Some chemical tags on DNA, called epigenetic factors, that are present at a young age can affect the maximum life spans of mammal species.


Rising levels of respiratory viruses, including flu and COVID-19, are being reported this season. CDC urges the public to get vaccinated, with fewer than two in five adults and children having received the flu vaccine. Visitor restrictions are in place at Riley Hospital due to the surge in illnesses.


There’s an unfortunate irony in cell therapy that holds it back from its full potential: Regenerating tissues often must be damaged to know if the treatment is working, such as surgically removing tissue to see if rejuvenation is occurring beneath.
The alternative isn’t much better: Patients can choose to wait and see if their health improves, but after weeks of uncertainty, they might find that no healing has taken place without a clear explanation as to why.
Jinhwan Kim, a new assistant professor of biomedical engineering at the University of California, Davis, who holds a joint appointment with the Department of Surgery at UC Davis Health, wants to change all of that. In his research program, he combines nanotechnology and novel bioimaging techniques to provide non-invasive, real-time monitoring of cellular function and health.
Biotech stocks could be at a major turning point after FDA approval of the first gene editing drug using CRISPR technology to treat sickle cell disease. Gove…
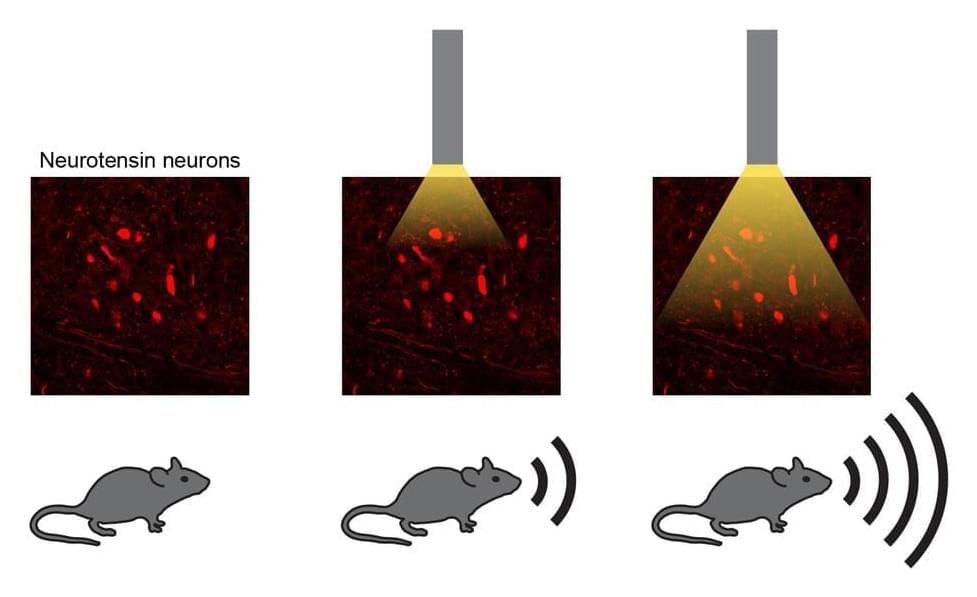
Humans and other mammals can produce a wide range of sounds, while also modulating their volume and pitch. These sounds, also known as mammalian vocalizations, play a central role in communication between both animals of the same and of different species.
Researchers at Stanford University School of Medicine recently carried out a study aimed at better understanding the neural mechanisms underpinning the production and modulation of mammal vocalizations. Their paper, published in Nature Neuroscience, identifies a neural circuit and a set of genetically defined neurons in the mouse brain that play a key role in the production of sound.
“All mammals, including humans, vocalize by pushing air past the vocal cords of the larynx, which vibrate to produce sound,” Avin Veerakumar, co-author of the paper, told Medical Xpress.
For the first time, researchers have used sound waves to 3D print an object from a distance—even with a wall in the way.
Producing fake sound reflections that simulate the presence or absence of an object could allow the military to hide assets underwater.
A hologram plate simulates the presence of a three-dimensional object by reflecting the appropriate light waves. Now researchers have demonstrated an equivalent behavior with sound by precisely mimicking the acoustic pattern scattered from an object [1]. The technique could be useful in military efforts to hide or disguise underwater objects, or it may be useful in modifying the reflected sounds of objects so that they are easier to identify by people with impaired vision.
The sound waves reflected from an object can be used to reconstruct its position and shape, an idea routinely exploited in sonar and ultrasound imaging. In principle, using similar concepts, a cleverly produced pattern of scattered waves streaming out of a small region could signify that an object is present when it is not. Several recent attempts to realize such “acoustic cloning” have been unsuccessful because of limitations in recording the precise pattern of waves an object reflects, a necessary preliminary step.
An experimental vaccine against human papillomavirus—HPV—appears to be safe, and most importantly, benefits patients who develop a rare airway cancer that manifests as recurrent obstructive growths requiring dozens, sometimes, hundreds of surgeries over a lifetime to keep the tumors at bay.
The tiny phase 1 clinical study of only 15 patients has served as a proof of concept, demonstrating that recurrent respiratory papillomatosis, a cancerous disorder of the upper airways, can respond to therapeutic vaccination. The tumors are caused by either type 6 or type 11 human papillomavirus.
Writing in Science Translational Medicine, scientists at the Center for Immune-Oncology, a division of the U.S. National Cancer Institute in Bethesda, Maryland, tackled the problem of recurrent respiratory papillomatosis by testing a vaccine strategy designed to prevent tumor development. Dr. Scott M. Norberg, lead author of the research, writes that the evolving approach is aimed at providing a pathway for the prevention of a condition for which there is no cure.