Page 11169
May 19, 2016
ORNL demonstrates large-scale technique to produce quantum dots
Posted by Karen Hurst in categories: electronics, quantum physics, solar power, sustainability
Q-Dots ORNL style.
VIDEO: A method to produce significant amounts of semiconducting nanoparticles for light-emitting displays, sensors, solar panels and biomedical applications has gained momentum with a demonstration by researchers at Oak Ridge National… view more
Continue reading “ORNL demonstrates large-scale technique to produce quantum dots” »
May 19, 2016
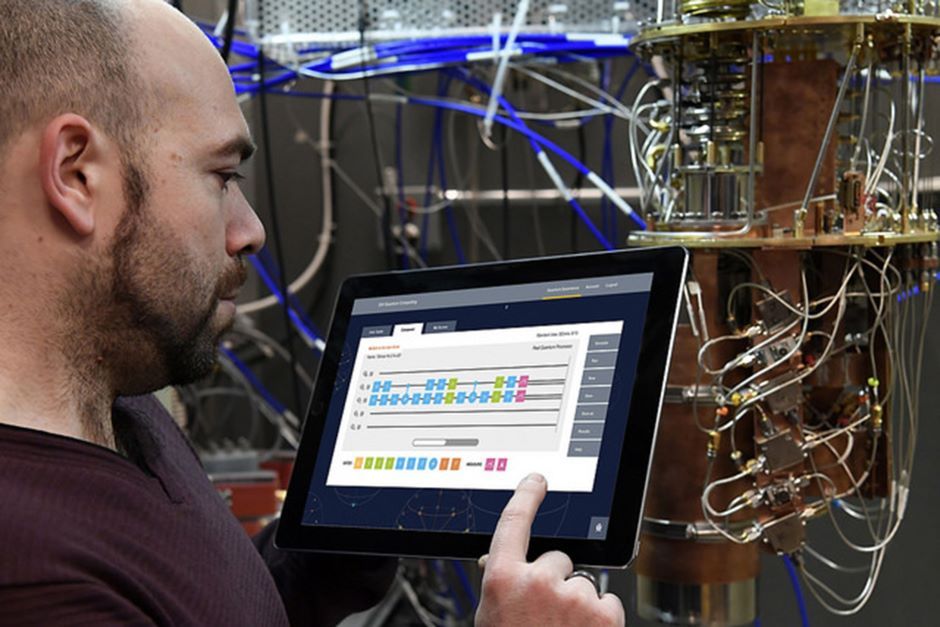
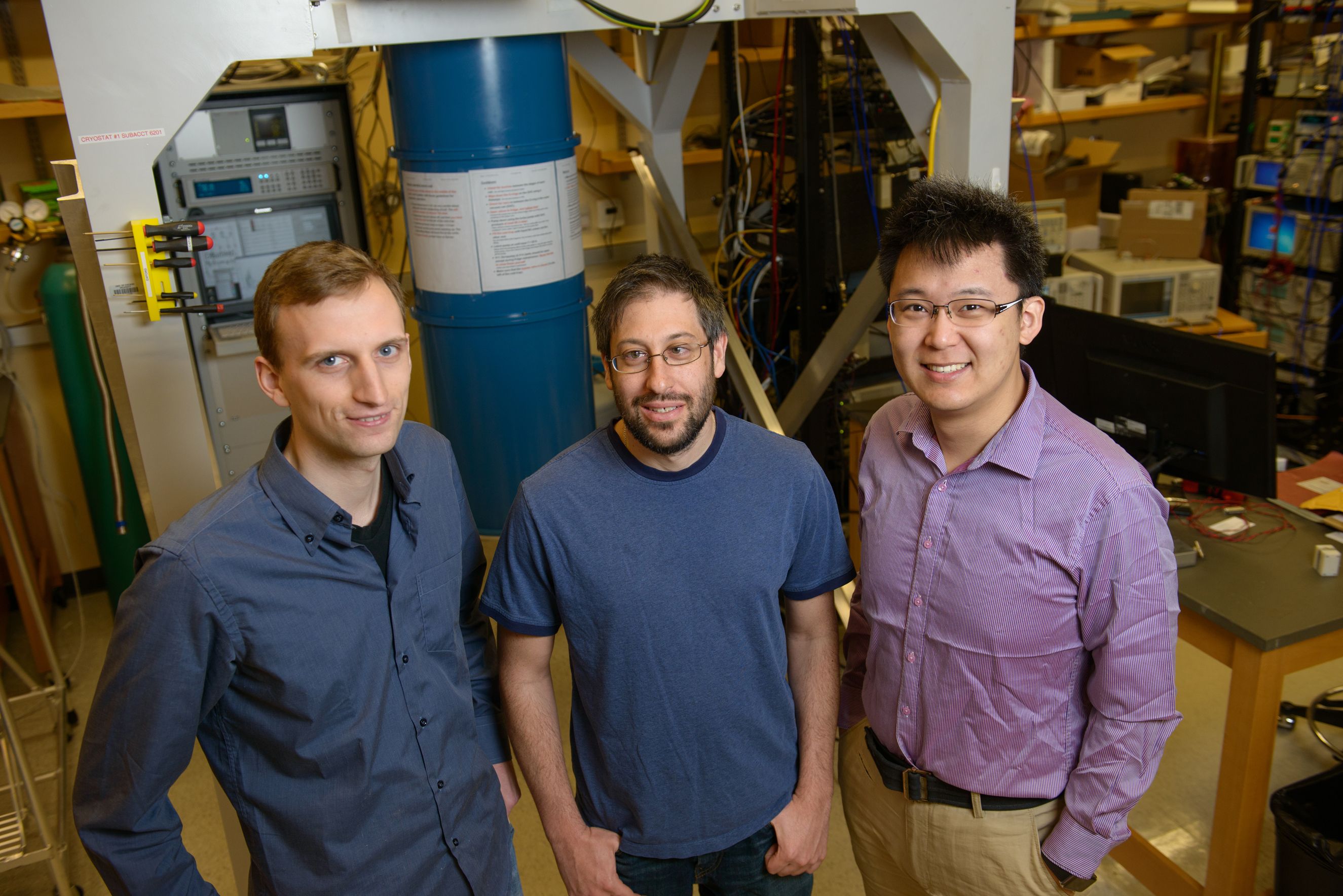
New device steps toward isolating single electrons for quantum computing
Posted by Karen Hurst in categories: computing, particle physics, quantum physics
Finally, some well deserved recogonition to Argonne Natl. Labs in their efforts on QC with the Univ. Of Chicago.
If biochemists had access to a quantum computer, they could perfectly simulate the properties of new molecules to develop novel drugs in ways that would take the fastest existing computers decades.
Electrons represent an ideal quantum bit, with a “spin” that when pointing up can represent a 0 and down can represent a 1. Such bits are small—even smaller than an atom—and because they do not interact strongly, they can remain quantum for long periods. However, exploiting electrons as qubits also poses a challenge because they must be trapped and manipulated. Which is exactly what David Schuster, assistant professor of physics, and his collaborators at UChicago, Argonne National Laboratory and Yale University have done.
