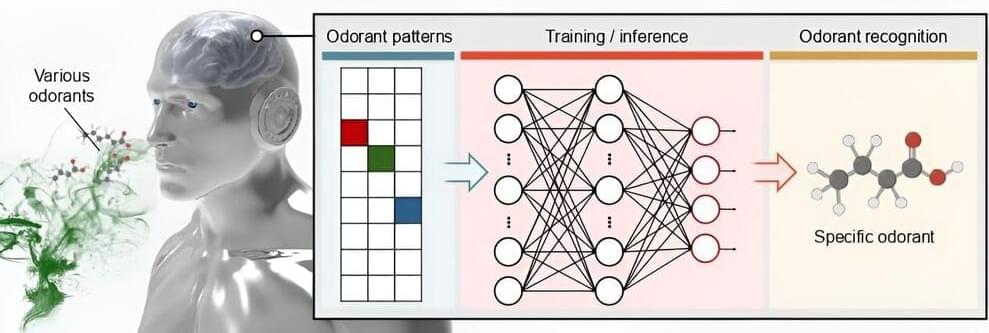
A team of chemical and biological engineers at Seoul National University in the Republic of Korea has developed a proof-of-concept device that could one day lead to the creation of an artificial nose.

Scientists have made a significant breakthrough in understanding the properties of promethium, a rare earth element with elusive characteristics despite its use in modern technology.
Researchers have uncovered the properties of a rare earth element that was first discovered 80 years ago at the very same laboratory. Their discoveries open a new pathway for the exploration of elements critical in modern technology, from medicine to space travel.
Promethium was discovered in 1945 at Clinton Laboratories, now the Department of Energy’s Oak Ridge National Laboratory, and continues to be produced at ORNL in minute quantities. Some of its properties have remained elusive despite the rare earth