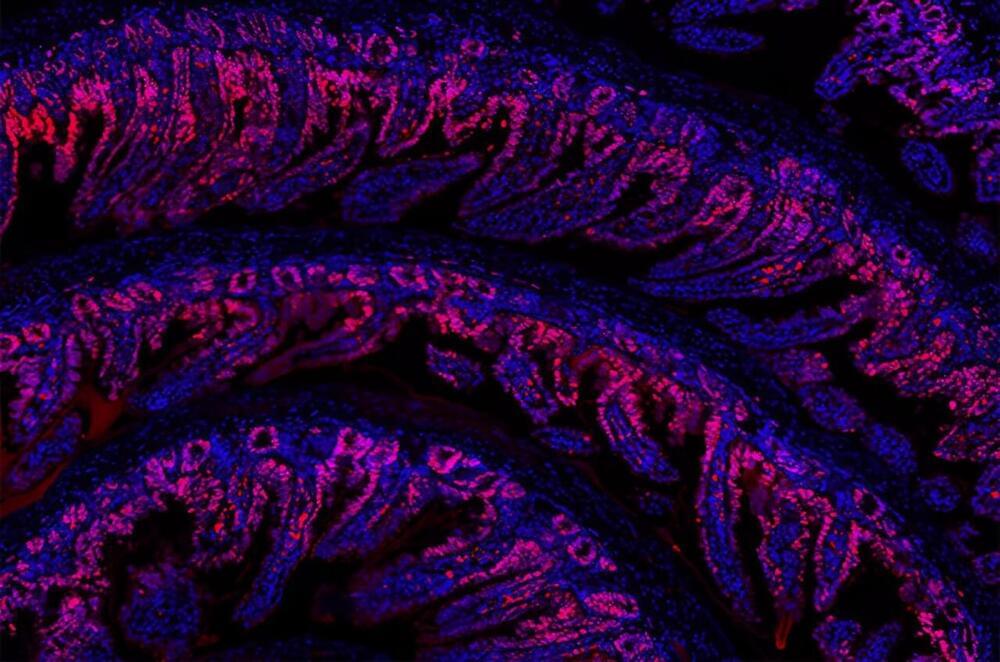
The tiny colons were grown from mouse stem cells, but human versions could one day be used to test new drugs for colorectal cancer, scientists say.
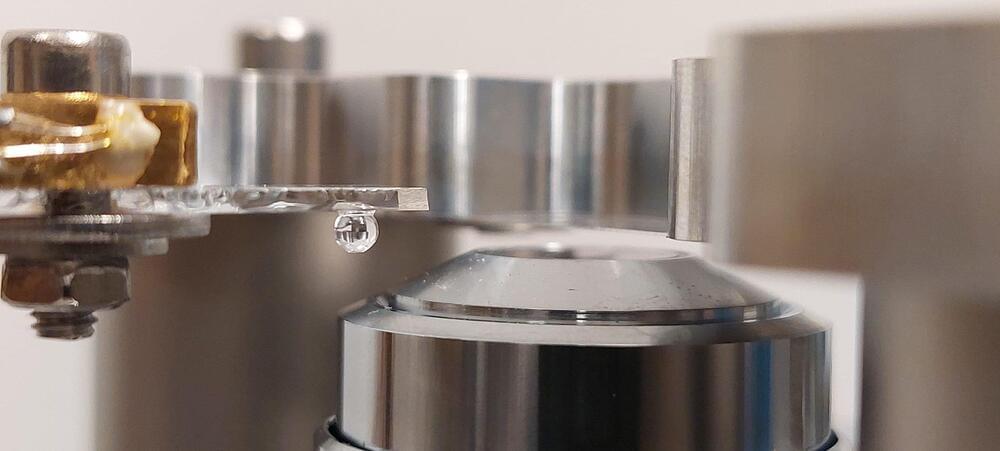
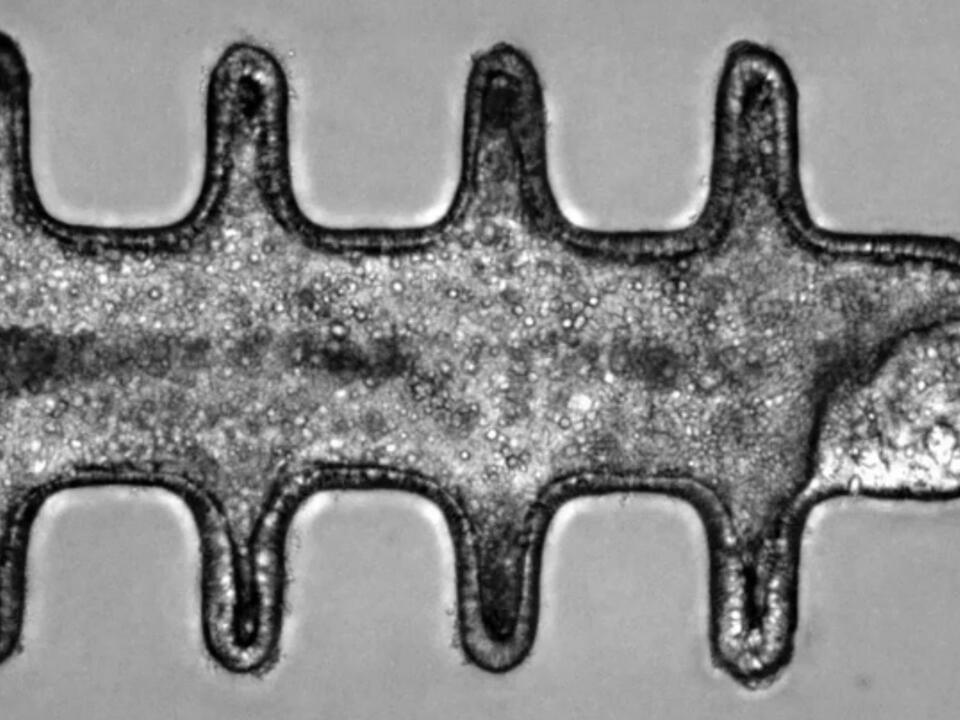


Studying tissues, cells, and proteins under a microscope is essential for disease prevention and treatment. This research requires accurately measuring the dimensions of these biological structures. However, when viewed through a light microscope, these samples can sometimes appear more flattened than their true form.
