Archive for the ‘climatology’ category: Page 144
Mar 11, 2018
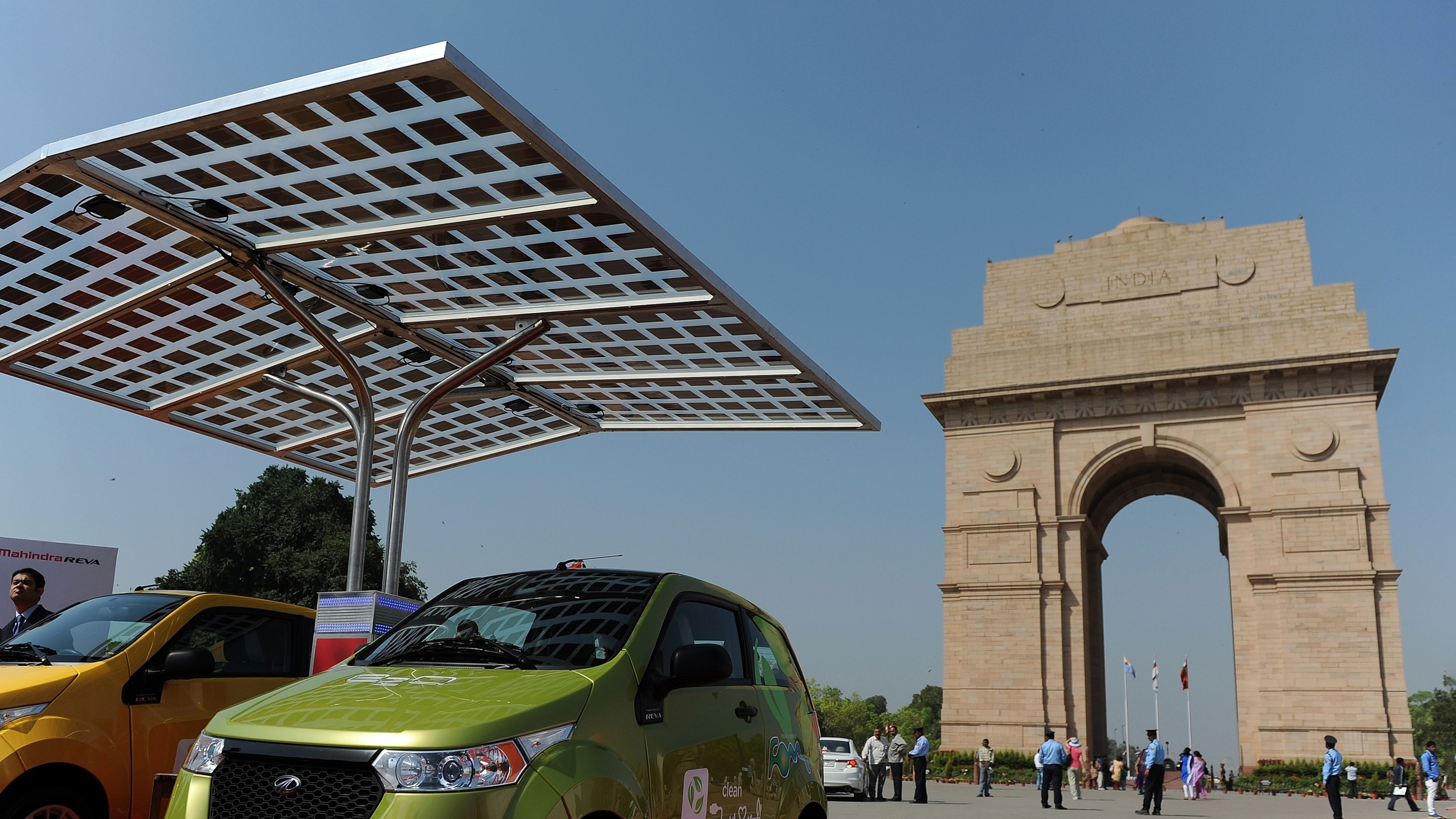
India’s Switch from Environmental Victim to Renewable Energy Champ
Posted by Dan Kummer in categories: climatology, sustainability
“A few months from now, a group of people will come here with something called an electric car. I need to know whether or not you have the right voltage connection for them to plug in their vehicles. Do you understand what I’m asking for?”
Mr. Dev Reddy, manager of a gas station in rural Anantapur district of India’s Andhra Pradesh looked at me as if he understood. It was 2008, and most people in India had never seen an electric car, but without flinching he took me to a shed to reveal a large plug point, which was used to power an electric sugar cane juicing machine. One look at it and I knew that there was sufficient voltage coming through the connection to be able to charge the lithium-ion battery in the REVA electric vehicles my friends and I would be driving 3,500 kilometers across India.
In 2008, it was folly to imagine India creating new technological solutions to address the climate crisis. For decades India had called itself a victim of climate change and thus incapable of acting to reduce emissions; what’s more, 400 million Indians had no access to electricity at all.