Continue reading “New device steps toward isolating single electrons for quantum computing” »
May 19, 2016
With Moore’s Law in doubt, eyes turn to quantum computing
Posted by Karen Hurst in categories: computing, quantum physics
Moore’s Law was already identified as a problem regardless of Quantum. And, the move to Quantum happened regardless of Moores Law and the excitment around QC was not the result of Moores Law limitations. Just like all things, we evolve to better level of maturity.
The chip industry is giving another sign that Moore’s Law is coming to an end, but IBM is offering a glimpse at what might be computing’s future.
Industry experts from around the world who have been working together for years for forecast technology advances in the tech industry are throwing in the towel.
Continue reading “With Moore’s Law in doubt, eyes turn to quantum computing” »
May 19, 2016
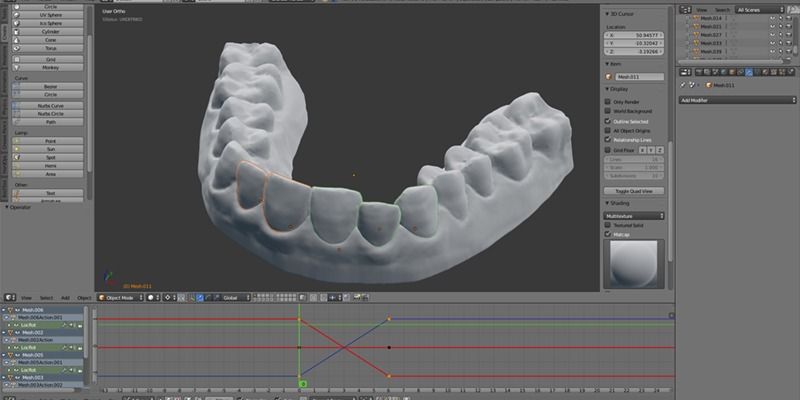
This college student 3D printed his own plastic braces for $60 — and they actually fixed his teeth
Posted by Karen Hurst in categories: 3D printing, education, health
Ever dream of becoming a dentist? Or, have family members needing new dentures? Or, know that one person who would look good if they only had some teeth. This 3D Printer is your answer.
