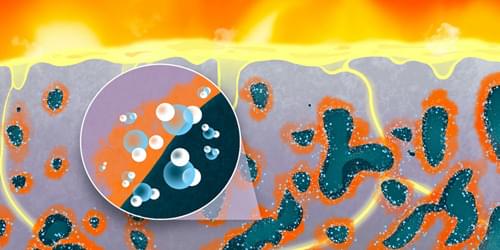
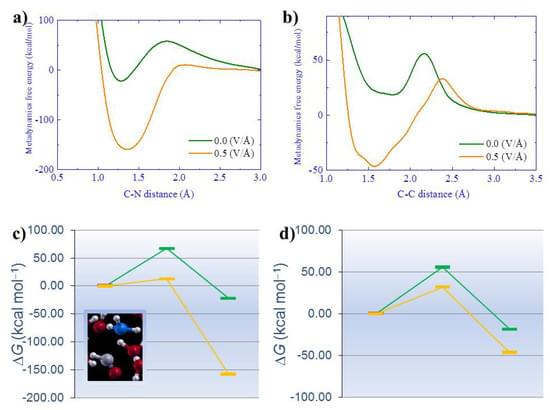
Researchers have investigated how pores in a solid change its chemical reactions with other materials. The result could make steel production more environmentally friendly.
Category: chemistry – Page 182
Texas A&M University scientists have discovered a 1,000% difference in the storage capacity of metal-free, water-based battery electrodes.
The metal-free water-based batteries are unique from those that utilize cobalt in their lithium-ion form. The research group’s focus on this type of battery stems from a desire for greater control over the domestic supply chain as cobalt and lithium are commonly sourced from outside the country. Additionally, the batteries’ safer chemistry could prevent fires.
Chemical engineering professor Dr. Jodie Lutkenhaus and chemistry assistant professor Dr. Daniel Tabor has published their findings about lithium-free batteries in Nature Materials.
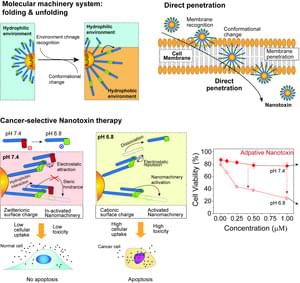
Proteins are involved in every biological process, and use the energy in the body to alter their structure via mechanical movements. They are considered biological ‘nanomachines’ because the smallest structural change in a protein has a significant effect on biological processes. The development of nanomachines that mimic proteins has received much attention to implement movement in the cellular environment. However, there are various mechanisms by which cells attempt to protect themselves from the action of these nanomachines. This limits the realization of any relevant mechanical movement of nanomachines that could be applied for medical purposes.
The research team led by Dr. Youngdo Jeong from the Center for Advanced Biomolecular Recognition at the Korea Institute of Science and Technology (KIST, President Seok-Jin Yoon) has reported the development of a novel biochemical nanomachine that penetrates the cell membrane and kills the cell via the molecular movements of folding and unfolding in specific cellular environments, such as cancer cells, as a result of a collaboration with the teams of Prof. Sang Kyu Kwak from the School of Energy and Chemical Engineering and Prof. Ja-Hyoung Ryu from the Department of Chemistry at the Ulsan National Institute of Science and Technology (UNIST, President Yong Hoon Lee), and Dr. Chaekyu Kim of Fusion Biotechnology, Inc.
The joint research team focused on the hierarchical structure of proteins, in which the axis of the large structure and the mobile units are hierarchically separated. Therefore, only specific parts can move around the axis. Most existing nanomachines have been designed so that the mobile components and axis of the large structure are present on the same layer. Thus, these components undergo simultaneous movement, which complicates the desired control of a specific part.
In the last decade, we have witnessed biology bring us some incredible products and technologies: from mushroom-based packaging to animal-free hotdogs and mRNA vaccines that helped curb a global pandemic. The power of synthetic biology to transform our world cannot be overstated: this industry is projected to contribute to as much as a third of the global economic output by 2030, or nearly $30 trillion, and could impact almost every area of our lives, from the food we eat to the medicine we put in our bodies.
The leaders of this unstoppable bio revolution – many of whom you can meet at the SynBioBeta conference in Oakland, CA, on May 23–25 – are bringing the future closer every day through their ambitious vision, long-range strategy, and proactive oversight. These ten powerful women are shaping our world as company leaders, biosecurity experts, policymakers, and philanthropists focused on charting a new course to a more sustainable, equitable, clean, and safe future.
As an early pioneer in the high-throughput synthesis and sequencing of DNA, Emily Leproust has dedicated her life to democratizing gene synthesis to catapult the growth of synthetic biology applications from medicine, food, agriculture, and industrial chemicals to DNA data storage. She was one of the co-founders of Twist Bioscience in 2013 and is still leading the expanding company as CEO. To say that Twist’s silicon platform was a game-changer for the industry is an understatement. And it is no surprise that Leproust was recently honored with the BIO Rosalind Franklin Award for her work in the biobased economy and biotech innovation.
