Nov 6, 2024
Scientists Create a Potent Bacterial Anti-Cancer Vaccine
Posted by Arthur Brown in category: biotech/medical
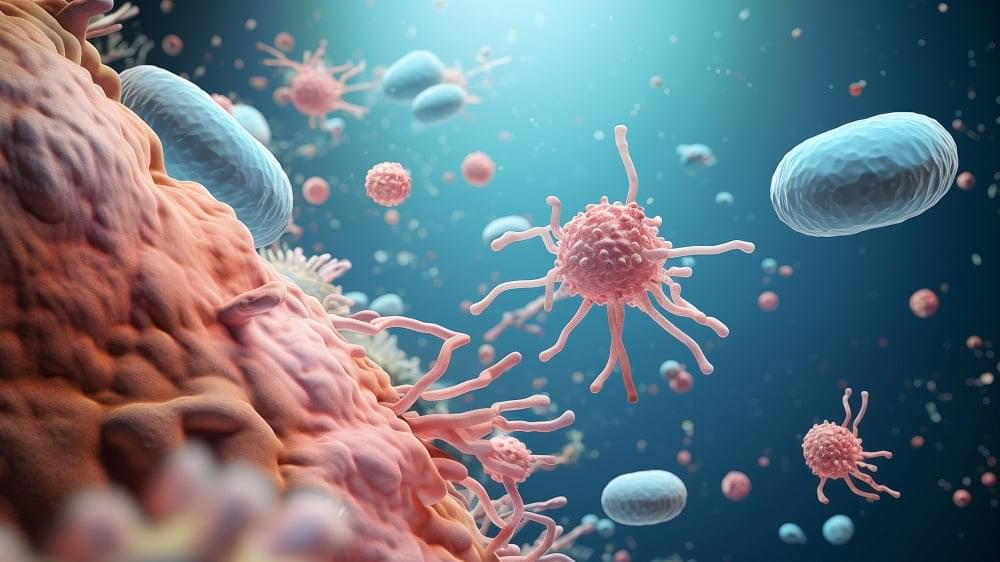
A new study describes a novel anti-cancer vaccine based on antigen-producing bacteria that can tackle solid and metastatic cancers [1].
Invading an invader
Years ago, scientists discovered that bacteria can colonize tumors [2]. Some bacteria are drawn to the tumor microenvironment due to factors such as necrotic tissue, hypoxia, and nutrient availability. For example, Clostridium species prefer anaerobic conditions and have been explored in tumor-targeting therapies. Salmonella and E. coli strains have also shown an affinity for tumors [3].