There are biological underpinnings to aging—and so researchers are investigating cell manipulations, transfusions of young blood, and chemical compounds that can mimic low-calorie diets.


Scientists have taken a significant step towards the development of tailor-made chiral nanocarriers with controllable release properties. These nanocarriers, inspired by nature’s helical molecules like DNA and proteins, hold immense potential for targeted drug delivery and other biomedical applications.
The study, led by Professors Emilio Quiñoá and Félix Freire at the Center for Research in Biological Chemistry and Molecular Materials (CiQUS), highlights the intricate relationship between the structure of helical polymers and their self-assembly into nanospheres. By carefully designing the secondary chain, the researchers were able to modulate the acidity of the polymers, influencing their aggregation patterns and leading to the formation of nanoespheres with varying densities.
Intriguingly, the size of these nanospheres could be precisely controlled by simply adjusting the water-to-solvent ratio during their preparation, eliminating the need for stabilizers. This eco-friendly approach paves the way for sustainable synthesis of these particles.
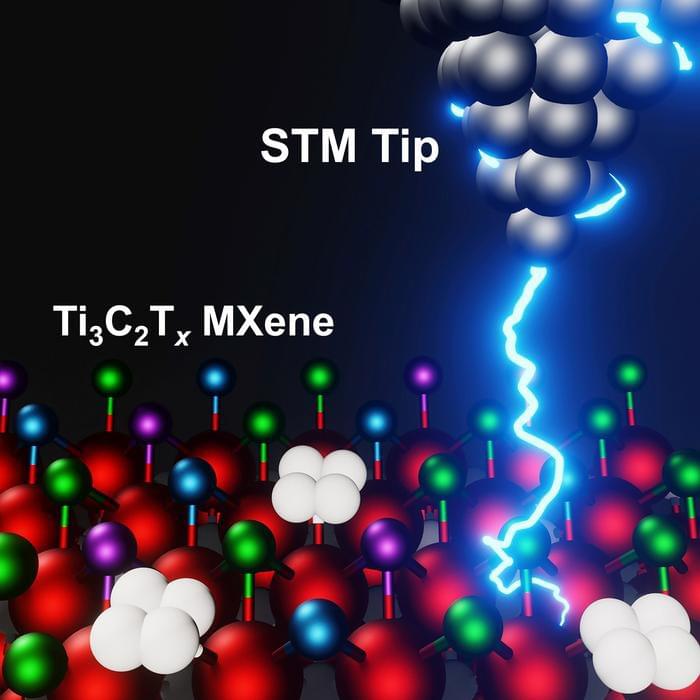
In the decade since their discovery at Drexel University, the family of two-dimensional materials called MXenes has shown a great deal of promise for applications ranging from water desalination and energy storage to electromagnetic shielding and telecommunications, among others. While researchers have long speculated about the genesis of their versatility, a recent study led by Drexel and the University of California, Los Angeles, has provided the first clear look at the surface chemical structure foundational to MXenes’ capabilities.
Using advanced imaging techniques, known as scanning tunneling microscopy (STM) and scanning tunneling spectroscopy (STS), the team, which also includes researchers from California State University Northridge, and Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory, mapped the electrochemical surface topography of the titanium carbide MXene — the most-studied and widely used member of the family.
Their findings, published in the 5th anniversary issue of the Cell Press journal Matter (“Atomic-scale investigations of Ti 3 C 2 Tx MXene surfaces”), will help to explain the range of properties exhibited by members of the MXene family and allow researchers to tailor new materials for specific applications.
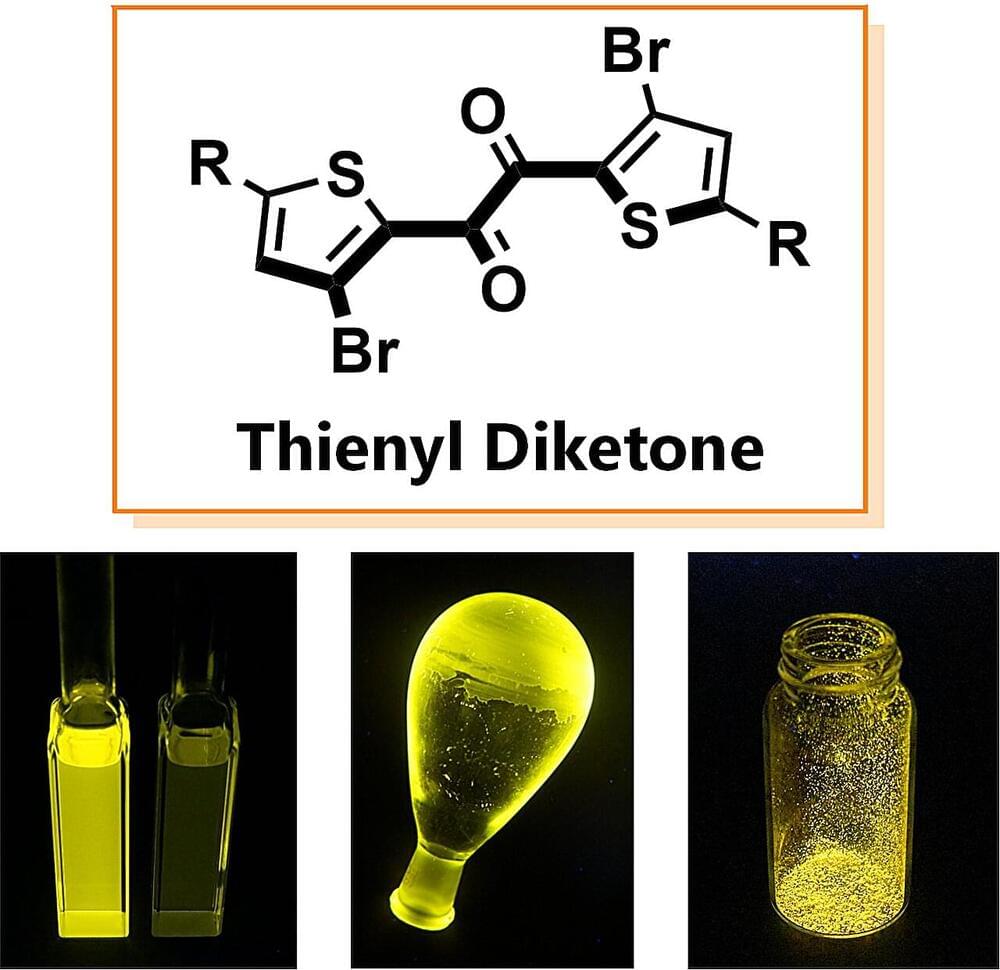
A research team led by Osaka University discovered that the new organic molecule thienyl diketone shows high-efficiency phosphorescence. It achieved phosphorescence that is more than ten times faster than traditional materials, allowing the team to elucidate this mechanism.