Continue reading “India’s Switch from Environmental Victim to Renewable Energy Champ” »
Mar 5, 2018
We Can Now Store Light as Sound, And It’s a Game Changer For Computing
Posted by Shane Hinshaw in categories: climatology, computing
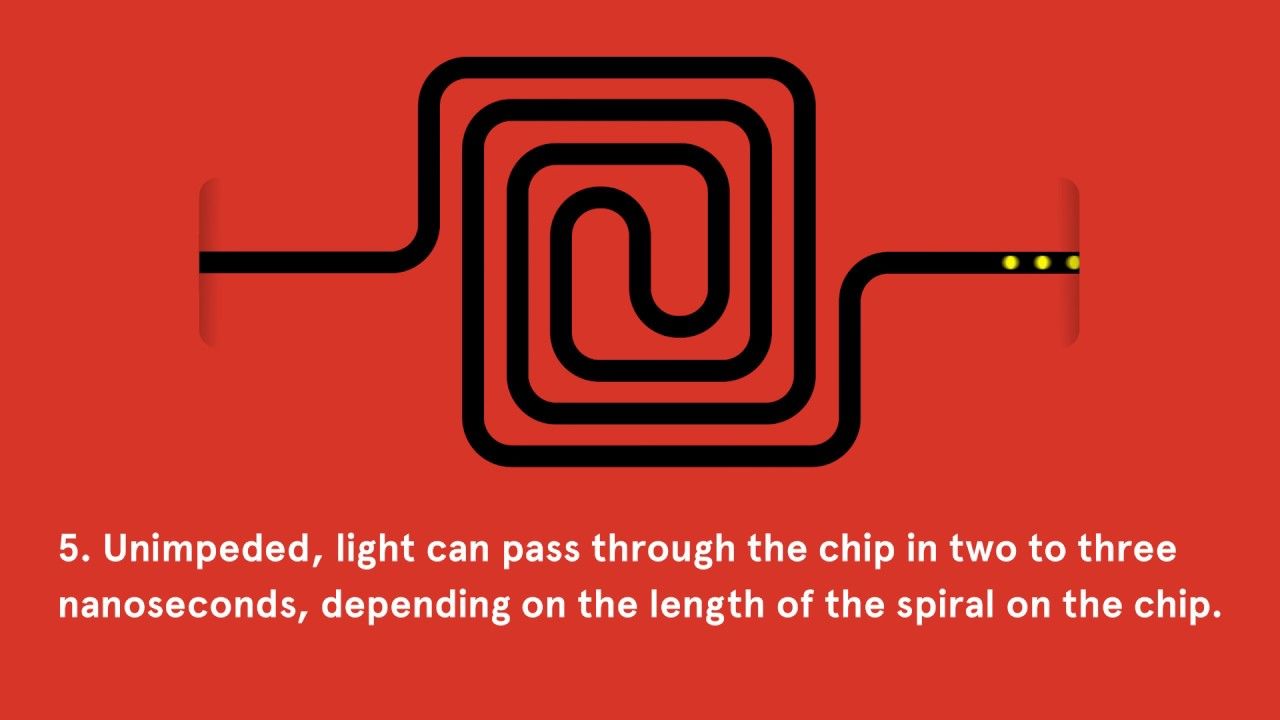
Last year, scientists took a big step towards creating the next generation of computers.
For the first time ever, they stored light-based information as sound waves on a computer chip — something the researchers compared to capturing lightning as thunder.
Continue reading “We Can Now Store Light as Sound, And It’s a Game Changer For Computing” »
Mar 3, 2018
Scientists observe a new quantum particle with properties of ball lightning
Posted by Genevieve Klien in categories: climatology, nuclear energy, particle physics, quantum physics
Scientists at Amherst College and Aalto University have created, for the first time a three-dimensional skyrmion in a quantum gas. The skyrmion was predicted theoretically over 40 years ago, but only now has it been observed experimentally.
In an extremely sparse and cold quantum gas, the physicists have created knots made of the magnetic moments, or spins, of the constituent atoms. The knots exhibit many of the characteristics of ball lightning, which some scientists believe to consist of tangled streams of electric currents. The persistence of such knots could be the reason why ball lightning, a ball of plasma, lives for a surprisingly long time in comparison to a lightning strike. The new results could inspire new ways of keeping plasma intact in a stable ball in fusion reactors.
‘It is remarkable that we could create the synthetic electromagnetic knot, that is, quantum ball lightning, essentially with just two counter-circulating electric currents. Thus, it may be possible that a natural ball lighting could arise in a normal lightning strike,’ says Dr Mikko Möttönen, leader of the theoretical effort at Aalto University.
Continue reading “Scientists observe a new quantum particle with properties of ball lightning” »
Mar 3, 2018
Scientists create ‘quantum ball lightning’ for the first time
Posted by Carse Peel in categories: climatology, nuclear energy, particle physics, quantum physics

Scientists create ‘quantum ball lightning’ in the lab in breakthrough that could pave the way for stable fusion reactors…
In the new research, led by scientists at Amherst College and Aalto University, the team created a three-dimensional skyrmion in an extremely cold quantum gas.
