A study in EBioMedicine reveals significant microplastic concentrations in thrombi from major blood vessels, linking microplastic levels to increased risk and severity of thrombotic events.

The FDA has allowed billionaire Elon Musk’s Neuralink to implant its brain chip in a second person after it proposed a fix for a problem that occurred in its first patient. Correspondent Brooke Shafer joins \.

Mao, H., Tian, Y., Wang, Z. et al. Discovery and engineering of Tsp2Cas9 for genome editing. Cell Discov 10, 55 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41421-024-00685-w.
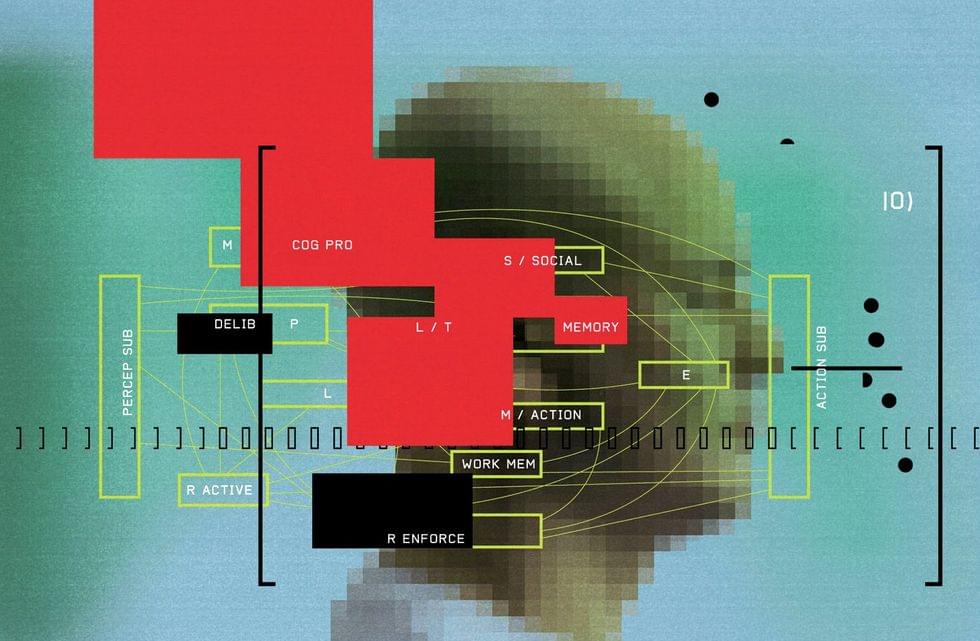
Theory of mind —the ability to understand other people’s mental states—is what makes the social world of humans go around. It’s what helps you decide what to say in a tense situation, guess what drivers in other cars are about to do, and empathize with a character in a movie. And according to a new study, the large language models (LLM) that power ChatGPT and the like are surprisingly good at mimicking this quintessentially human trait.
“Before running the study, we were all convinced that large language models would not pass these tests, especially tests that evaluate subtle abilities to evaluate mental states,” says study coauthor Cristina Becchio, a professor of cognitive neuroscience at the University Medical Center Hamburg-Eppendorf in Germany. The results, which she calls “unexpected and surprising,” were published today —somewhat ironically, in the journal Nature Human Behavior.
The results don’t have everyone convinced that we’ve entered a new era of machines that think like we do, however. Two experts who reviewed the findings advised taking them “with a grain of salt” and cautioned about drawing conclusions on a topic that can create “hype and panic in the public.” Another outside expert warned of the dangers of anthropomorphizing software programs.

“Neuralink to implant 2nd human with brain chip as 85% of threads retract. Neuralink’s first patient, 29-year-old Noland Arbaugh, opened up about the roller-coaster experience. ” I was on such a high and then to be brought down that low. It was very, very hard,” Arbaugh said. ” I cried.” What a disaster!
Algorithm tweaks made up for the loss, and Neuralink thinks it has fix for next patient.

How do you define consciousness?
Some theories are even duking it out in a mano-a-mano test by imaging the brains of volunteers as they perform different tasks in clinical test centers across the globe.
But unlocking the neural basis of consciousness doesn’t have to be confrontational. Rather, theories can be integrated, wrote the authors, who were part of the Human Brain Project —a massive European endeavor to map and understand the brain—and specialize in decoding brain signals related to consciousness.
Not all authors agree on the specific brain mechanisms that allow us to perceive the outer world and construct an inner world of “self.” But by collaborating, they merged their ideas, showing that different theories aren’t necessarily mutually incompatible—in fact, they could be consolidated into a general framework of consciousness and even inspire new ideas that help unravel one of the brain’s greatest mysteries.

Nightmares and hallucinations could be early signs of autoimmune diseases like lupus, potentially improving early diagnosis and treatment, according to a new study.
An increase in nightmares and hallucinations – or ‘daymares’ – could indicate the beginning of autoimmune diseases such as lupus. This is according to an international team led by researchers at the University of Cambridge and King’s College London.
They emphasize the importance of recognizing these mental health and neurological symptoms as early warning signs of an impending ‘flare,’ a phase during which the disease intensifies temporarily.

