Page 11019
Jul 29, 2016
China’s new quantum satellite paves the way for unhackable satellite internet
Posted by Karen Hurst in categories: cybercrime/malcode, encryption, internet, quantum physics, satellites
All that I can say is “WOW!”
CHINA is on the brink of launching a groundbreaking new satellite capable of conducting quantum experiments in space, leading some to predict it will usher in the beginning of a new space race.
The world will be watching very closely after the Chinese-led satellite launches in August. If it proves successful in carrying out the quantum experiments, China is expected to follow it with many more in a bid to create a super secure network that uses an encryption technique based on the principles of quantum communication.
Continue reading “China’s new quantum satellite paves the way for unhackable satellite internet” »
Jul 29, 2016
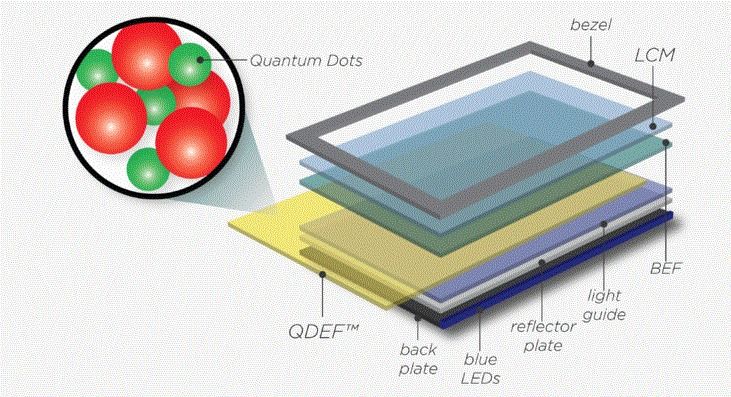
Apple Advances Work on Quantum Dot Displays for Future Macs, iOS Devices & Possible TV
Posted by Karen Hurst in categories: energy, mobile phones, quantum physics
Apple and Q-Dots.
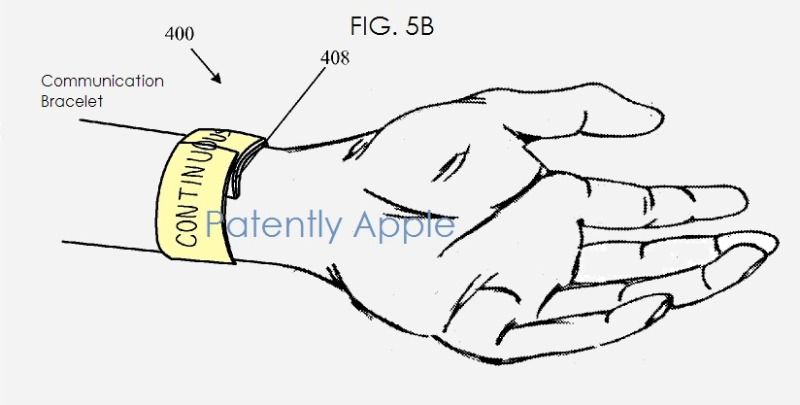
While we know that Apple’s next display shift will be to OLED for their 2017 Anniversary edition iPhone, Apple is always looking to the next wave technology just on the horizon. So what’s beyond OLED? At the moment, many think the next trend points to Quantum Dot LED or QDLED. While the structure of a QLED is very similar to OLED technology, the difference is that the light emitting centers are cadmium selenide nanocrystals, or quantum dots. Theoretically, the advantages to this type of display is that it could reportedly deliver brighter ‘pure color’ and consumes less power, in fact close to 50% less power. The technology is also ideal for consumer devices that demand a flexible display. When Apple first introduced their vision of an Apple Watch in 2013, they presented it with a ‘continuous’ display that completely wraps around a users wrist as noted in the patent figure below. A QDLED type of display would allow such a form factor to come to market.
Jul 29, 2016
The Quantum Experiment that Broke Reality
Posted by Karen Hurst in category: quantum physics

Nice history.
(via PBS Space Time) The double slit experiment radically changed the way we understand reality. Find out what the ramifications of this experiment were and how we can use it to better comprehend our universe.
Continue reading “The Quantum Experiment that Broke Reality” »
Jul 29, 2016
Scientia Professor Michelle Yvonne Simmons
Posted by Karen Hurst in categories: computing, quantum physics
Professor Michelle Simmons of the Univ. of Sydney is an early pioneer of QC and will go down in history as the 1st Mother of Quantum Computing and a person that all (women and men) can look up to and be a true role model for many in tech and science. I hope to continue to make young girls and women everywhere to learn about her and hopefully they (like me) will consider her a role model to follow.
Fields of research: Quantum Physics, Condensed Matter Physics Campus: Kensington Tags: Expanding Knowledge in the Information and Computing Sciences, Expanding Knowledge in the Physical Sciences.
Jul 29, 2016
PV Nano Cell’s nanometric silver conductive ink enables non-contact digital inkjet printing
Posted by Karen Hurst in categories: solar power, sustainability
Nice.
PV Nano Cell has commercially developed ‘Sicrys’, a single-crystal, nanometric silver conductive ink delivering enhanced performance for digital conductive printing in mass production applications. The inks are also available in copper-based form, delivering all of the product’s properties and advantages with improved cost efficiency.