Continue reading “Scientists create ‘quantum ball lightning’ for the first time” »
Feb 23, 2018
CERN scientists get antimatter ready for its first road trip
Posted by Klaus Baldauf in categories: climatology, cosmology, particle physics
Antimatter is notoriously tricky to store and study, thanks to the fact that it will vanish in a burst of energy if it so much as touches regular matter. The CERN lab is one of the only places in the world that can readily produce the stuff, but getting it into the hands of the scientists who want to study it is another matter (pun not intended). After all, how can you transport something that will annihilate any physical container you place it in? Now, CERN researchers are planning to trap and truck antimatter from one facility to another.
Antimatter is basically the evil twin of normal matter. Each antimatter particle is identical to its ordinary counterpart in almost every way, except it carries the opposite charge, leading the two to destroy each other if they come into contact. Neutron stars and jets of plasma from black holes may be natural sources, and it even seems to be formed in the Earth’s atmosphere with every bolt of lightning.
Feb 12, 2018
The high-tech cities of the future
Posted by Shailesh Prasad in categories: climatology, habitats, sustainability
New cities are currently being planned to ease the strain on existing ones. In an ideal world, they should provide work and housing, and be sustainable and climate-neutral at the same time. Is this a realistic objective?
Feb 10, 2018
TAE Technologies pushes plasma machine to a new high on the nuclear fusion frontier
Posted by Klaus Baldauf in categories: climatology, nuclear energy, sustainability
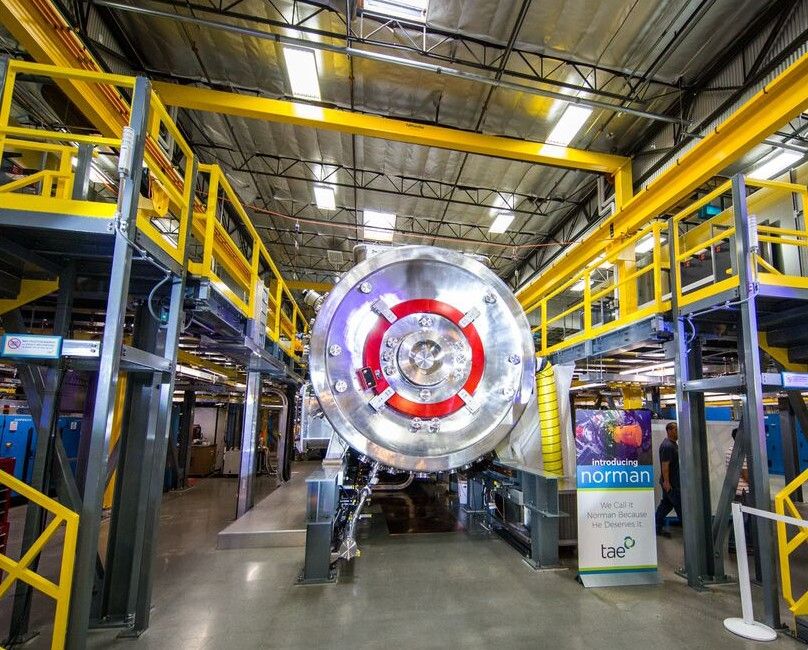

TAE Technologies, the California-based fusion company backed by Microsoft co-founder Paul Allen, said its latest and greatest plasma generator has exceeded the headline-grabbing performance of its previous machine.
“This announcement is an important milestone on our quest to deliver world-changing, clean fusion energy to help combat climate change and improve the quality of life for people globally,” Michl Binderbauer, the company’s president and chief technology officer, said in a news release. “This achievement further validates the robustness of TAE’s underlying science and unique pathway.”
Jan 9, 2018
A Fully Solar-Powered Car May Be Hitting The Road by 2019
Posted by Shailesh Prasad in categories: climatology, sustainability

Lightyear One, a car whose ability to use solar power has been thought of as an impossible feat, just won a Climate Change Innovator Award.
Designed by the Dutch startup Lightyear, the “car that charges itself” can supposedly drive for months without charging and has a 400–800 km range. But is a solar-powered car feasible?
Continue reading “A Fully Solar-Powered Car May Be Hitting The Road by 2019” »
Jan 5, 2018
Oxygen disappearing from world’s oceans, including Canada’s
Posted by Aleksandar Vukovic in categories: climatology, sustainability
All animals need to breathe oxygen and we know that regions of the ocean that are losing oxygen are becoming more and more common. We’re seeing the marine animals leaving those areas.
Almost two dozen marine scientists from around the world have issued a warning about an often-overlooked side effect of climate change and pollution.
In a paper published this week in Science, they say oxygen is disappearing from increasingly large areas of ocean and threatening marine life.
Continue reading “Oxygen disappearing from world’s oceans, including Canada’s” »