Researchers at Delft University of Technology have now demonstrated for the first time that this distortion is not constant, contrary to what many scientists have assumed for decades. The breakthrough, published in Optica, confirms a prediction by Nobel laureate Stefan Hell from the 90s. With an online calculation tool and software, every researcher can now determine the correct depth of a biological sample.
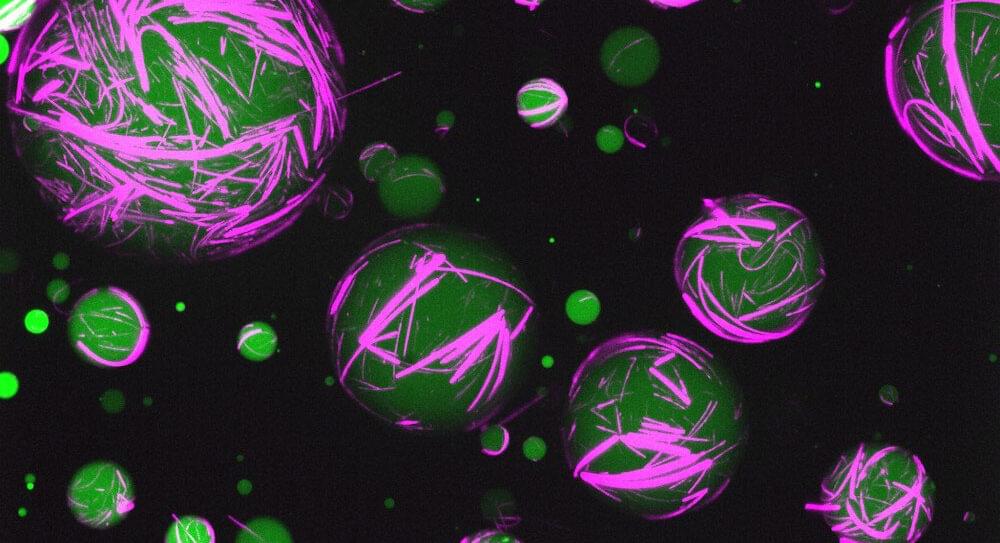
Unlike the rigid skeletons within our bodies, the skeletons within individual cells—cytoskeletons—are changeable, even fluid. And when these cytoskeletons reorganize themselves, they do more than support different cell shapes. They permit different functions.
