Feb 26, 2024
Nutrients Direct Intestinal Stem Cell Function and Affect Aging
Posted by Natalie Chan in categories: biotech/medical, life extension
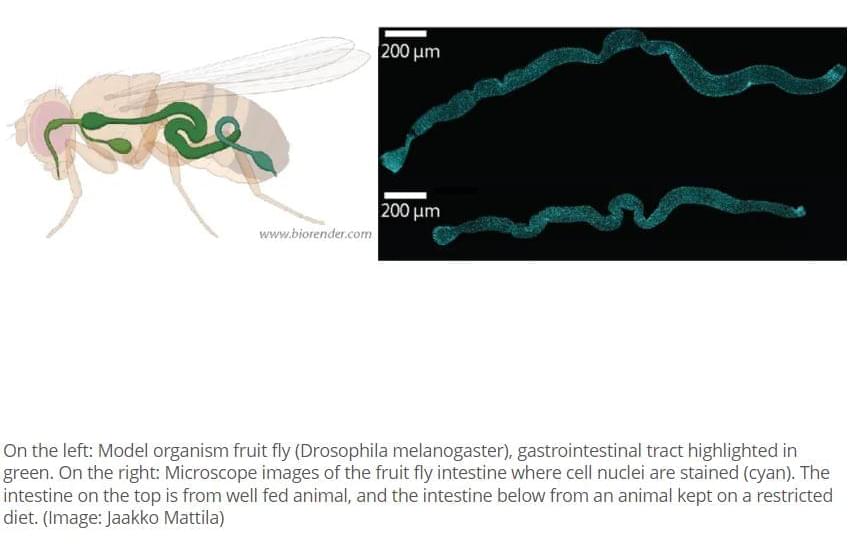
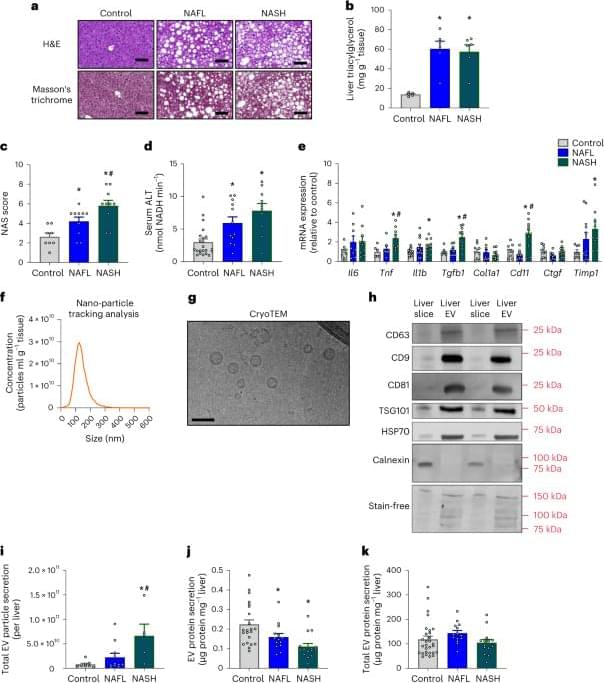
The capacity of intestinal stem cells to maintain cellular balance in the gut decreases upon ageing. Researchers at the University of Helsinki have discovered a new mechanism of action between the nutrient adaptation of intestinal stem cells and ageing. The finding may make a difference when seeking ways to maintain the functional capacity of the ageing gut.
The cellular balance of the intestine is carefully regulated, and it is influenced, among other things, by nutrition: ample nutrition increases the total number of cells in the gut, whereas fasting decreases their number.
The relative number of different types of cells also changes according to nutrient status.