Humans and other mammals can produce a wide range of sounds, while also modulating their volume and pitch. These sounds, also known as mammalian vocalizations, play a central role in communication between both animals of the same and of different species.
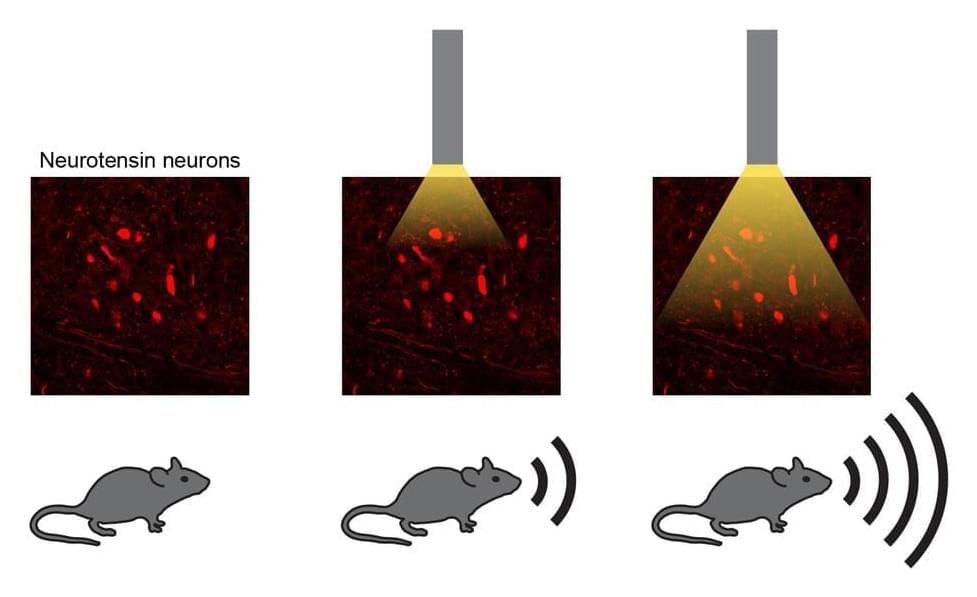
Researchers at Stanford University School of Medicine recently carried out a study aimed at better understanding the neural mechanisms underpinning the production and modulation of mammal vocalizations. Their paper, published in Nature Neuroscience, identifies a neural circuit and a set of genetically defined neurons in the mouse brain that play a key role in the production of sound.
“All mammals, including humans, vocalize by pushing air past the vocal cords of the larynx, which vibrate to produce sound,” Avin Veerakumar, co-author of the paper, told Medical Xpress.









Comments are closed.