Humongous Fungus, a specimen of Armillaria ostoyae, has claimed the title of world’s largest single organism. Though it features honey mushrooms above ground, the bulk of this creature’s mass arises from its vast subterranean mycelial network of filamentous tendrils. It has spread across more than 2,000 acres of soil and weighs over 30,000 metric tons. Yet I would contend that Humongous Fungus represents a mere microcosm of the world’s true largest organism, a creature that I will call Cyborg Earth. What is Cyborg Earth? Eastern religions have suggested that all life is fundamentally interconnected. Cyborg Earth represents an extension of this concept.
All across the globe, biological life thrives. Quintillions upon quintillions of biomolecular computations happen every second, powering all life. Mycoplasma bacteria. Communities of leafcutter ants. The Humongous Fungus. Beloved beagles. Seasonal influenza viruses. Parasitic roundworms. Families of Canadian elk. Vast blooms of cyanobacteria. Humanity. Life works because of complexity that arises from simplicity that in turn arises from whatever inscrutable quantum mechanical rules lay beneath the molecular scale.
All creatures rearrange atoms in various ways. Termites and beavers rearrange larger bunches of atoms than most organisms. As humans progressed from paleolithic to metalwork to industrialization and then to the space age, information revolution, and era of artificial intelligence, they learned to converse with the atoms around them in an ever more complex fashion. We are actors in an operatic performance, we are subroutines of evolution, we are interwoven matryoshka patterns, an epic chemistry.
Exciting.
The search for the chemical origins of life represents a long-standing and continuously debated enigma. Despite its exceptional complexity, in the last decades the field has experienced a revival, also owing to the exponential growth of the computing power allowing for efficiently simulating the behavior of matter—including its quantum nature—under disparate conditions found, e.g., on the primordial Earth and on Earth-like planetary systems (i.e., exoplanets). In this minireview, we focus on some advanced computational methods capable of efficiently solving the Schrödinger equation at different levels of approximation (i.e., density functional theory)—such as ab initio molecular dynamics—and which are capable to realistically simulate the behavior of matter under the action of energy sources available in prebiotic contexts.
After lightning struck a tree in New Port Richey, Florida, a team of scientists from the University of South Florida (USF) discovered that this strike led to the formation of a new phosphorous material in a rock. This is the first time such a material has been found in solid form on Earth and could represent a member of a new mineral group.
“We have never seen this material occur naturally on Earth – minerals similar to it can be found in meteorites and space, but we’ve never seen this exact material anywhere,” said study lead author Matthew Pasek, a geoscientist at USF.
According to the researchers, high-energy events such as lightning can sometimes cause unique chemical reactions which, in this particular case, have led to the formation of a new material that seems to be transitional between space minerals and minerals found on Earth.
Electric vehicles feature lithium-ion battery packs today. They are heavy. But in the future lithium-air batteries that are more energy dense, lighter, and smaller could revolutionize EV design.
Lithium-air provides 4x greater energy density, and gets the oxygen needed in the chemical process from the surrounding air.
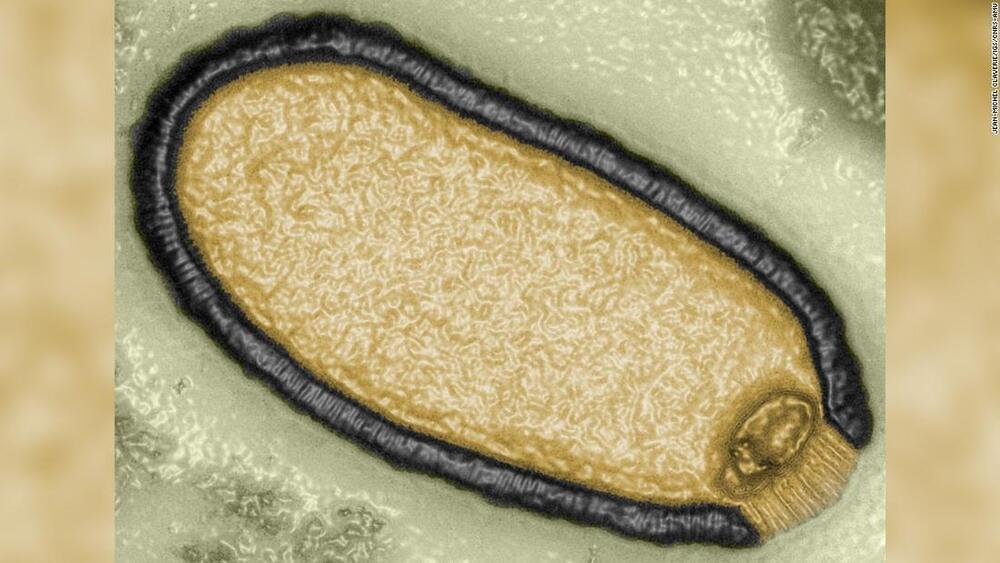
While a pandemic unleashed by a disease from the distant past sounds like the plot of a sci-fi movie, scientists warn that the risks, though low, are underappreciated. Chemical and radioactive waste that dates back to the Cold War, which has the potential to harm wildlife and disrupt ecosystems, may also be released during thaws.