element’s use in medical studies and long-lived nuclear batteries. It is named after the mythological Titan who delivered fire to humans and whose name symbolizes human striving.
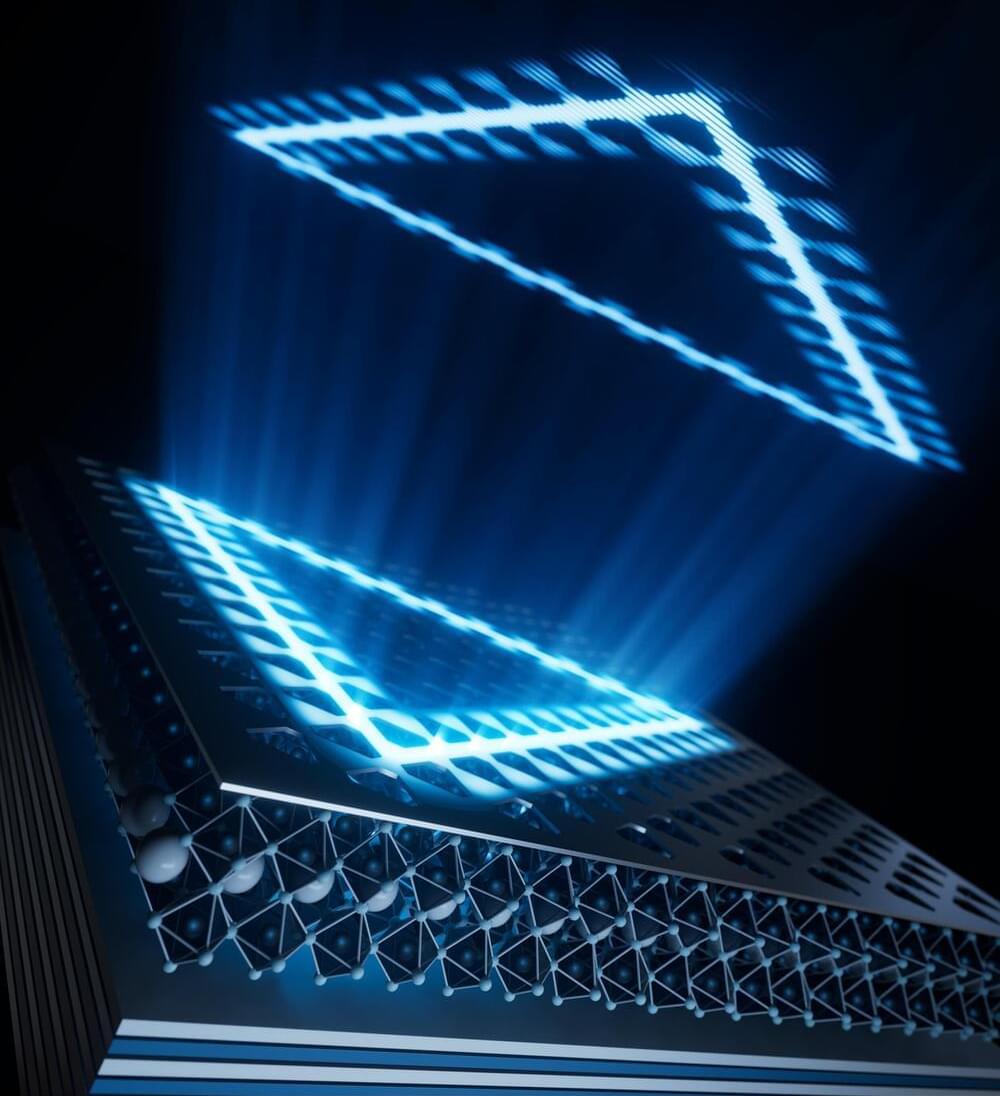
Researchers at Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute have fabricated a device no wider than a human hair that will help physicists investigate the fundamental nature of matter and light. Their findings, published in the journal Nature Nanotechnology, could also support the development of more efficient lasers, which are used in fields ranging from medicine to manufacturing.
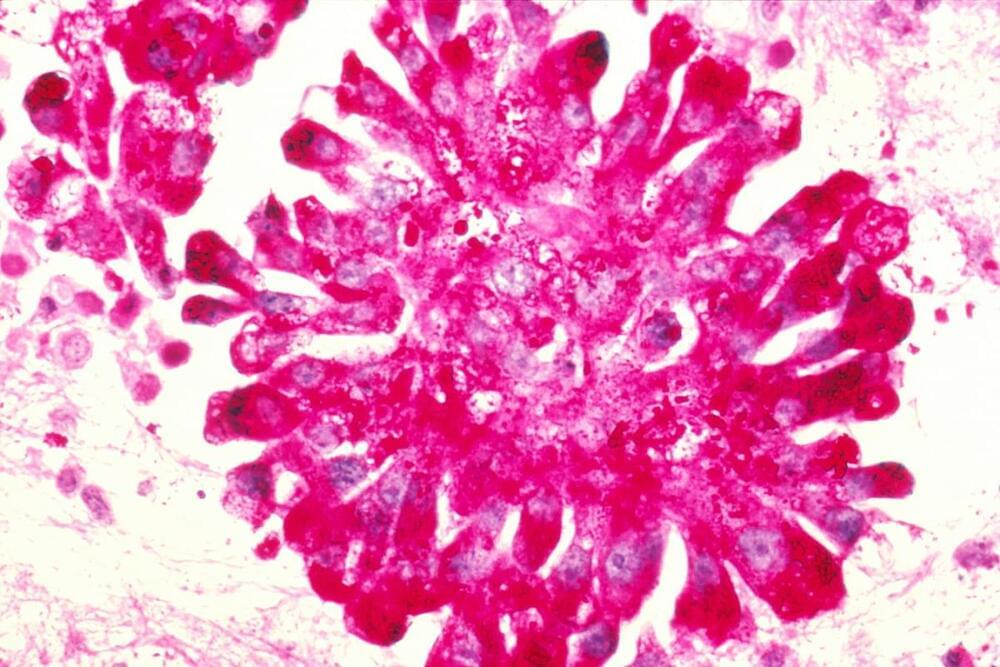
Researchers at Texas Children’s Cancer Center and the Center for Cell and Gene Therapy at Baylor College of Medicine, Texas Children’s Hospital and Houston Methodist published results of a phase I clinical trial of a novel immunotherapy for high-risk sarcomas in the journal Nature Cancer.