Little wonder, then, that scientists who build artificial cells hope to create synthetic cytoskeletons that act like natural cytoskeletons. Synthetic cytoskeletons capable of supporting dynamic changes in cell shape and function could enable the development of novel drug delivery systems, diagnostic tools, and regenerative medicine applications.
Synthetic cytoskeletons have incorporated building blocks such as polymers, small molecules, carbon nanotubes, peptides, and DNA nanofilaments. Mostly DNA nanofilaments. Although they offer programmability, they can be hard to fine tune. To get around this difficulty, scientists based at UNC Chapel Hill led by Ronit Freeman, PhD, investigated the relatively unexplored possibilities offered by peptides. Specifically, the scientists engineered artificial cells using a programmable peptide–DNA nanotechnology approach.

Cognitive decline and dementia already affect more than 55 million people worldwide. This number is projected to skyrocket over the next few decades as the global population ages.
There are certain risk factors of cognitive decline and dementia that we cannot change – such as having a genetic predisposition to these conditions. But other risk factors we may have more power over – with research showing certain modifiable lifestyle habits, such as smoking, obesity and lack of exercise, are all linked to higher risk of dementia.
What role nutrition plays in preventing cognitive decline and dementia has also been the focus of scientific research for quite some time.
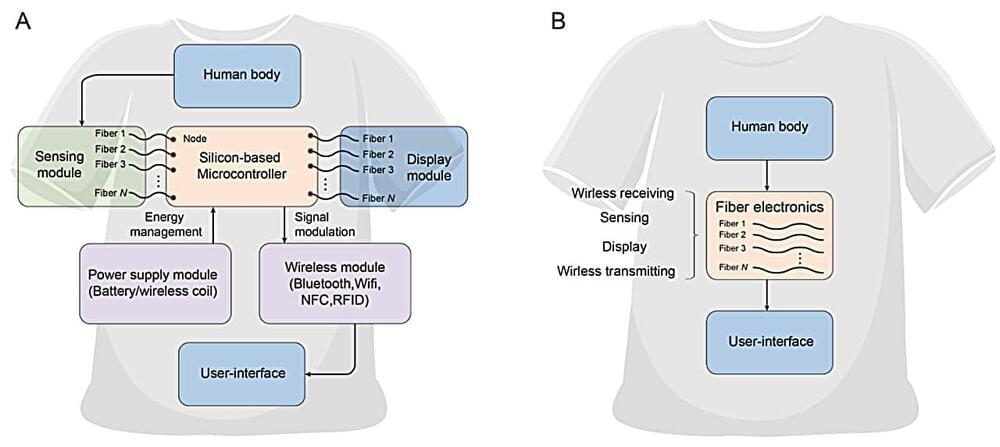
A team of materials scientists and engineers from Donghua University, in China, and the National University of Singapore, has developed a type of fiber that does not rely on chips or batteries to convert visual signals to digital transmissions as it interacts with the human body.
The paper is published in the journal Science. Yunzhu Li and Yiyue Luo with the University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign and MIT, respectively, have published a Perspective piece in the same journal issue outlining the work done by the team on this new effort.
Over the past several years, scientists have been trying to find a way to integrate electronic devices with textiles for such applications as clothes that can display colors, patterns or even messages. Unfortunately, previous efforts involve adding stiff batteries and chips to materials, making them too uncomfortable to wear. In this new effort, the researchers have found a way to get around these problems.