An undergraduate at New Jersey Institute of Technology made his own plastic braces using a 3D printer, $60 of materials, and a healthy dose of ingenuity — and they actually worked.
Amos Dudley had braces in middle school, but he didn’t wear a retainer like he was supposed to, so his teeth slowly shifted back.
May 19, 2016
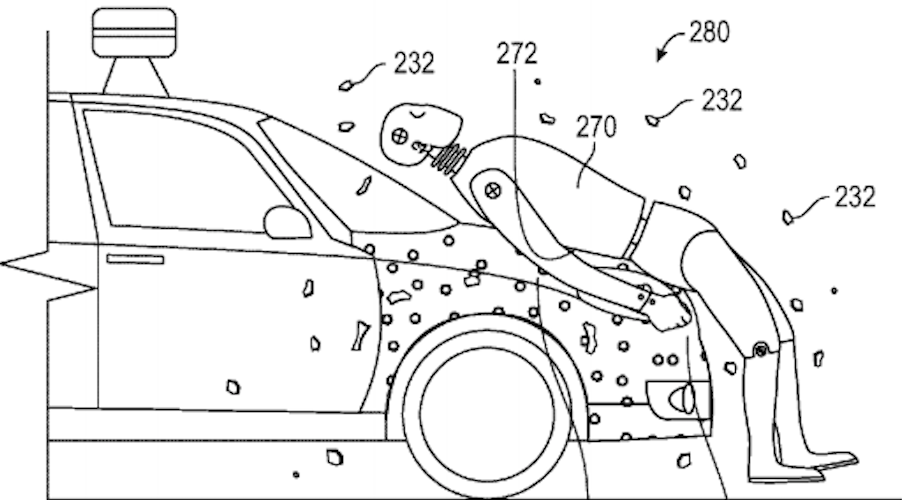
Google has patented a self-driving car that will glue people to the hood if you crash into them
Posted by Karen Hurst in categories: robotics/AI, transportation
Hmmm, no thanks.
The glue would be covered by an outer layer that peels away during an accident.
May 19, 2016
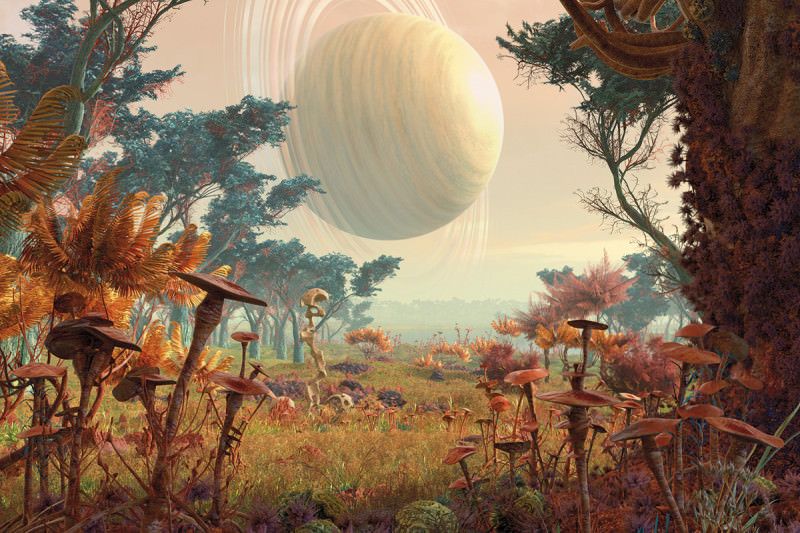
There might be a planet better than Earth – right next door
Posted by Sean Brazell in category: futurism
There should be worlds out there so balmy they make Earth look stale, and there are signs of one just four light years away. That’s close enough to visit…

May 19, 2016
NASA’s Mars rover has measured something in the air that scientists can’t explain
Posted by Sean Brazell in category: space

Watch the video NASA’s Mars rover has measured something in the air that scientists can’t explain on Yahoo Finance. VIDEO: NASA just uncovered another clue.
May 19, 2016
There’s a Workaround for the Heisenberg Uncertainty Principle: Time Travel
Posted by Andreas Matt in categories: physics, time travel
May 19, 2016
Multicellular Life Was Caused By The Same Gene That Suppresses Cancer
Posted by Shailesh Prasad in categories: biotech/medical, evolution
Biologists have identified the one gene that caused the evolution of single-celled organisms into multicellularity, debunking previous theories that several genes were at play. The gene retinoblastoma is also the same gene that is found to be defective in cancer patients, and suppresses tumors.