The therapy uses chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T cells engineered to target the HER2 protein, which is overexpressed on the surface of sarcoma cells. Sarcoma is a type of solid cancer that develops in the bones and soft tissues. The HEROS 2.0 trial showed that this therapeutic approach is safe and is associated with clinical benefit.
“CAR T cell therapy has been a highly successful strategy for recurrent or high-risk leukemias or lymphomas, but challenges remain in using this therapy for solid tumors,” said first and corresponding author Dr. Meenakshi Hegde, associate professor of pediatrics – hematology and oncology at Baylor and pediatric oncologist at Texas Children’s Cancer Center. “The results of this trial show that we are moving the dial in harnessing the power of CAR T cells as an effective anticancer therapy for sarcomas.”
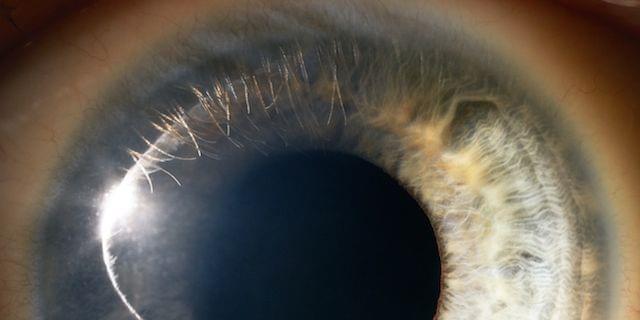
Retinitis pigmentosa and macular degeneration lead to photoreceptor death and loss of visual perception. Despite recent progress, restorative technologies for photoreceptor degeneration remain largely unavailable. Here, we describe a novel optogenetic visual prosthesis (FlexLED) based on a combination of a thin-film retinal display and optogenetic activation of retinal ganglion cells (RGCs). The FlexLED implant is a 30 µm thin, flexible, wireless µLED display with 8,192 pixels, each with an emission area of 66 µm2. The display is affixed to the retinal surface, and the electronics package is mounted under the conjunctiva in the form factor of a conventional glaucoma drainage implant. In a rabbit model of photoreceptor degeneration, optical stimulation of the retina using the FlexLED elicits activity in visual cortex. This technology is readily scalable to hundreds of thousands of pixels, providing a route towards an implantable optogenetic visual prosthesis capable of generating vision by stimulating RGCs at near-cellular resolution.
### Competing Interest Statement.
All authors have a financial interest in Science Corporation.

Researcher Kenneth Hu, Ph.D., runs an immunology lab studying cell-to-cell interactions in the tumor microenvironment and how that dictates the body’s response to immunotherapy. Here, he shares how he got started in the field and how he hopes his research will influence future advances in cancer immunotherapy.
ESA’s newly graduated astronauts reach the end of one year of rigorous basic astronaut training. Discover the journey of Sophie Adenot, Rosemary Coogan, Pablo Álvarez Fernández, Raphaël Liégeois, Marco Sieber, and Australian Space Agency astronaut candidate Katherine Bennell-Pegg. Selected in November 2022, the group began their training in April 2023.
Basic astronaut training provides the candidates with an overall familiarisation and training in various areas, such as spacecraft systems, spacewalks, flight engineering, robotics and life support systems as well as survival and medical training. They received astronaut certification at ESA’s European Astronaut Centre on 22 April 2024.
Following certification, the new astronauts will move on to the next phases of pre-assignment and mission-specific training — paving the way for future missions to the International Space Station and beyond.
Credits:
Video: ESA — European Space Agency.
ISS and EVA footage: ESA/NASA
Music: Scorekeepers.
★ Subscribe: http://bit.ly/ESAsubscribe and click twice on the bell button to receive our notifications.

Prime editing, a mightier version of CRISPR/Cas9 technology, has been part of rigorous research and development in recent years. Now, U.S. regulators have greenlit the first-ever clinical trial for this technology.
Massachusetts-based Prime Medicine received the go-ahead from the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) after preclinical data showed that its candidate was able to correct mutations in chronic granulomatous disease (CGD).
CGD is a rare condition and affects around one in 200,000 people worldwide. It is caused by mutations in any of the six genes that code for the molecule nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NADPH), which is responsible for carrying electrons within cells. White blood cells called phagocytes don’t function properly, and as a result, they fail to protect the body from bacterial and fungal infections.