Jan 24, 2024
New Antidepressant Could Restore The Body’s Ability to Fight Cancer
Posted by Joseph Barney in categories: biotech/medical, life extension
I hope more research is fruitful because I got the doctor’s results from my recent colonoscopy. The polyps are benign but pre cancerous. I go back in 5 years and I’ll be eating healthier and exercising. I gotta admit I don’t feel great but it could be something I ate.
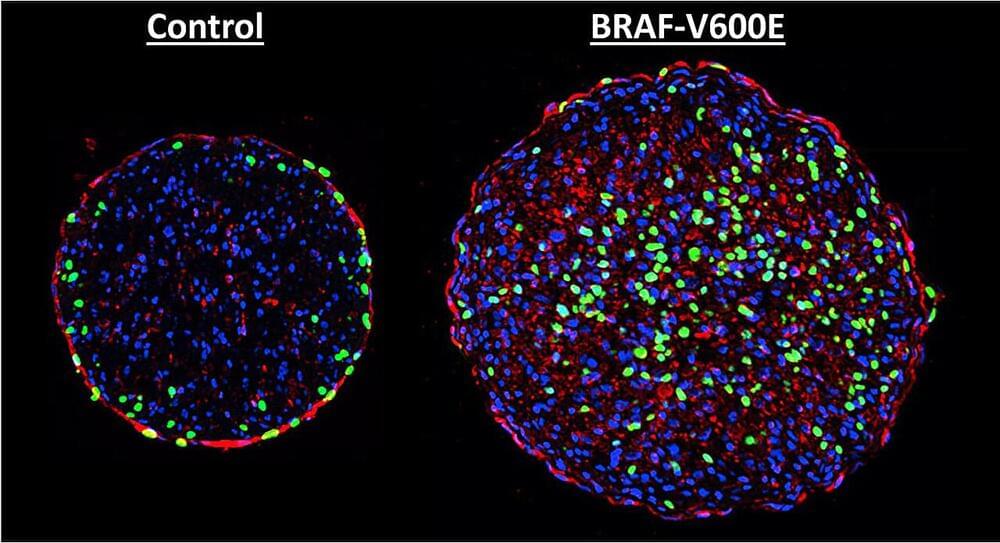
Scientists in China have demonstrated a new kind of antidepressant could also have the potential to restore the body’s ability to fight some types of cancer.
In strategic combination with anti-tumor drugs, the oral antidepressant ansofaxine hydrochloride appears to inhibit colon cancer cell growth in cell cultures and in mice, strengthening the immune system and inducing a form of programmed cell death.
Continue reading “New Antidepressant Could Restore The Body’s Ability to Fight Cancer” »