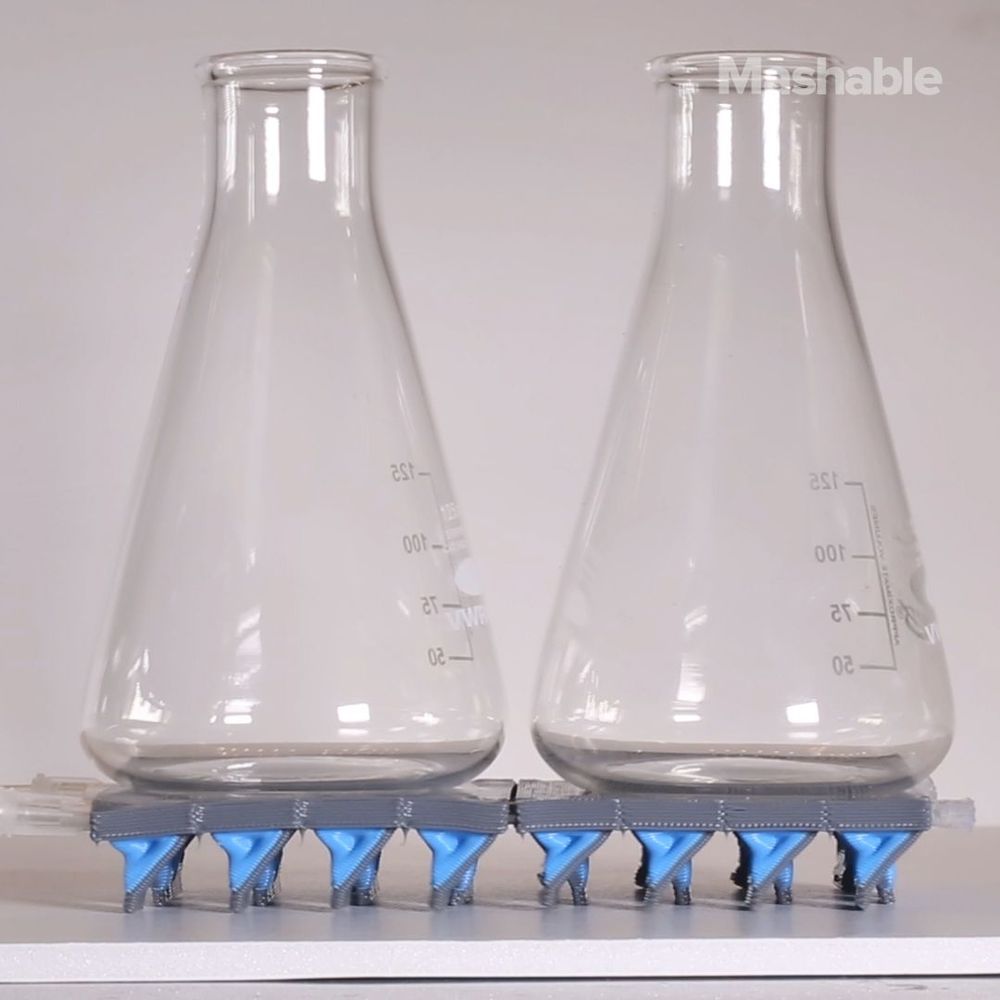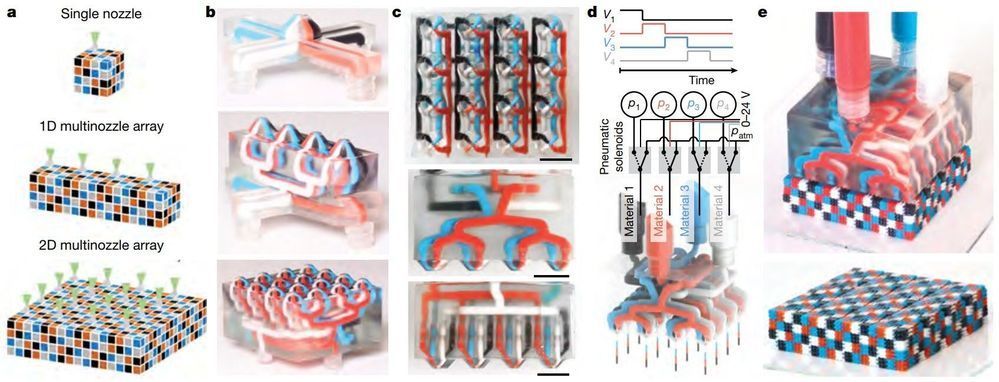
3D printers are revolutionizing manufacturing by allowing users to create any physical shape they can imagine on-demand. However, most commercial printers are only able to build objects from a single material at a time and inkjet printers that are capable of multimaterial printing are constrained by the physics of droplet formation. Extrusion-based 3D printing allows a broad palette of materials to be printed, but the process is extremely slow. For example, it would take roughly 10 days to build a 3D object roughly one liter in volume at the resolution of a human hair and print speed of 10 cm/s using a single-nozzle, single-material printhead. To build the same object in less than 1 day, one would need to implement a printhead with 16 nozzles printing simultaneously!
Now, a new technique called multimaterial multinozzle 3D (MM3D) printing developed at Harvard’s Wyss Institute for Biologically Inspired Engineering and John A. Paulson School of Engineering and Applied Sciences (SEAS) uses high-speed pressure valves to achieve rapid, continuous, and seamless switching between up to eight different printing materials, enabling the creation of complex shapes in a fraction of the time currently required using printheads that range from a single nozzle to large multinozzle arrays. These 3D printheads themselves are manufactured using 3D printing, enabling their rapid customization and facilitating adoption by others in the fabrication community. Each nozzle is capable of switching materials at up to 50 times per second, which is faster than the eye can see, or about as fast as a hummingbird beats its wings. The research is reported in Nature.
“When printing an object using a conventional extrusion-based 3D printer, the time required to print it scales cubically with the length of the object, because the printing nozzle has to move in three dimensions rather than just one,” said co-first author Mark Skylar-Scott, Ph.D., a Research Associate at the Wyss Institute. “MM3D’s combination of multinozzle arrays with the ability to switch between multiple inks rapidly effectively eliminates the time lost to switching printheads and helps get the scaling law down from cubic to linear, so you can print multimaterial, periodic 3D objects much more quickly.”