Sep 14, 2024
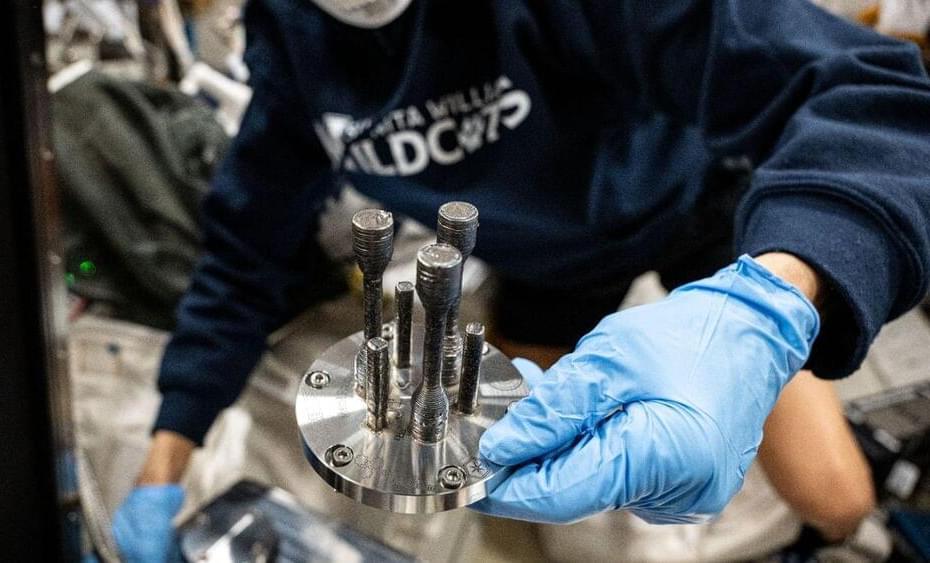
Astronauts 3D-print first metal part while on ISS
Posted by Genevieve Klien in categories: 3D printing, biotech/medical, robotics/AI, space travel
Related: Future moon astronauts may 3D-print their supplies using lunar minerals
“With the printing of the first metal 3D shape in space, ESA Exploration teams have achieved a significant milestone in establishing in-orbit manufacturing capabilities. This accomplishment, made possible by an international and multidisciplinary team, paves the way for long-distance and long-duration missions where creating spare parts, construction components, and tools on demand will be essential,” said Daniel Neuenschwander, director of Human and Robotic Exploration at ESA, in a statement.
This groundbreaking technology continues to expand its applications on Earth, revolutionizing fields such as medicine, fashion, art, construction, food production and manufacturing. In space, as long-duration missions to the moon and potentially Mars take shape, astronauts will need a means of independently repairing or creating tools or parts for machinery or structures that would be difficult to carry onboard a spacecraft, which have limited capacity.