Nov 24, 2024
Coffee consumption is associated with intestinal Lawsonibacter asaccharolyticus abundance and prevalence across multiple cohorts
Posted by Cecile G. Tamura in category: sex
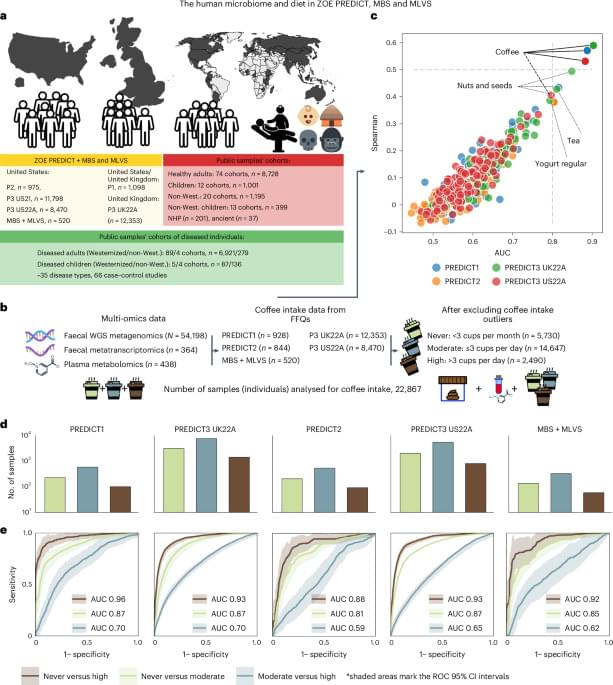
We further investigated whether these associations were driven by caffeine by performing two meta-analyses on the PREDICT1 and PREDICT3 22UKA samples for which the intake of decaffeinated and caffeinated coffee was available. Partial correlations between SGB-ranked abundances and decaffeinated versus caffeinated coffee were run independently (excluding individuals who drank exclusively caffeinated or decaffeinated coffee, respectively). In addition, partial correlations were also adjusted for the other type of coffee consumed by the individuals in case their record reported both kinds. We identified 150 correlations, which remained highly significant after controlling for the decaffeinated coffee intake (q 0.001, nparticipants = 12,089; Extended Data Fig. 4c and Supplementary Table 8). This indicated a substantial independence on caffeine of the observed impact on the microbiome. Next, we analysed the decaffeinated coffee association with the microbiome in individuals consuming decaffeinated coffee and adjusting by caffeinated coffee as well as by sex, age and BMI. In this reduced set of samples (nparticipants = 6,089) we identified 22 correlations at q 0.001 and 66 at q 0.1 (Supplementary Table 9). The top three correlations identified were L. asaccharolyticus (ρ = 0.27 (0.21–0.33), q 10−10), the Lachnospiraceae SGB4777 (ρ = 0.18 (0.16–0.21), q 10−10), and M. coli (SGB29305, ρ = 0.17 (0.13–0.2), q 10−10; Fig. 2b).
As expected, several coffee-associated SGBs were also L. asaccharolyticus co-abundant SGBs, possibly indicating similar independent stimulatory effects of coffee rather than ecological relations (Extended Data Fig. 5 and Supplementary Table 10). The top-five SGBs associated with L. asaccharolyticus abundance were, however, not among the strongest associations with coffee. In particular, the two SGBs with the strongest co-abundance pattern with L. asaccharolyticus were Dysosmobacter welbionis (SGB15078) and the Clostridiales bacterium SGB15143 (ρ = 0.57 and 0.51, respectively, q 1 × 10−10; Extended Data Fig. 5), which were both only weakly associated with total coffee (ρ ≤ 0.05; Supplementary Table 7). Overall, these results indicate that a panel of species, and in particular L. asaccharolyticus is robustly associated with total and decaffeinated coffee consumption, suggesting that the association is not purely due to caffeine.
Among the top coffee-associated SGBs, L. asaccharolyticus showed the highest and the most uniform prevalence across all the cohorts (93.5%; Fig. 2c). In the ‘never’ group from the USA, its prevalence was uniformly high (average prevalence of 87.8 ± 2%) across nine different regions (samples from PREDICT2 and PREDICT3 US22A, n = 9,210). Over and above this, however, it was uniformly increased in all regions when considering coffee consumption; it increased from 87.8% to 95.6% in moderate drinkers and from 95.6% to 97.7% in high drinkers (Fig. 2d and Supplementary Table 11). Degree of urbanization (rural versus urban living context) was not associated with L. asaccharolyticus in the microbiome (Extended Data Fig. 6 and Supplementary Table 12). Overall, the median abundance of L. asaccharolyticus ranged from 4.5-to 8-fold higher in the high compared with the never group (in the PREDICT3 US22A and MBS–MLVS cohorts), and 3.4-to 6.4-fold higher in the moderate versus the never group (in the PREDICT2 and MBS–MLVS cohorts; Supplementary Table 13). By contrast, the highest median fold change between moderate and high drinkers was only 1.4 and did not reach statistical significance in three out of five cohorts (Fig. 3a and Supplementary Table 14).