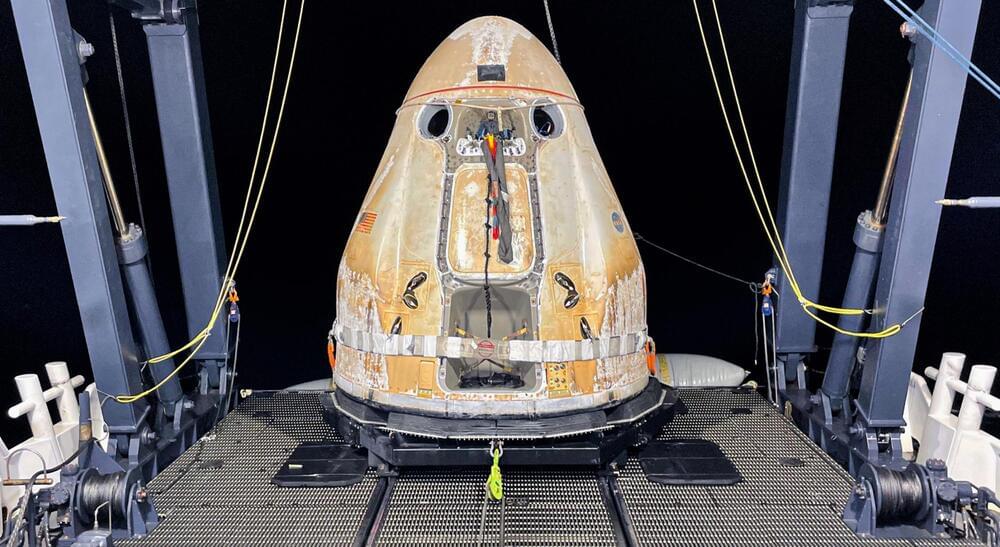
A SpaceX Cargo Dragon 2 spacecraft has safely returned to Earth after delivering several tons of NASA supplies to the International Space Station (ISS).
A little over six weeks after Falcon 9 launched SpaceX’s 26th Commercial Resupply Services 2 (CRS2) mission for NASA, Dragon departed the ISS on January 9th. Efficiently lowering its orbit with several small Draco thrusters took about 36 hours, and reusable Dragon 2 capsule C211 eventually slowed to the point that it began impacting Earth’s atmosphere. Using its ablative heat shield like a brake pad, Dragon slowed from a velocity of 7.5 kilometers per second (16,800 mph) to about 155 meters per second (~350 mph) before beginning parachute deployment.
At 5:19 am on January 11th, the Dragon capsule gently splashed down off the coast of Tampa, Florida, and was quickly secured by a SpaceX recovery ship. Once onboard, the capsule was opened up, and cargo fresh from orbit was loaded onto a helicopter as quickly as possible. That system – primarily created to rapidly transport astronauts back to NASA medical facilities – also means that scientists can get access to their recovered ISS experiments just a handful of hours after Cargo Dragon splashes down.