Jun 8, 2023
Researchers build on Human Genome Project advances
Posted by Dan Breeden in categories: biotech/medical, chemistry, genetics, government
The Human Genome Project (HGP), the world’s largest collaborative biological project, was a 13-year effort led by the U.S. government with the goal of generating the first full sequence of the human genome. In 2003, HGP produced a genome sequence that accounted for more than 90% of the human genome and was considered as close to complete as was possible with the technologies of the time. HGP unlocked the door to a vast but unannotated collection of genes.
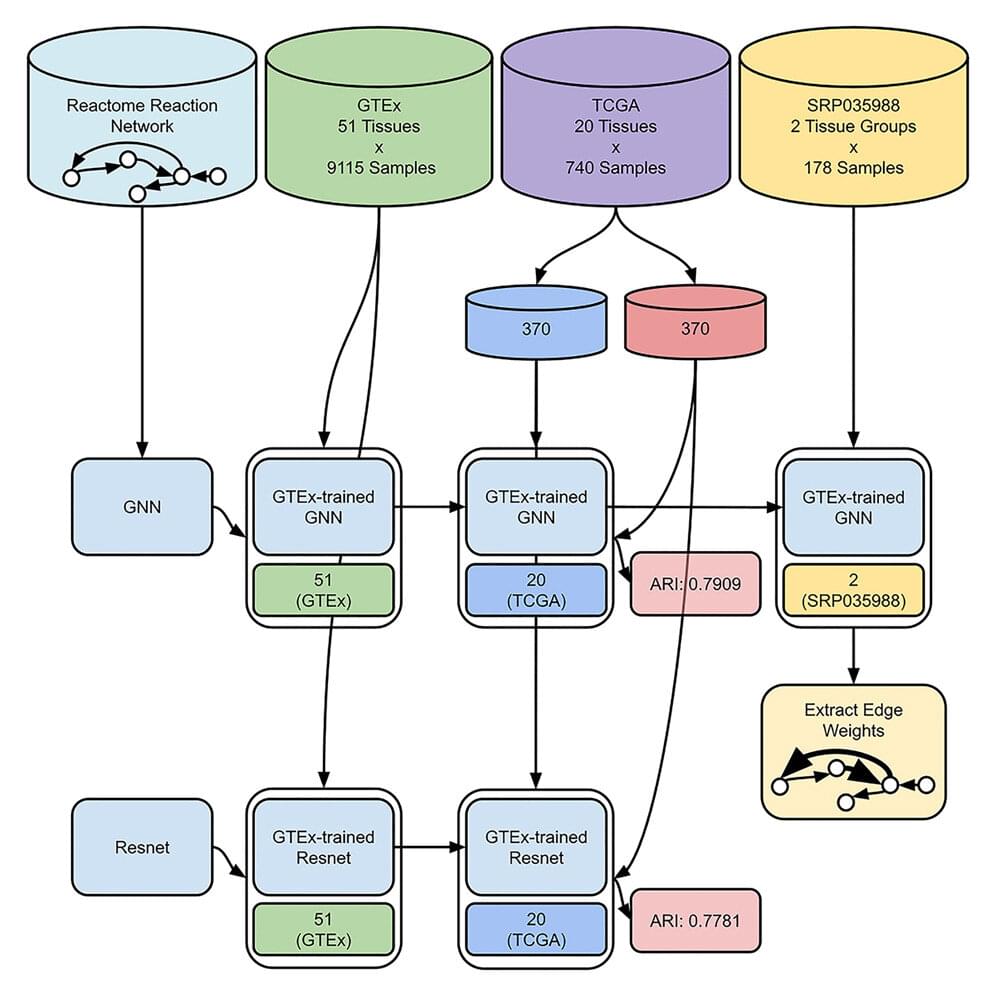
In the following decades, via experimental studies, researchers painstakingly curated reannotations in the form of biochemical reaction graphs. Though gene set enrichment analysis considers groups within these annotation graphs, it disregards group dependencies.
Researchers from the University of Hawaii at Mānoa John A. Burns School of Medicine (JABSOM) are utilizing data from HGP and making advancements in biochemical reaction network analysis. Their work, published in the May 22, 2023 issue of Patterns, demonstrates their approach and may help predict the effects of rare or indistinct genetic variations and guide precision medicine (treatment that can use a patient’s own genes to help fight disease or guide specific therapy).