Permafrost covers a fifth of the Northern Hemisphere, having underpinned the Arctic tundra and boreal forests of Alaska, Canada and Russia for millennia. It serves as a kind of time capsule, preserving — in addition to ancient viruses — the mummified remains of a number of extinct animals that scientist have been able to unearth and study in recent years, including two cave lion cubs and a woolly rhino.
Warmer temperatures in the Arctic are thawing the region’s permafrost — a frozen layer of soil beneath the ground — and potentially stirring viruses that, after lying dormant for tens of thousands of years, could endanger animal and human health.
“There’s a lot going on with the permafrost that is of concern, and (it) really shows why it’s super important that we keep as much of the permafrost frozen as possible,” said Kimberley Miner, a climate scientist at the NASA Jet Propulsion Laboratory at the California Institute of Technology in Pasadena, California.
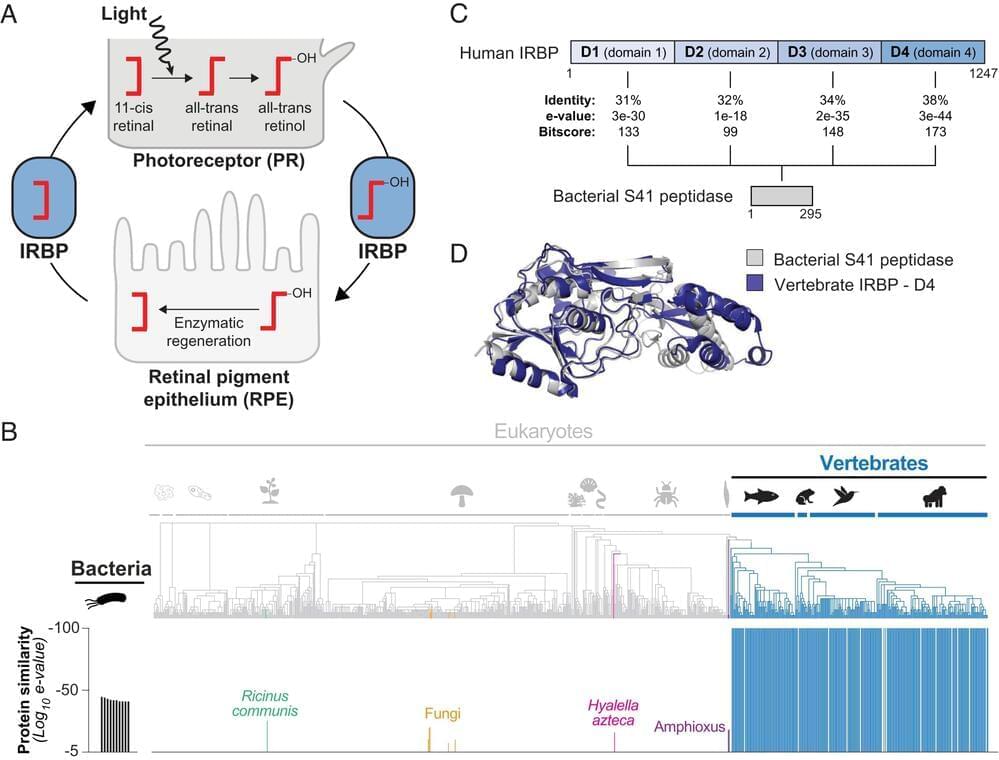
A group of molecular and chemical biologists at the University of California, San Diego, has found possible evidence of interdomain horizontal gene transfer leading to the development of the eye in vertebrates. In their study, reported in Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, Chinmay Kalluraya, Alexander Weitzel, Brian Tsu and Matthew Daugherty used the IQ-TREE software program to trace the evolutionary history of genes associated with vision.
Ever since scientists proved that humans, along with other animals, developed due to evolutionary processes, one problem has stood out—how could evolution possibly account for the development of something as complicated as the eyeball? Even Charles Darwin was said to be stumped by the question. In recent times, this seeming conundrum has been used by some groups as a means to discredit evolutionary theory altogether. In this new effort, the team in California sought to answer the question once and for all.
Their work began with the idea that vision in vertebrates may have got its start by using light-sensitive genes transferred from microbes. To find out if that might be the case, the team submitted likely human gene candidates to the IQ-TREE program to look for similar genetic sequences in other creatures, most specifically, microbes.