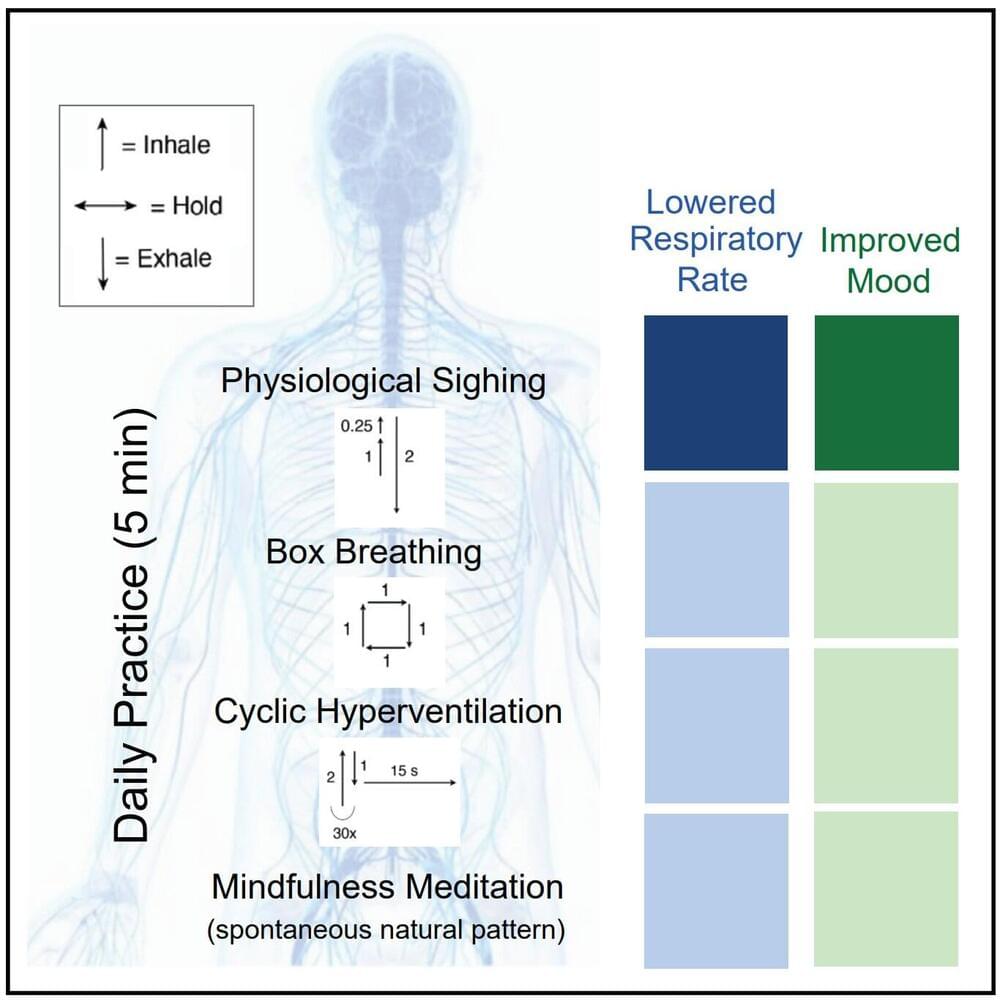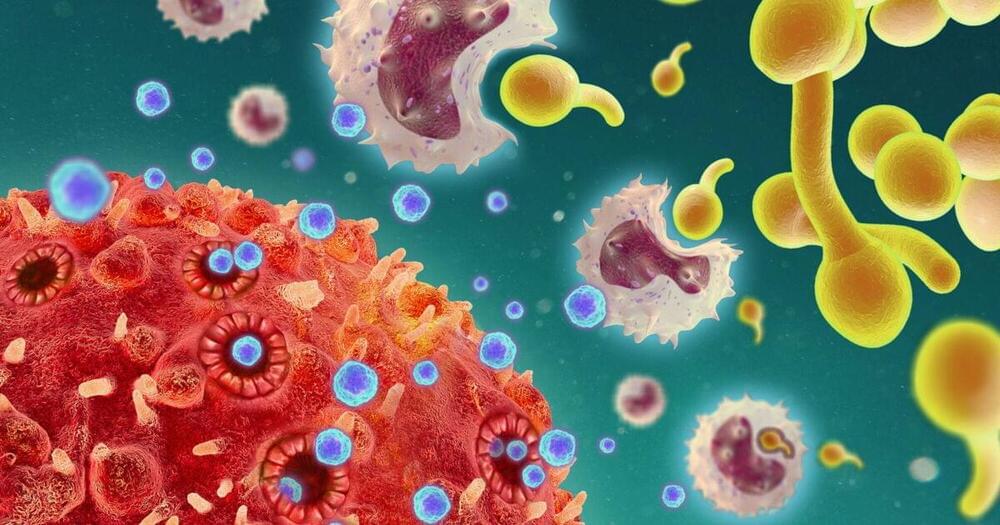
Certain T cells can secrete cytokines that are normally part of the innate immune system, as researchers from the Leibniz Institute for Natural Product Research and Infection Biology (Leibniz-HKI) and an international research team discovered. They have thus revealed several previously unknown properties of these immune cells that are relevant regarding both autoimmune diseases as well as fighting fungal infections. The study was published in Nature Immunology.
