Magnets are magnificent. Made of iron, aluminum, nickel, cobalt, and various other metals, they’re used in compasses for navigation, in medical imaging machines to see inside the human body, in kitchens to keep cabinets and refrigerators closed, in computers to store data and in new high-speed “hyperloop” trains that can travel at speeds of up to 76 miles per hour.
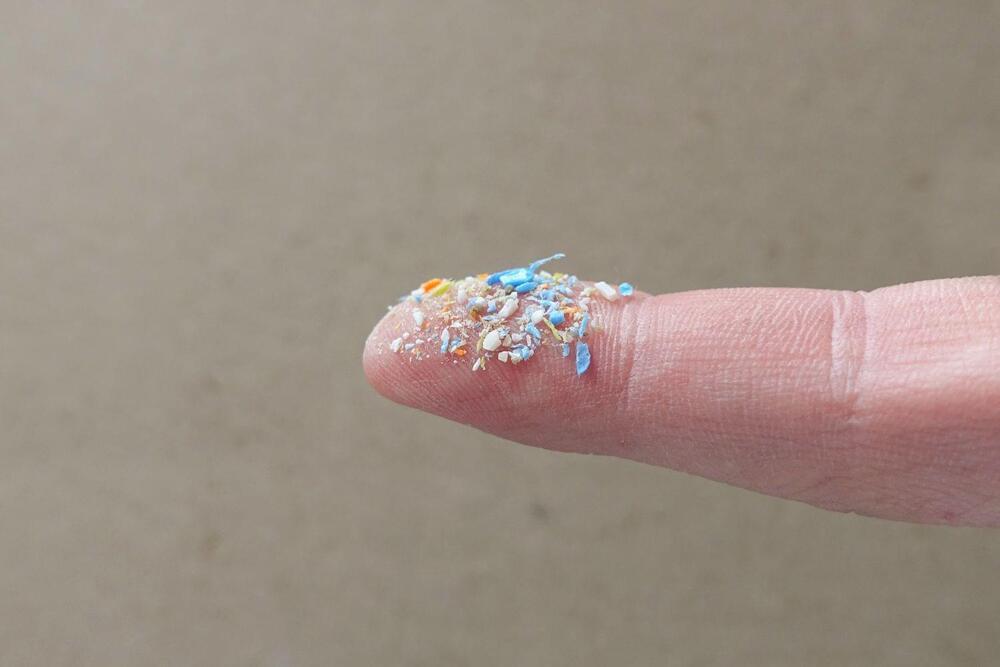
For environmentalists, however, the most exciting use yet for magnets might be a newly discovered application out of Australia’s Royal Melbourne Institute of Technology, otherwise known as RMIT University: Using magnets, researchers there have discovered a novel way of removing harmful microplastics from water.
“[Microplastics] can take up to 450 years to degrade, are not detectable and removable through conventional treatment systems, resulting in millions of tons being released into the sea every year,” co-lead research Nasir Mahmood said in a statement. “This is not only harmful for aquatic life, but also has significant negative impacts on human health.”