Problem
Jul 28, 2016
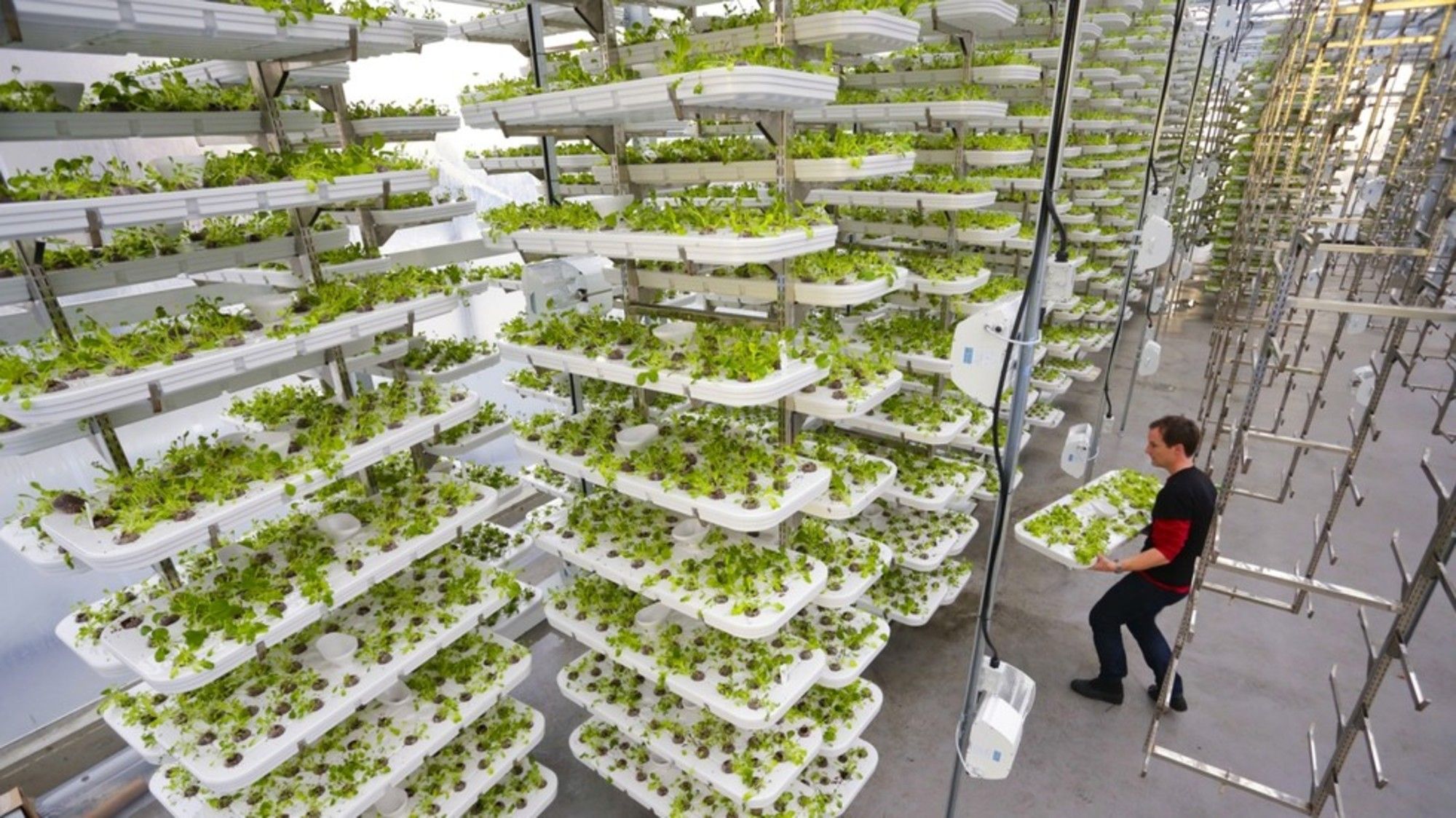
This Farm of the Future Uses No Soil and 95% Less Water
Posted by Shailesh Prasad in categories: food, sustainability
Considering it uses 95% less water than regular farms, could vertical farming be the future of agriculture?
Jul 28, 2016
Will You Ever Love a Robot?
Posted by Shailesh Prasad in categories: biological, robotics/AI

“In a sense, we’re all meat robots.” Chief Scientist at Hanson Robotics blurs the lines between biological and engineered robotics in this short yet fascinating excerpt.
Jul 28, 2016
Dirty to drinkable: Novel hybrid nanomaterials quickly transform water
Posted by Shailesh Prasad in categories: engineering, nanotechnology
Now, a team of engineers at Washington University in St. Louis has found a way to use graphene oxide sheets to transform dirty water into drinking water, and it could be a global game-changer.
“We hope that for countries where there is ample sunlight, such as India, you’ll be able to take some dirty water, evaporate it using our material, and collect fresh water,” said Srikanth Singamaneni, associate professor of mechanical engineering and materials science at the School of Engineering & Applied Science.
The new approach combines bacteria-produced cellulose and graphene oxide to form a bi-layered biofoam. A paper detailing the research is available online in Advanced Materials.