It’s one of the basic facts of science: Heat something and it expands. But a team of US scientists has gone counterintuitive and invented a 3D-printed material that shrinks when heated. Developed as part of DARPA’s program to study materials with controlled microstructure architecture, the lightweight metamaterial exhibits what the researchers call “negative thermal expansion.”
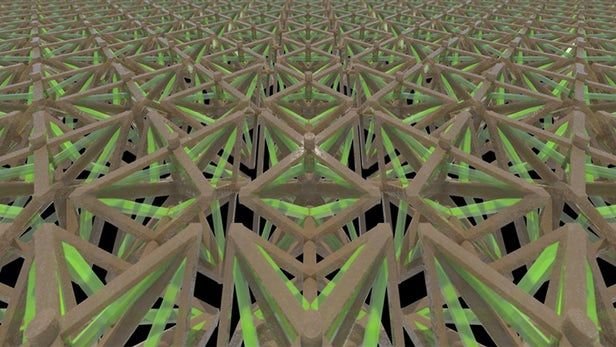
Metamaterials are one of those things that come out of the lab with an air of enchantment about them. Basically, they’re made up of composite materials, like metals, plastics, or ceramics, engineered into repeating, microscopic structures. Depending on how these structures are designed, they can give the metamaterial properties that aren’t found in nature and may not even be derived from the source materials themselves.
The study by a team from the Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory’s (LLNL) Additive Manufacturing Initiative in partnership with the University of Southern California, MIT, and the University of California, Los Angeles, used a 3D printing process called projection microstereolithograpy to form a polymer and a polymer/copper composite into a highly complex 3D bi-material microlattice structure. To put it more simply, they printed a material made of two substances to form a pattern by printing out the polymer in a layer, cleaning the surface to avoid contamination, then printing the polymer/copper composite, then repeating.









Comments are closed.