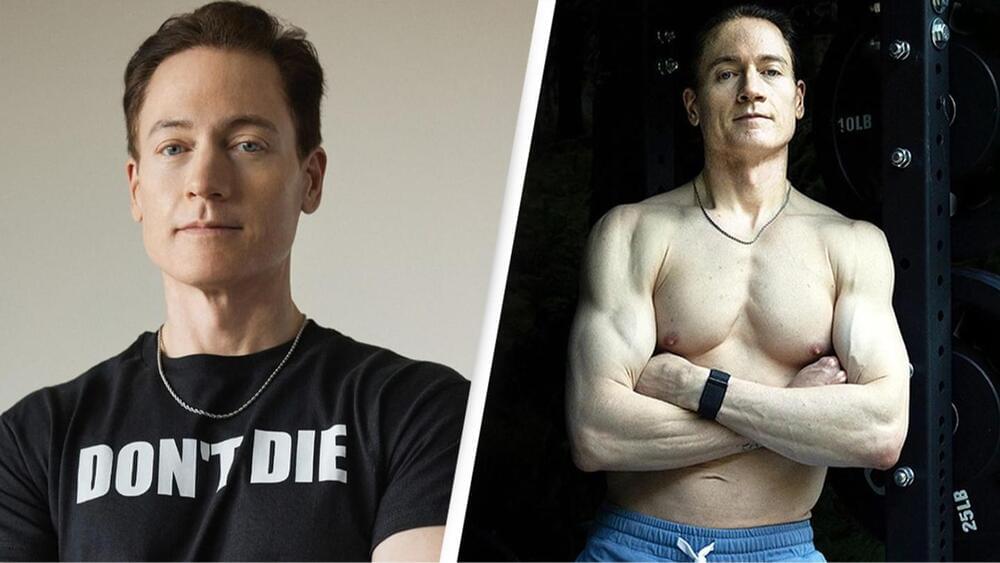

He added: “Their target: follistatin gene therapy. A pioneering technology with the potential to improve muscle and strength [and] slow the speed of aging and many more benefits.”
The millionaire explained that the procedure involves an injection in the stomach and in the buttocks.
It also costs $20,000, so not exactly cheap.