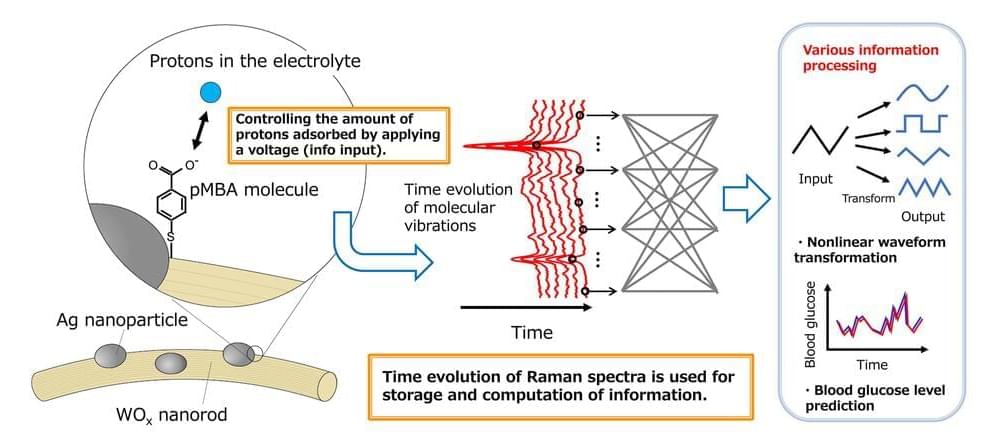
A collaborative research team from NIMS and Tokyo University of Science has successfully developed an artificial intelligence (AI) device that executes brain-like information processing through few-molecule reservoir computing. This innovation utilizes the molecular vibrations of a select number of organic molecules.
By applying this device for the blood glucose level prediction in patients with diabetes, it has significantly outperformed existing AI devices in terms of prediction accuracy.
The work is published in the journal Science Advances.









Comments are closed.