The paper is published in the journal Chemical Science.
Phosphorescence is a valuable optical function used in applications such as organic EL displays (OLEDs) and cancer diagnostics. Until now, achieving high-efficiency phosphorescence without using rare metals such as iridium and platinum has been a significant challenge. Phosphorescence, which occurs when a molecule transitions from a high-energy state to a low-energy state, often competes with non-radiative processes where the molecule loses energy as heat.
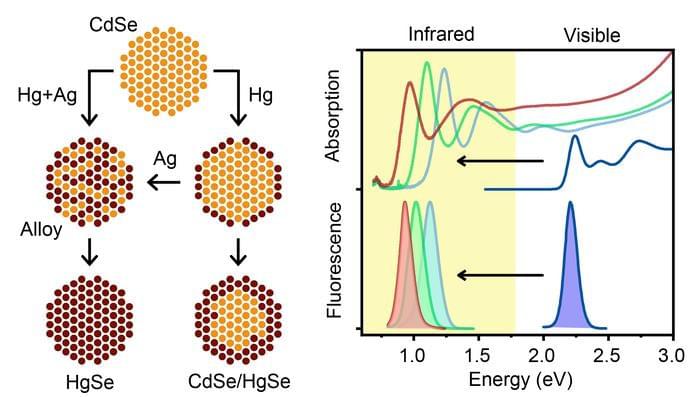
Awarded the 2023 Nobel Prize in Chemistry, quantum dots have a wide variety of applications ranging from displays and LED lights to chemical reaction catalysis and bioimaging. These semiconductor nanocrystals are so small – on the order of nanometers – that their properties, such as color, are size dependent, and they start to exhibit quantum properties. This technology has been really well developed, but only in the visible spectrum, leaving untapped opportunities for technologies in both the ultraviolet and infrared regions of the electromagnetic spectrum.
In new research published in Nature Synthesis (“Interdiffusion-enhanced cation exchange for HgSe and HgCdSe nanocrystals with infrared bandgaps”), University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign bioengineering professor Andrew Smith and postdoctoral researcher Wonseok Lee have developed mercury selenide (HgSe) and mercury cadmium selenide (HgCdSe) nanocrystals that absorb and emit in the infrared, made from already well-developed, visible spectrum cadmium selenide (CdSe) precursors. The new nanocrystal products retained the desired properties of the parent CdSe nanocrystals, including size, shape and uniformity.
“This is the first example of infrared quantum dots that are at the same level of quality as the ones that are in the visible spectrum,” Smith says.
Eexxeccellent.
Human brains outperform computers in many forms of processing and are far more energy efficient. What if we could harness their power in a new form of biological computing?
In this Frontiers Forum Deep Dive session on 21 June 2023, Professor Thomas Hartung, Dr Lena Smirnova and other renowned researchers, explored the future of organoid intelligence and the scientific, technological and ethical steps required for realizing its full potential.
The session brought together the authors of the Frontiers in Science lead article ‘Organoid intelligence (OI): the new frontier in biocomputing and intelligence-in-a-dish’ which presents a roadmap for the strategic development of organoid intelligence as a scientific discipline. It was attended by hundreds of representatives from science, policy, and business across the world.
