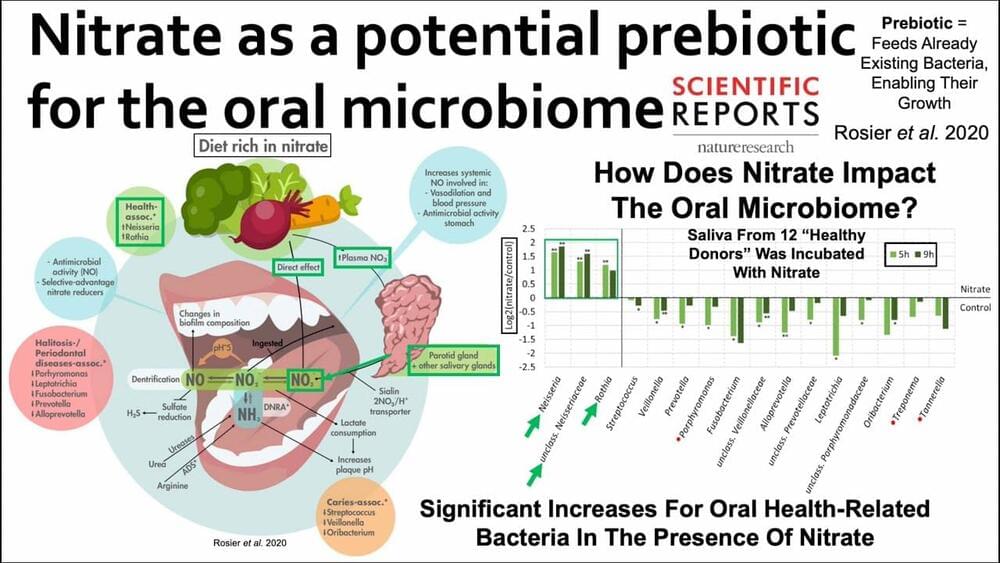
Machine learning is transforming all areas of biological science and industry, but is typically limited to a few users and scenarios. A team of researchers at the Max Planck Institute for Terrestrial Microbiology led by Tobias Erb has developed METIS, a modular software system for optimizing biological systems. The research team demonstrates its usability and versatility with a variety of biological examples.
Though engineering of biological systems is truly indispensable in biotechnology and synthetic biology, today machine learning has become useful in all fields of biology. However, it is obvious that application and improvement of algorithms, computational procedures made of lists of instructions, is not easily accessible. Not only are they limited by programming skills but often also insufficient experimentally-labeled data. At the intersection of computational and experimental works, there is a need for efficient approaches to bridge the gap between machine learning algorithms and their applications for biological systems.
Now a team at the Max Planck Institute for Terrestrial Microbiology led by Tobias Erb has succeeded in democratizing machine learning. In their recent publication in Nature Communications, the team presented together with collaboration partners from the INRAe Institute in Paris, their tool METIS. The application is built in such a versatile and modular architecture that it does not require computational skills and can be applied on different biological systems and with different lab equipment. METIS is short from Machine-learning guided Experimental Trials for Improvement of Systems and also named after the ancient goddess of wisdom and crafts Μῆτις, or “wise counsel.”