Two RNA-editing therapies for genetic diseases have recently gained approval for clinical trials, raising hopes for safer treatments.


The challenge is huge: There’s a lot we don’t understand about Alzheimer’s disease, but we do know that patient’s brains tend to accumulate toxic tau and amyloid-beta proteins, so most research has focused on those targets.
That approach has led to new drugs that can slow the progression of Alzheimer’s to a small degree, but we’ve yet to find anything that can reverse the damage the disease does to the brain.
The big idea: Synapses — the connections between brain neurons — need a protein called “KIBRA” in order to form memories, and there’s a link between certain variants of the KIBRA gene and developing Alzheimer’s.

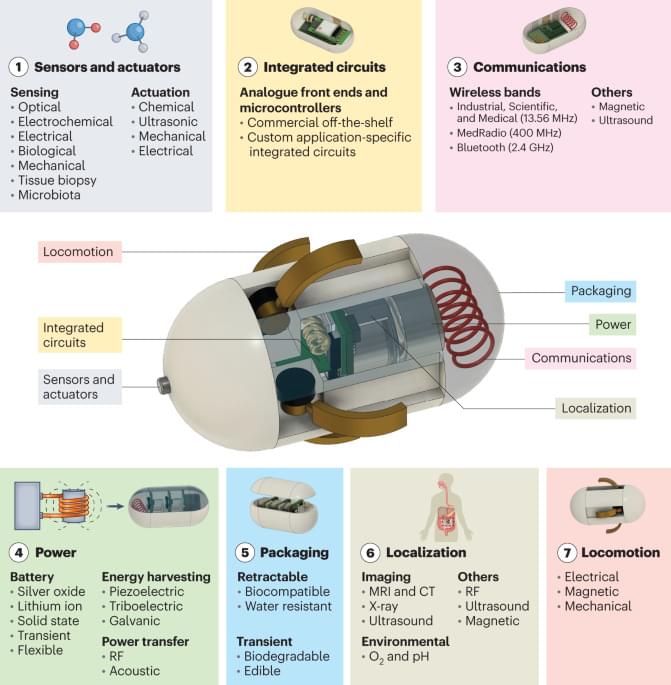
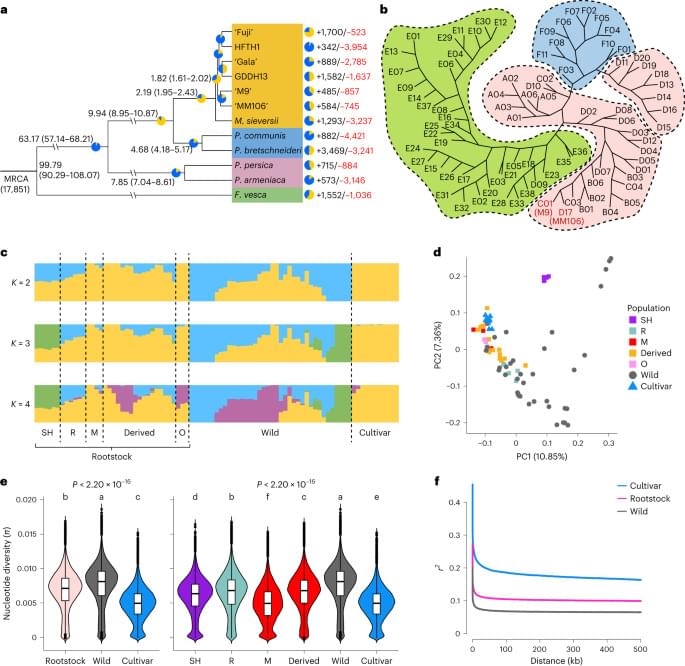
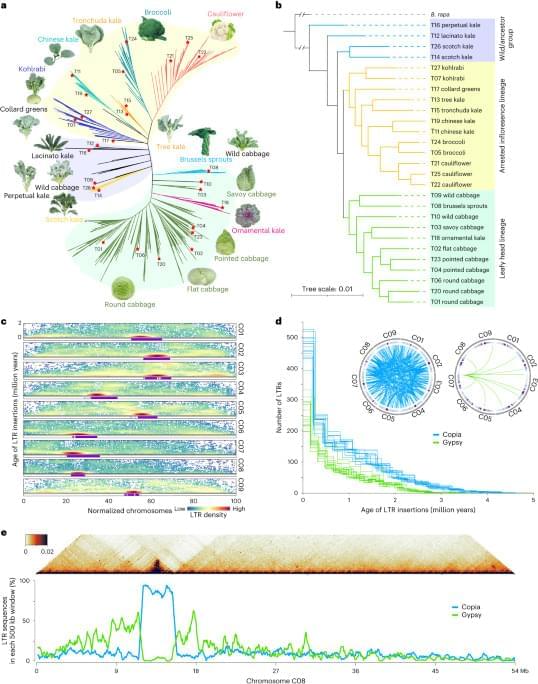
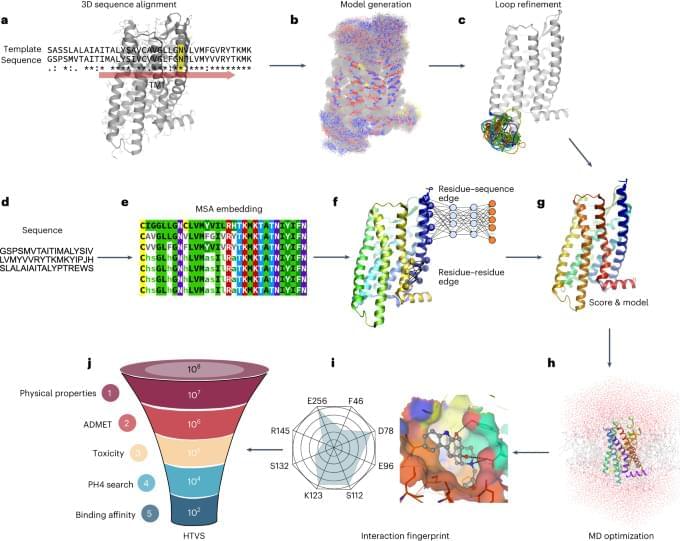
To construct a pan-genome that encompasses the full range of genetic diversity in B. ole racea, we analyzed the resequencing data of 704 globally distributed B. ole racea accessions covering all different morphotypes and their wild relatives (Supplementary Tables 1 and 2). We identified 3,792,290 SNPs and 528,850 InDels in these accessions using cabbage JZS as reference genome22. A phylogenetic tree was then constructed using SNPs, which classified the 704 accessions into the following three main groups: wild B. ole racea and kales, arrested inflorescence lineage (AIL) and leafy head lineage (LHL; Fig. 1a and Supplementary Note 2). The phylogenetic relationship revealed in our study was generally consistent with those reported previously4,5,24,25. Based on the phylogeny and morphotype diversity, we selected 22 representative accessions for de novo genome assembly (Table 1).
We assembled genome sequences of the 22 accessions by integrating long-reads (PacBio or Nanopore sequencing), optical mapping molecules (BioNano) or high-throughput chromosome conformation capture data (Hi-C) and Illumina short-reads (Methods; Supplementary Note 2 and Supplementary Tables 3–7). The total genome size of these assemblies ranged from 539.87 to 584.16 Mb with an average contig N50 of 19.18 Mb (Table 1). An average of 98% contig sequences were anchored to the nine pseudochromosomes of B. ole racea. The completeness of these genome assemblies was assessed using benchmarking universal single-copy orthologs (BUSCO), with an average of 98.70% complete score in these genomes (Supplementary Table 8).
To minimize artifacts that could arise from different gene prediction approaches, we predicted gene models of both the 22 newly assembled genomes and the five reported high-quality genomes5,21,22,23 using the same annotation pipeline (Methods). Using an integrated strategy combining ab initio, homology-based and transcriptome-assisted prediction, we obtained a range of 50,346 to 55,003 protein-coding genes with a mean BUSCO value of 97.9% in these genomes (Table 1). After gene prediction, a phylogenetic tree constructed based on single-copy orthologous genes clustered the 27 genomes into three groups, similar to the results observed in the population (Fig. 1a and b).

