Oct 5, 2016
(Im)mortality: Researchers Find That Human Lifespan Has A Max Limit
Posted by Aleksandar Vukovic in categories: bioengineering, biotech/medical, life extension
In Brief.
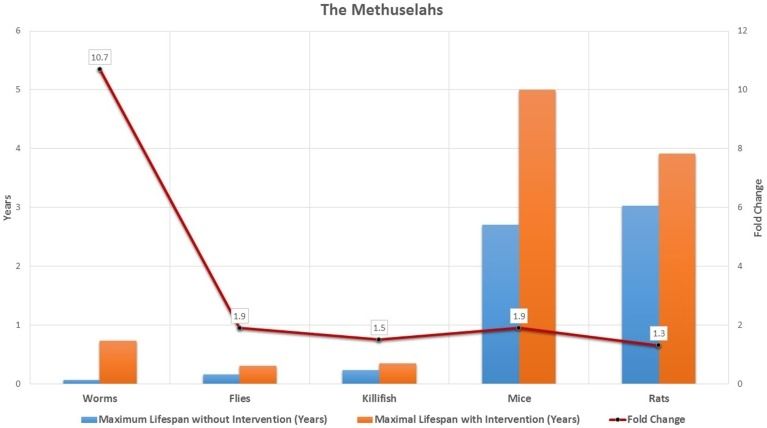
- New research concludes that human lifespan has already reached its peak of 125 years.
- The research does not take into account synthetic biology and advancements in biotech that could extend lifespans further.
Scientists at the Albert Einstein College of Medicine assert that they have discovered the maximum lifespan of human beings, and it’s a range we may no longer be able to exceed. Dr. Jan Vijg, professor of ophthalmology and visual sciences at Einstein, lead the research, which was published online today in the journal Nature.