An international team of researchers of the Cluster of Excellence “Balance of the Microverse” at the University of Jena has investigated the mechanism that makes some types of bacteria reflect light without using pigments. The researchers were interested in the genes responsible and discovered important ecological connections. Their findings appear in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.
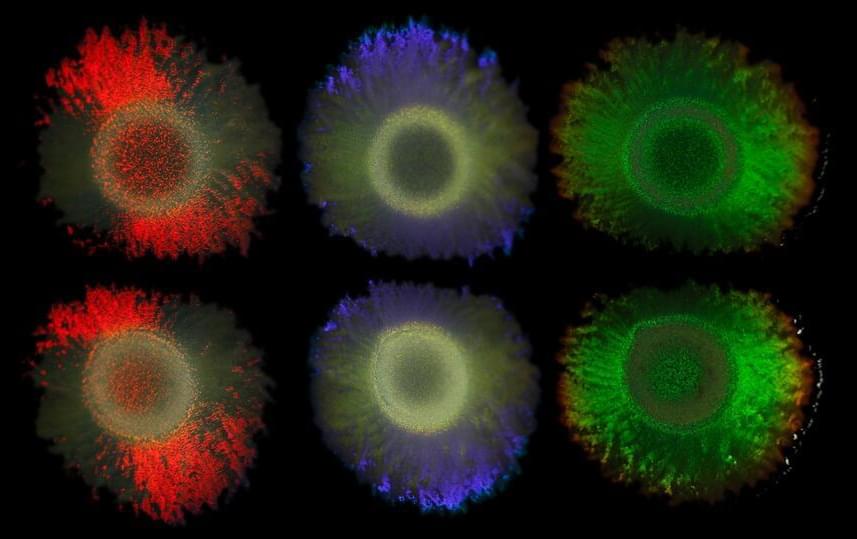
The iridescent colors known from peacock feathers or butterfly wings are created by tiny structures that reflect light in a special way. Some bacterial colonies form similar glittering structures.
In collaboration with the Max Planck Institute of Colloids and Interfaces, Leibniz Institute DSMZ-German Collection of Microorganisms and Cell Cultures, Utrecht University, University of Cambridge, and the Netherlands Institute for Sea Research, the scientists sequenced the DNA of 87 structurally colored bacteria and 30 colorless strains and identified genes that are responsible for these fascinating colonies. These findings could lead to the development of environmentally-friendly dyes and materials, a key interest of the collaborating biotechnology company Hoekmine BV.









Leave a reply