In March, the United States reported its first detection of the highly pathogenic H5N1 avian influenza in dairy cattle, with outbreaks spreading to nine states by May. The transmission method among cattle remains unclear. However, a study published in the journal Nature Communications revealed that a similar H5N1 strain, subtype clade 2.3.4.4b, which previously caused an outbreak in farmed mink in 2022, was capable of airborne transmission to a small group of ferrets.
This is the first time that a member of the group of H5N1 clade 2.3.4.4b viruses has been shown to exhibit this ability. According to the Penn State researchers who led the study, the findings suggest these viruses are evolving to infect mammals and with potentially increased risk to humans.
“While there is no evidence that the strain of H5N1 that is presently affecting dairy cattle is capable of airborne transmission, our study suggests that another member of this family of viruses has evolved some degree of airborne transmissibility,” said Troy Sutton, associate professor of veterinary and biomedical sciences, Penn State, and corresponding author on the paper. “This finding underscores the importance of continued surveillance to monitor the evolution of these viruses and their spillover into other mammals, including humans.”
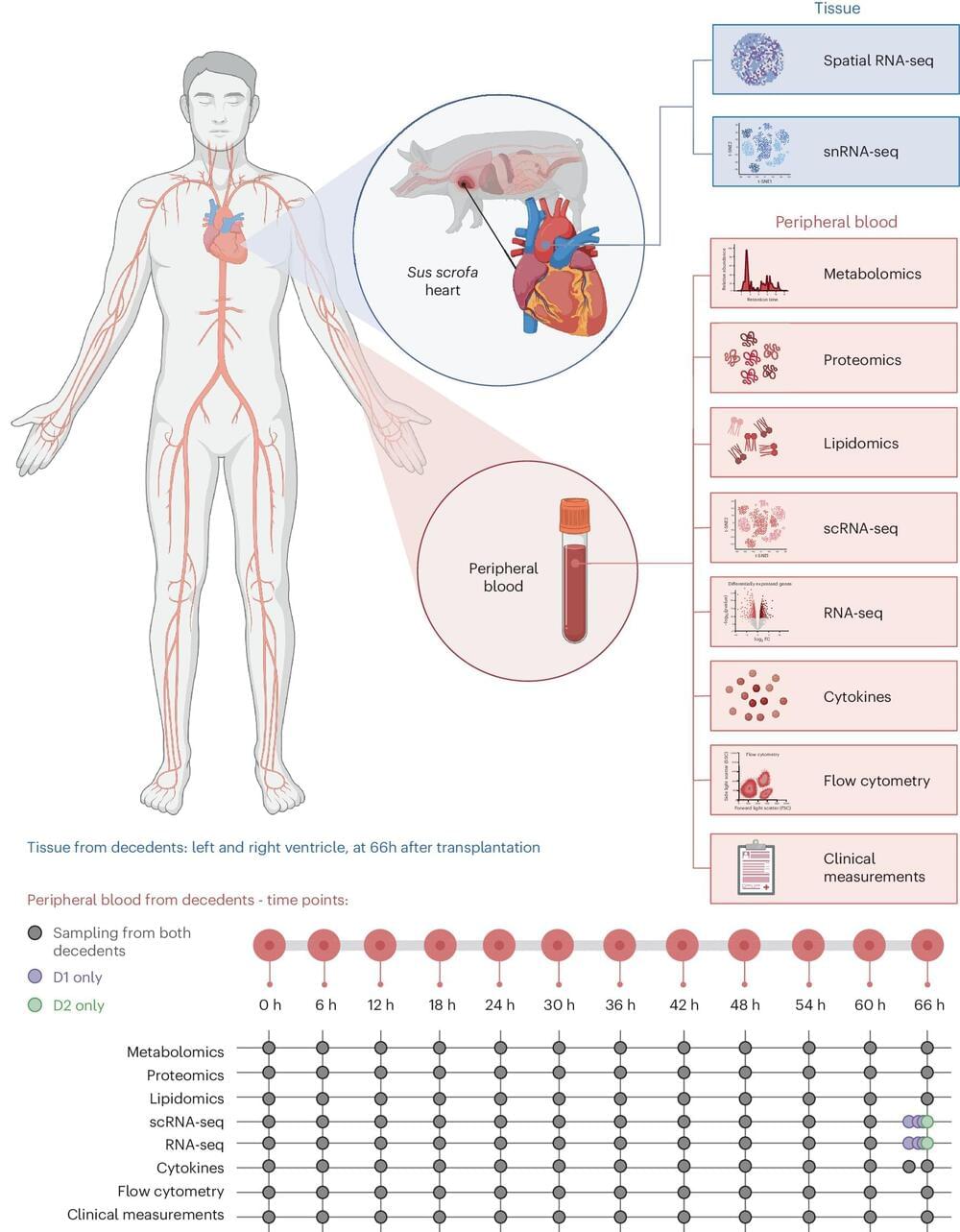
A large team of biomedical researchers affiliated with a host of institutions across the U.S., the U.K., Saudi Arabia and France, has learned more about many of the factors involved in xenotransplantation as they conducted a large number of tests on two brain-dead human patients that had received genetically engineered pig hearts.

A hormone already present in the human body could be used to stop Alzheimer’s disease in its tracks, scientists have announced.
Researchers discovered that a small part of an appetite-suppressing hormone called leptin, which is present in everyone, can have dramatic effects on the brain, including stopping the development of Alzheimer’s disease in its earliest stages.
Their tests have shown that leptin can reduce the effects of two toxic proteins in the brain called amyloid and tau, which build up and lead to memory loss and development of Alzheimer’s disease.