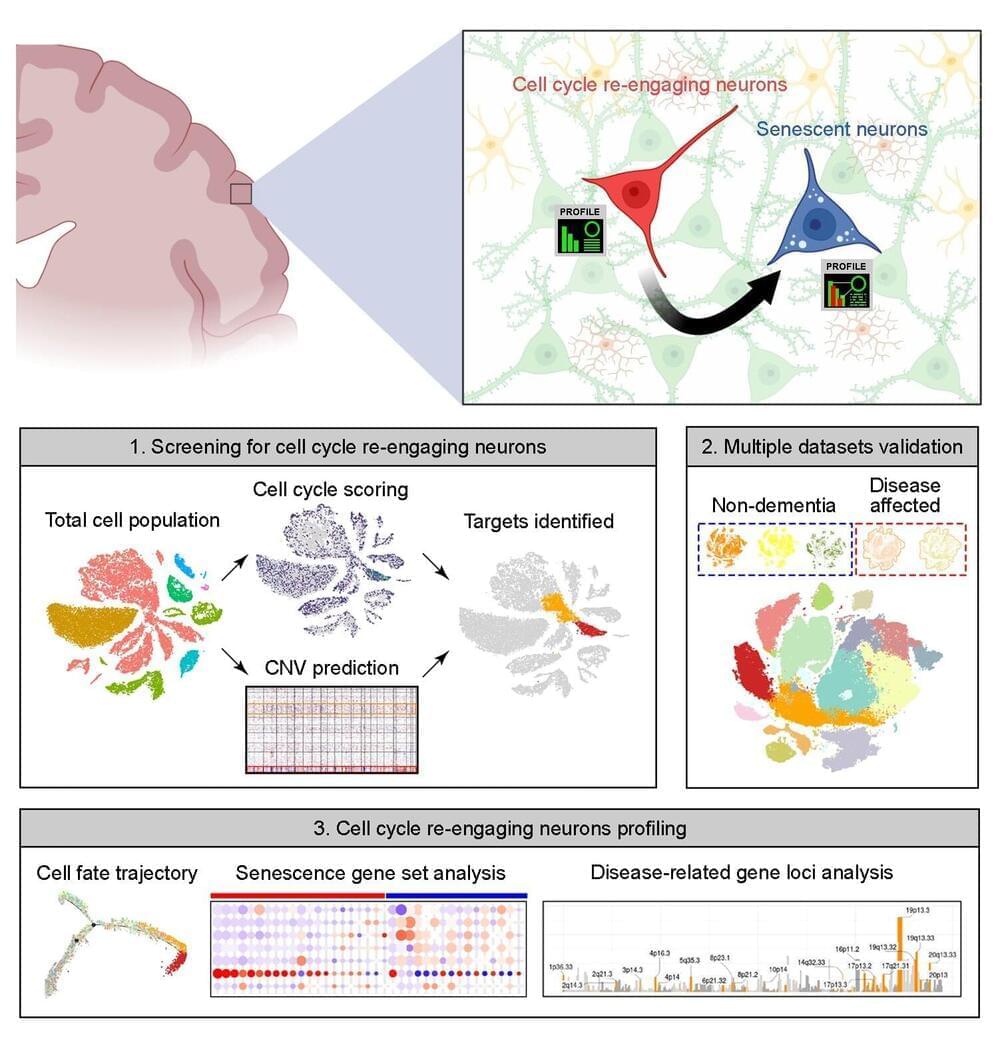
Post-mitotic neurons in the brain that re-enter the cell cycle quickly succumb to senescence, and this re-entry is more common in Alzheimer’s disease, according to a new study published April 9 in the open-access journal PLOS Biology by Kim Hai-Man Chow and colleagues at the Chinese University of Hong Kong.
The phenomenon may provide an opportunity to learn more about the neurodegeneration process, and the technique used to make this discovery is readily applicable to other inquiries about unique populations of cells in the brain.
Most neurons in the brain are post-mitotic, meaning they have ceased to divide. For many years, it had been assumed that this post-mitotic state was permanent. Recent discoveries have shown that a small proportion of neurons re-enter the cell cycle, but little is known about their fate after they do.









Comments are closed.