This could lead to biological teleportation. :3.
Photosynthesis is a highly optimized process from which valuable lessons can be learned about the operating principles in nature. Its primary steps involve energy transport operating near theoretical quantum limits in efficiency. Recently, extensive research was motivated by the hypothesis that nature used quantum coherences to direct energy transfer. This body of work, a cornerstone for the field of quantum biology, rests on the interpretation of small-amplitude oscillations in two-dimensional electronic spectra of photosynthetic complexes. This Review discusses recent work reexamining these claims and demonstrates that interexciton coherences are too short lived to have any functional significance in photosynthetic energy transfer. Instead, the observed long-lived coherences originate from impulsively excited vibrations, generally observed in femtosecond spectroscopy. These efforts, collectively, lead to a more detailed understanding of the quantum aspects of dissipation. Nature, rather than trying to avoid dissipation, exploits it via engineering of exciton-bath interaction to create efficient energy flow.
Over the past decade, the field of quantum biology has seen an enormous increase in activity, with detailed studies of phenomena ranging from the primary processes in vision and photosynthesis to avian navigation (1, 2). In principle, the study of quantum effects in complex biological systems has a history stretching back to the early years of quantum mechanics (3); however, only recently has it truly taken center stage as a scientifically testable concept. While the overall discussion has wide-ranging ramifications, for the purposes of this Review, we will focus on the subfield where the debate is most amenable to direct experimental tests of purported quantum effects—photosynthetic light harvesting.
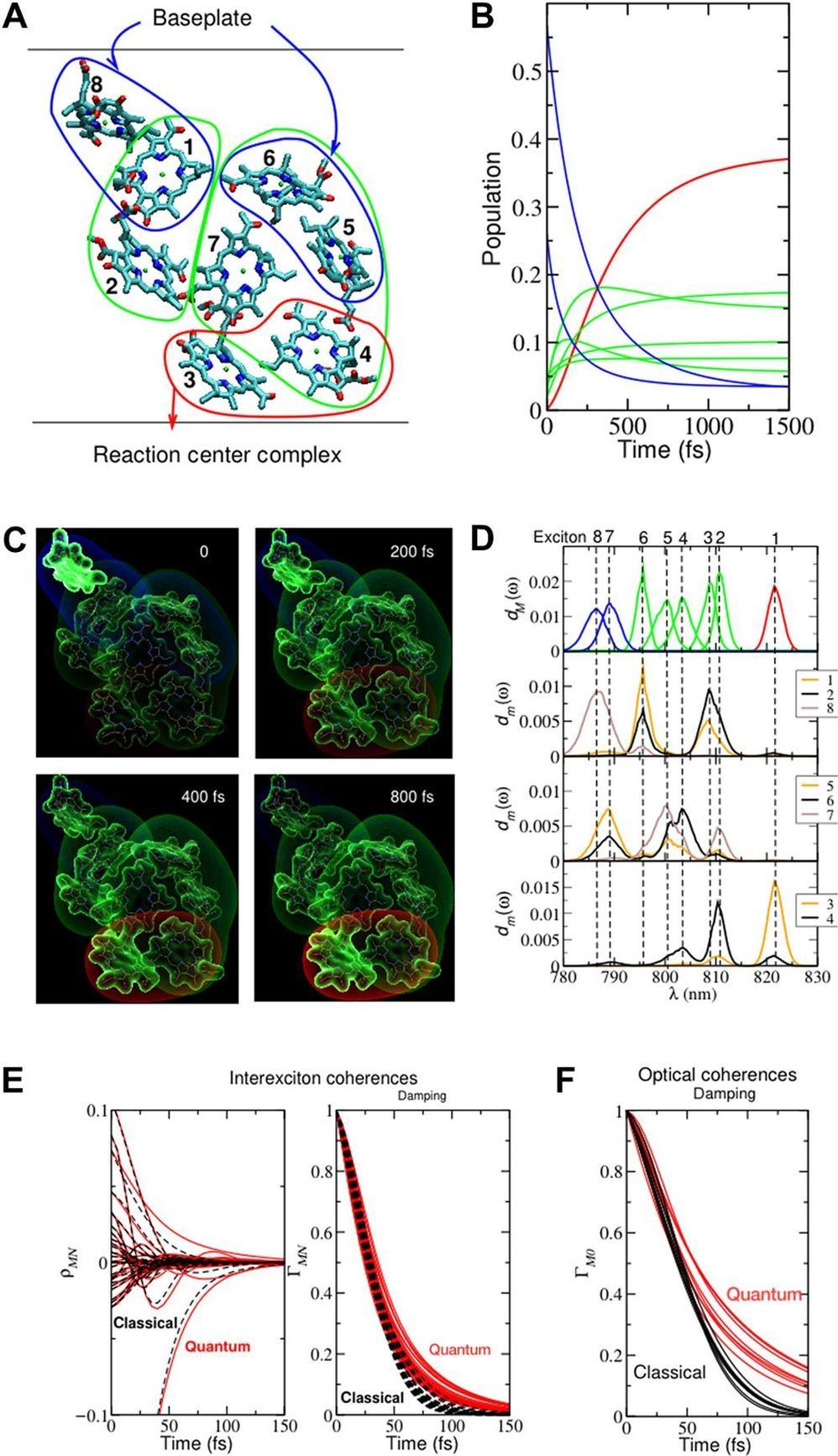
In femtosecond multidimensional spectroscopy of several pigment-protein complexes (PPCs), we find what has been widely considered the experimental signature of nontrivial quantum effects in light harvesting: oscillatory signals—the spectroscopic characteristic of “quantum coherence.” These signals, or rather their interpretation with the associated claims of a direct link to the system’s “quantumness” (4), have drawn enormous attention, much of it from scientists outside the immediate community of photosynthetic light harvesting (5). While significant efforts have been spent on interpreting these weak signals, the overall debate has raised important questions of a general nature (6). What is uniquely “quantum” in biology? What “nontrivial quantum effects” can be considered as the origin of observable biological phenomena?