It watches, saps the very spirit. And the worst thing of all is I watch it. I can’t not look. It’s like a drug, a horrible drug. You can’t resist it. It’s an addiction. These words of testimony are babbled by the crumbling Colonel Grover to describe O.B.I.T. — The Outer Band Individuated Teletracer — a hellishly precise surveillance machine of questionable origin. Uncovered by a murder investigation at a Defense Department research center, O.B.I.T. proves to be an insidious instrument that breeds fear and hostility. Both cautionary tale and tight courtroom drama, this haunting episode explores the fear and hostility that result when all privacy is eliminated…and all secrets are revealed! Alan Baxter, Jeff Corey and Peter Breck star!
Regenerating damaged tissues or organs has been a dream of scientists for decades. Now, researchers at the FMI and Novartis Biomedical Research have discovered a new molecule that activates a protein involved in regeneration. The tool holds promise for advancing our understanding of how organisms repair damaged tissue.
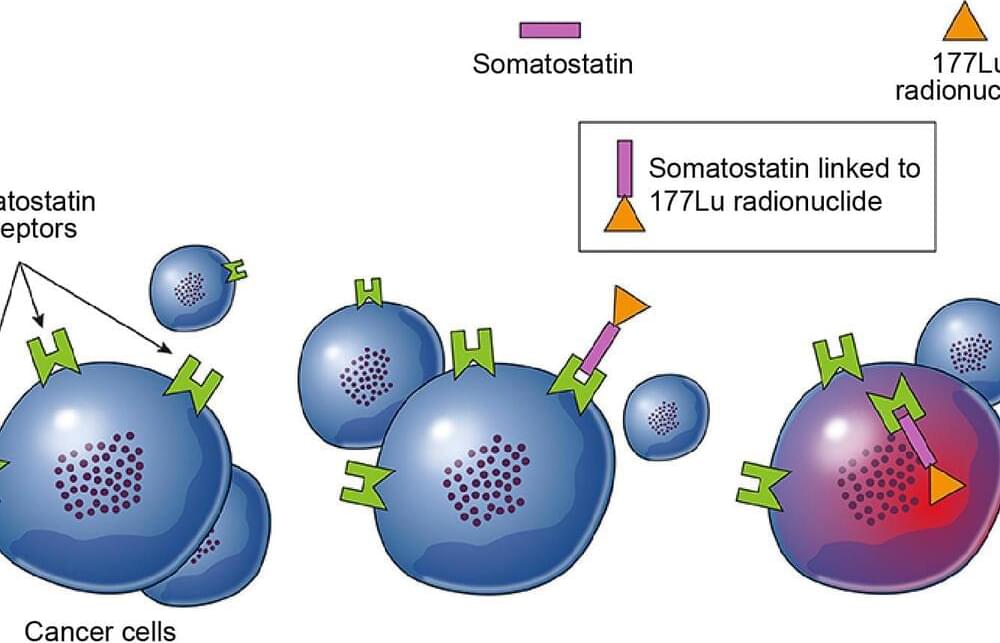
People with advanced neuroendocrine tumors in the digestive system may benefit from a treatment combination that includes the drug Lu 177-dotatate (Lutathera), according to the results of a first-of-its-kind clinical trial.
All participants in the trial, called NETTER-2, had advanced neuroendocrine tumors in the gastrointestinal tract or pancreas that had not yet been treated.
Those who received Lu 177-dotatate plus octreotide (Sandostatin) lived almost three times as long without their cancer getting worse (progression-free survival) as those who received octreotide alone—a median of nearly 23 months, versus 8.5 months. And the number of people whose tumors shrank, sometimes completely, was nearly five times greater in those who received both drugs compared to those who only received octreotide.