T cells belong to the adaptive immune system, which recognizes foreign antigens and specifically fights pathogens. Different T cells perform different functions in this process. So-called T helper cells secrete cytokines that attract other immune cells to the site of infection and trigger inflammation there. However, T helper cells can also counteract inflammation. Better understanding these mechanisms helps in the development of therapeutics against pathogens or autoimmune diseases.
“We found a cytokine in a subset of T helper cells, the Th17 cells, that was previously known to be part of the innate immune system,” explains study leader Christina Zielinski. She heads the Department of Infection Immunology at Leibniz-HKI and is a professor at Friedrich Schiller University in Jena. The cytokine, called IL-1α, is strongly pro-inflammatory. “It is a signal molecule for danger. Even the smallest amounts are enough to trigger fever,” Zielinski said. It is thought to be involved in autoimmune diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis in children.



 CRISPR/Cas9 technology-mediated genome editing has significantly improved the targeted inactivation of genes in vitro and in vivo in many organisms. In this study, we have reported a novel CRISPR-based vector system for conditional tissue-specific gene ablation in zebrafish. Specifically, the cardiac-specific cardiac myosins light chain 2 (cmlc2) promoter drives Cas9 expression to silence the neuropilin-1(nrp1) gene in cardiomyocytes in a heat-shock inducible manner. This vector system establishes a unique tool to regulate the gene knockout in both the developmental and adult stages and hence, widens the possibility of loss-of-function studies in zebrafish at different stages of development and adulthood. Using this approach, we investigated the role of neuropilin isoforms nrp1a and nrp1b in response to cardiac injury and regeneration in adult zebrafish hearts. We observed that both the isoforms (nrp1a and nrp1b) are upregulated after the cryoinjury. Interestingly, the nrp1b-knockout significantly altered heart regeneration and impaired cardiac function in the adult zebrafish, demonstrated by reduced heart rate (ECG), ejection fractions, and fractional shortening. In addition, we show that the knockdown of nrp1b but not nrp1a induces activation of the cardiac remodeling genes in response to cryoinjury. To our knowledge, this is the first study where we have reported a heat shock-mediated conditional knockdown of nrp1a and nrp1b isoforms using CRISPR/Cas9 technology in the cardiomyocyte in zebrafish, and furthermore have identified a crucial role for nrp1b isoform in zebrafish cardiac remodeling and eventually heart function in response to injury.
CRISPR/Cas9 technology-mediated genome editing has significantly improved the targeted inactivation of genes in vitro and in vivo in many organisms. In this study, we have reported a novel CRISPR-based vector system for conditional tissue-specific gene ablation in zebrafish. Specifically, the cardiac-specific cardiac myosins light chain 2 (cmlc2) promoter drives Cas9 expression to silence the neuropilin-1(nrp1) gene in cardiomyocytes in a heat-shock inducible manner. This vector system establishes a unique tool to regulate the gene knockout in both the developmental and adult stages and hence, widens the possibility of loss-of-function studies in zebrafish at different stages of development and adulthood. Using this approach, we investigated the role of neuropilin isoforms nrp1a and nrp1b in response to cardiac injury and regeneration in adult zebrafish hearts. We observed that both the isoforms (nrp1a and nrp1b) are upregulated after the cryoinjury. Interestingly, the nrp1b-knockout significantly altered heart regeneration and impaired cardiac function in the adult zebrafish, demonstrated by reduced heart rate (ECG), ejection fractions, and fractional shortening. In addition, we show that the knockdown of nrp1b but not nrp1a induces activation of the cardiac remodeling genes in response to cryoinjury. To our knowledge, this is the first study where we have reported a heat shock-mediated conditional knockdown of nrp1a and nrp1b isoforms using CRISPR/Cas9 technology in the cardiomyocyte in zebrafish, and furthermore have identified a crucial role for nrp1b isoform in zebrafish cardiac remodeling and eventually heart function in response to injury.