Diagnosing schizophrenia as early as possible helps minimize the toll the neurological disorder takes on the body and the mind. Unfortunately the condition’s signs can be difficult to spot in the early stages.
That’s why researchers led by a team from the Indiana University School of Medicine have developed a test which offers a relatively simple and reliable way to check for current schizophrenia severity and future risk.
“Psychosis usually manifests in young adulthood – a prime period of life,” says neuroscientist Alexander Niculescu from the Indiana University School of Medicine. “Stress and drugs, including marijuana, are precipitating factors on a background of genetic vulnerability.”

Researchers from the University of Wisconsin-Madison (UW-Madison) have developed a novel approach for 3D printing functional human brain tissue.
The 3D printing process can create active neural networks in and between tissues that grow in a matter of weeks.
The researchers believe that their 3D bioprinted brain tissue provides an effective tool for modeling brain network activity under physiological and pathological conditions, and can also serve as a platform for drug testing.
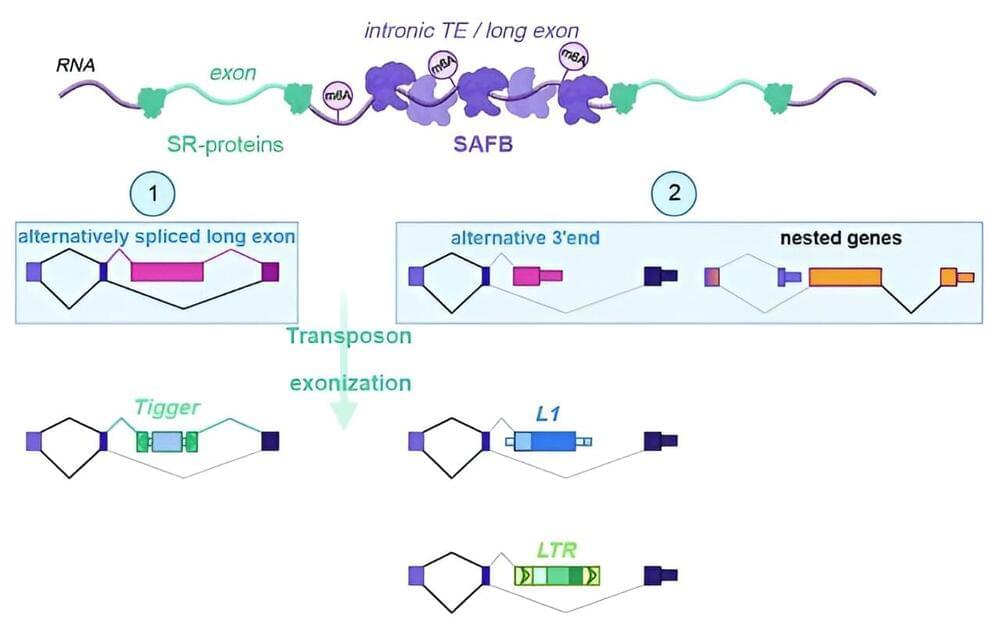
Transposable elements are mobile genetic elements that can relocate within the genome and disrupt the normal function of genes, but are at the same time a source of evolutionary diversity. The lab of Tugce Aktas at the Max Planck Institute for Molecular Genetics has identified a novel pathway that keeps the activity of transposons in somatic cells in check after they have been transcribed.
Their findings have now been published in Nature. The work is a collaboration with the labs of Zachary D. Smith at the Yale Stem Cell Center, U.S., and Franz-Josef Müller from the Universitätsklinikum Schleswig-Holstein, Germany.
Over the course of evolution, the genomes of many organisms have become cluttered with ancient genetic remnants from evolution or parts of retroviruses that inserted their genetic code millions of years ago. Nearly half of the human genome consists of these transposable elements, or transposons.