Links:
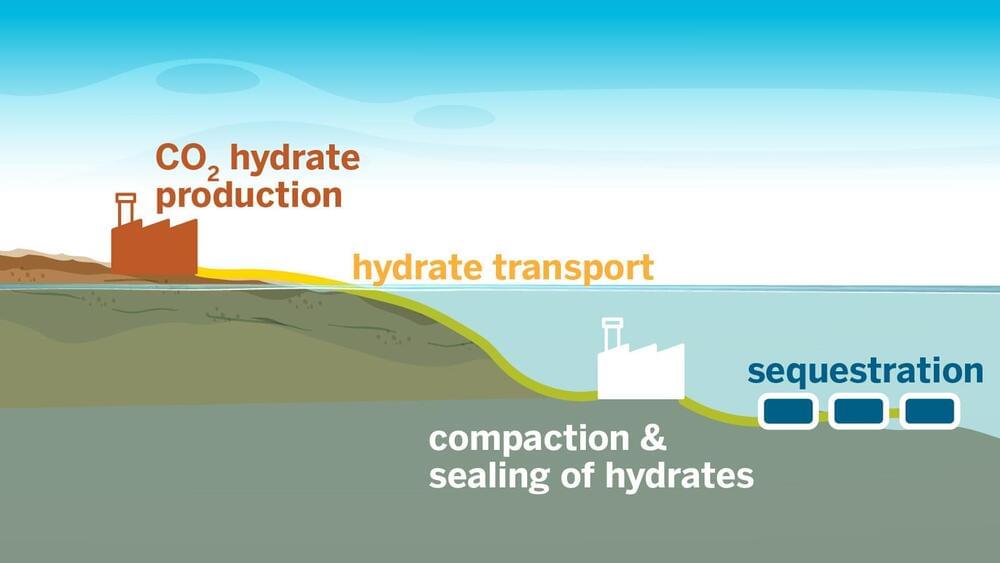
A new way to store carbon captured from the atmosphere, developed by researchers at The University of Texas at Austin, works much faster than current methods without the harmful chemical accelerants they require.
In new research published in ACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering, the team developed a technique for ultrafast formation of carbon dioxide hydrates. These unique ice-like materials can bury carbon dioxide in the ocean, preventing it from being released into the atmosphere.
“We’re staring at a huge challenge—finding a way to safely remove gigatons of carbon from our atmosphere—and hydrates offer a universal solution for carbon storage. For them to be a major piece of the carbon storage pie, we need the technology to grow them rapidly and at scale,” said Vaibhav Bahadur, a professor in the Walker Department of Mechanical Engineering who led the research. “We’ve shown that we can quickly grow hydrates without using any chemicals that offset the environmental benefits of carbon capture.”
Consciousness is comprised of arousal (i.e., wakefulness) and awareness. Substantial progress has been made in mapping the cortical networks that modulate awareness in the human brain, but knowledge about the subcortical networks that sustain arousal is lacking. We integrated data from ex vivo diffusion MRI, immunohistochemistry, and in vivo 7 Tesla functional MRI to map the connectivity of a subcortical arousal network that we postulate sustains wakefulness in the resting, conscious human brain, analogous to the cortical default mode network (DMN) that is believed to sustain self-awareness. We identified nodes of the proposed default ascending arousal network (dAAN) in the brainstem, hypothalamus, thalamus, and basal forebrain by correlating ex vivo diffusion MRI with immunohistochemistry in three human brain specimens from neurologically normal individuals scanned at 600–750 µm resolution. We performed deterministic and probabilistic tractography analyses of the diffusion MRI data to map dAAN intra-network connections and dAAN-DMN internetwork connections. Using a newly developed network-based autopsy of the human brain that integrates ex vivo MRI and histopathology, we identified projection, association, and commissural pathways linking dAAN nodes with one another and with cortical DMN nodes, providing a structural architecture for the integration of arousal and awareness in human consciousness. We release the ex vivo diffusion MRI data, corresponding immunohistochemistry data, network-based autopsy methods, and a new brainstem dAAN atlas to support efforts to map the connectivity of human consciousness.
One sentence summary We performed ex vivo diffusion MRI, immunohistochemistry, and in vivo 7 Tesla functional MRI to map brainstem connections that sustain wakefulness in human consciousness.
BF has a financial interest in CorticoMetrics, a company whose medical pursuits focus on brain imaging and measurement technologies. BF’s interests were reviewed and are managed by Massachusetts General Hospital and Mass General Brigham HealthCare in accordance with their conflict-of-interest policies.

UChicago Pritzker Molecular Engineering Prof. Y. Shirley Meng’s Laboratory for Energy Storage and Conversion has created the world’s first anode-free sodium solid-state battery.
With this research, the LESC – a collaboration between the UChicago Pritzker School of Molecular Engineering and the University of California San Diego’s Aiiso Yufeng Li Family Department of Chemical and Nano Engineering – has brought the reality of inexpensive, fast-charging, high-capacity batteries for electric vehicles and grid storage closer than ever.
“Although there have been previous sodium, solid-state, and anode-free batteries, no one has been able to successfully combine these three ideas until now,” said UC San Diego PhD candidate Grayson Deysher, first author of a new paper outlining the team’s work.