May 16, 2022
Evolvable neural units that can mimic the brain’s synaptic plasticity
Posted by Dan Breeden in categories: biological, robotics/AI
Machine learning techniques are designed to mathematically emulate the functions and structure of neurons and neural networks in the brain. However, biological neurons are very complex, which makes artificially replicating them particularly challenging.
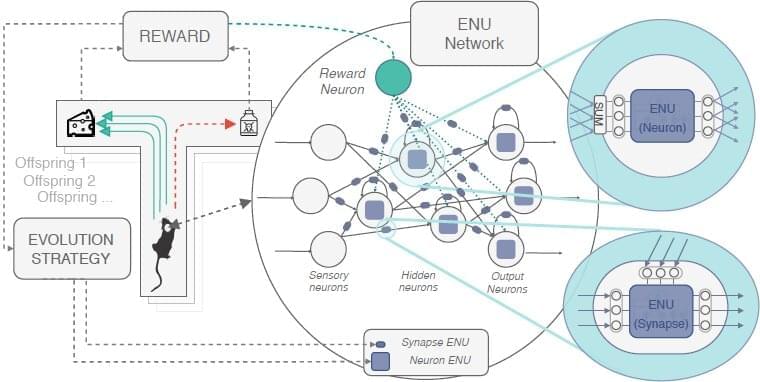
Researchers at Korea University have recently tried to reproduce the complexity of biological neurons more effectively by approximating the function of individual neurons and synapses. Their paper, published in Nature Machine Intelligence, introduces a network of evolvable neural units (ENUs) that can adapt to mimic specific neurons and mechanisms of synaptic plasticity.
“The inspiration for our paper comes from the observation of the complexity of biological neurons, and the fact that it seems almost impossible to model all of that complexity produced by nature mathematically,” Paul Bertens, one of the researchers who carried out the study, told TechXplore. “Current artificial neural networks used in deep learning are very powerful in many ways, but they do not really match biological neural network behavior. Our idea was to use these existing artificial neural networks not to model the entire brain, but to model each individual neuron and synapse.”