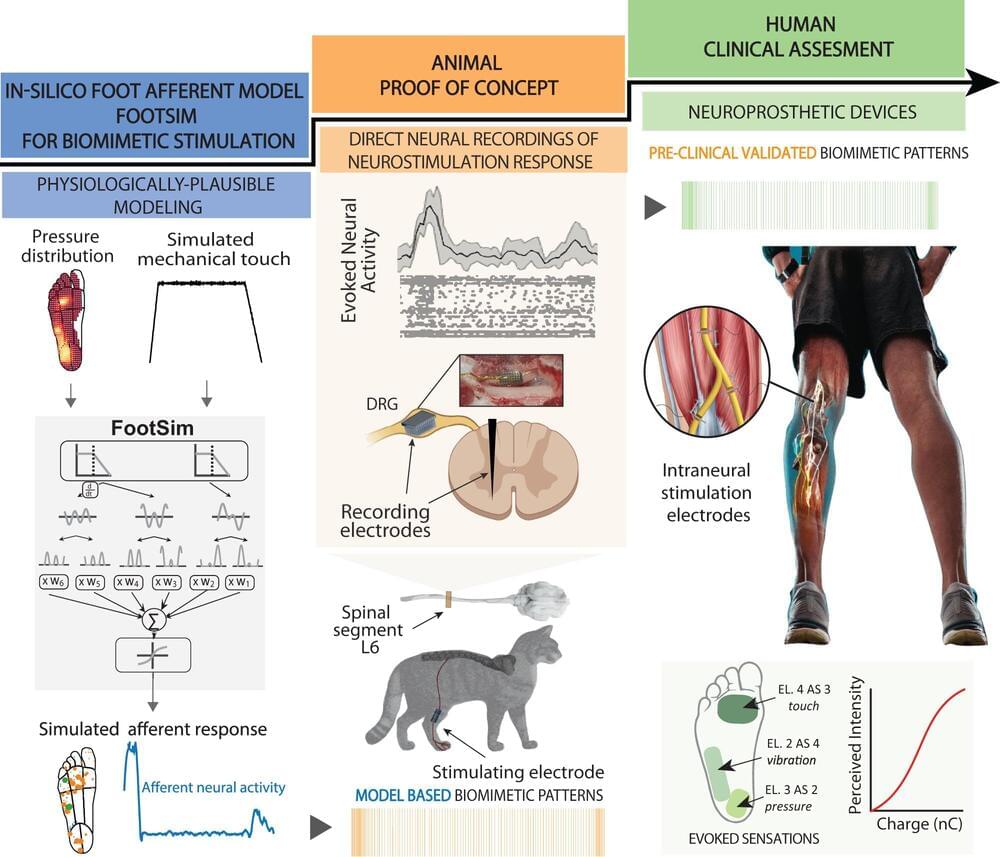
A few years ago, a team of researchers working under Professor Stanisa Raspopovic at the ETH Zurich Neuroengineering Lab gained worldwide attention when they announced that their prosthetic legs had enabled amputees to feel sensations from this artificial body part for the first time.
Unlike commercial leg prostheses, which simply provide amputees with stability and support, the ETH researchers’ prosthetic device was connected to the sciatic nerve in the test subjects’ thigh via implanted electrodes.
This electrical connection enabled the neuroprosthesis to communicate with the patient’s brain, for example relaying information on the constant changes in pressure detected on the sole of the prosthetic foot when walking. This gave the test subjects greater confidence in their prosthesis—and it enabled them to walk considerably faster on challenging terrains.









Comments are closed.