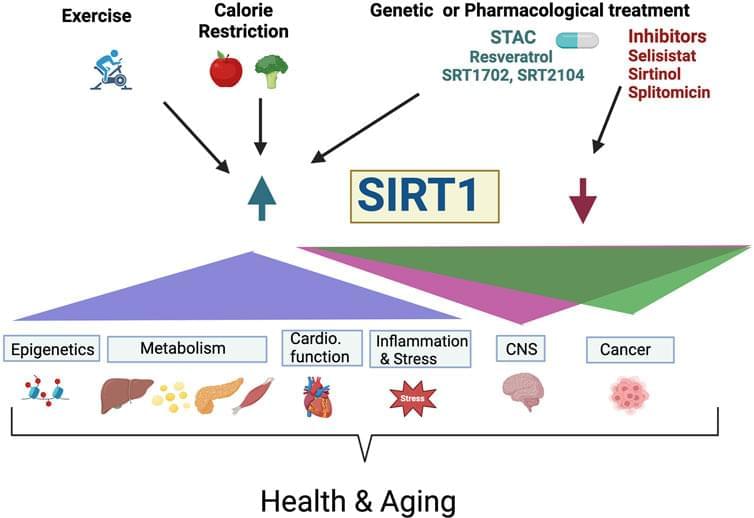
Increased frailty, higher incidence of diseases, and death. As the population grows older, there is a need to reveal mechanisms associated with aging that could spearhead treatments to postpone the onset of age-associated decline, extend both healthspan and lifespan. One possibility is targeting the sirtuin SIRT1, the founding member of the sirtuin family, a highly conserved family of histone deacetylases that have been linked to metabolism, stress response, protein synthesis, genomic instability, neurodegeneration, DNA damage repair, and inflammation. Importantly, sirtuins have also been implicated to promote health and lifespan extension, while their dysregulation has been linked to cancer, neurological processes, and heart disorders. SIRT1 is one of seven members of sirtuin family; each requiring nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD+) as co-substrate for their catalytic activity. Overexpression of yeast, worm, fly, and mice SIRT1 homologs extend lifespan in each animal, respectively. Moreover, lifespan extension due to calorie restriction are associated with increased sirtuin activity. These findings led to the search for a calorie restriction mimetic, which revealed the compound resveratrol; (3, 5, 4′-trihydroxy-trans-stilbene) belonging to the stilbenoids group of polyphenols. Following this finding, resveratrol and other sirtuin-activating compounds have been extensively studied for their ability to affect health and lifespan in a variety of species, including humans via clinical studies.
Aging is associated with a progressive metabolic, physiological decline and can be genetically and environmentally modified (Helfand and Rogina, 2000). The search for the molecular basis of aging led to the identification of several pathways associated with longevity including insulin/IGF-1, target of rapamycin (TOR) and the Sirtuins (Kenyon, 2010; Chen et al., 2022). The sirtuins are a family of nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD+)-dependent histone deacetylases (Haigis and Sinclair, 2010; Hall et al., 2013; Bonkowski and Sinclair, 2016; Dai et al., 2018; Singh et al., 2018). Sirtuins are also categorized as deacetylases because they catalyze the post-translational modification of signaling molecules including decrotonylation, ADP-ribosylation, diacylation, desuccinylation, demalonylation, depropynylation, delipoamidation, and deglutarylation, and other long-chain fatty acid deacylations (Feldman, Baeza, and Denu, 2013; Choudhary et al., 2014; Fiorentino et al., 2022).
In mammals, there are seven members (SIRT1-SIRT7) including SIRT1, SIRT6 and SIRT7, which are localized to the nucleus, and SIRT3, SIRT4, and SIRT5 localized to the mitochondria, SIRT2 localized to the cytosol, and SIRT1 also localized to cytosol in some cell types (Bonkowski and Sinclair, 2016). As histone deacetylases, sirtuins function by removing acetyl groups from the target proteins resulting in either inhibition or activation. SIRT1, SIRT6 and SIRT7 have many functions including: regulators of transcription, control of cellular metabolism, DNA repair, cell survival, tissue regeneration, inflammation, circadian rhythms and neuronal signaling (Haigis and Sinclair, 2010). SIRT3-5 are important for switching to mitochondrial oxidative metabolism during CR and modulate stress tolerance (Verdin et al., 2010).