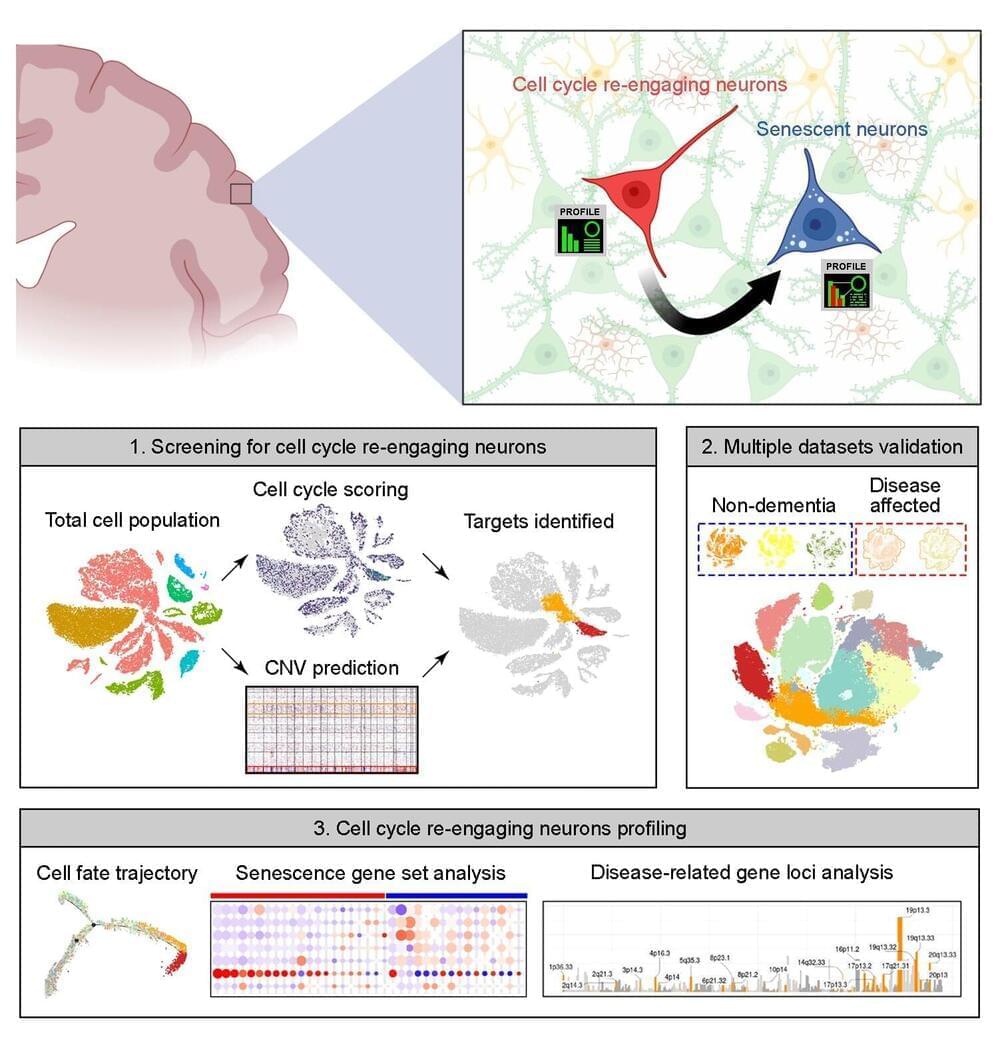
Post-mitotic neurons in the brain that re-enter the cell cycle quickly succumb to senescence, and this re-entry is more common in Alzheimer’s disease, according to a new study published April 9 in the open-access journal PLOS Biology by Kim Hai-Man Chow and colleagues at the Chinese University of Hong Kong.
The phenomenon may provide an opportunity to learn more about the neurodegeneration process, and the technique used to make this discovery is readily applicable to other inquiries about unique populations of cells in the brain.
Most neurons in the brain are post-mitotic, meaning they have ceased to divide. For many years, it had been assumed that this post-mitotic state was permanent. Recent discoveries have shown that a small proportion of neurons re-enter the cell cycle, but little is known about their fate after they do.