Archive for the ‘computing’ category: Page 138
Feb 17, 2024
Algorithms don’t understand sarcasm. Yeah, right!
Posted by Dan Breeden in categories: computing, information science
Sarcasm, a complex linguistic phenomenon often found in online communication, often serves as a means to express deep-seated opinions or emotions in a particular manner that can be in some sense witty, passive-aggressive, or more often than not demeaning or ridiculing to the person being addressed. Recognizing sarcasm in the written word is crucial for understanding the true intent behind a given statement, particularly when we are considering social media or online customer reviews.
While spotting that someone is being sarcastic in the offline world is usually fairly easy given facial expression, body language and other indicators, it is harder to decipher sarcasm in online text. New work published in the International Journal of Wireless and Mobile Computing hopes to meet this challenge. Geeta Abakash Sahu and Manoj Hudnurkar of the Symbiosis International University in Pune, India, have developed an advanced sarcasm detection model aimed at accurately identifying sarcastic remarks in digital conversations, a task crucial for understanding the true intent behind online statements.
The team’s model comprises four main phases. It begins with text pre-processing, which involves filtering out common, or “noise,” words such as “the,” “it,” and “and.” It then breaks down the text into smaller units. To address the challenge of dealing with a large number of features, the team used optimal feature selection techniques to ensure the model’s efficiency by prioritizing only the most relevant features. Features indicative of sarcasm, such as information gain, chi-square, mutual information, and symmetrical uncertainty, are then extracted from this pre-processed data by the algorithm.
Feb 17, 2024
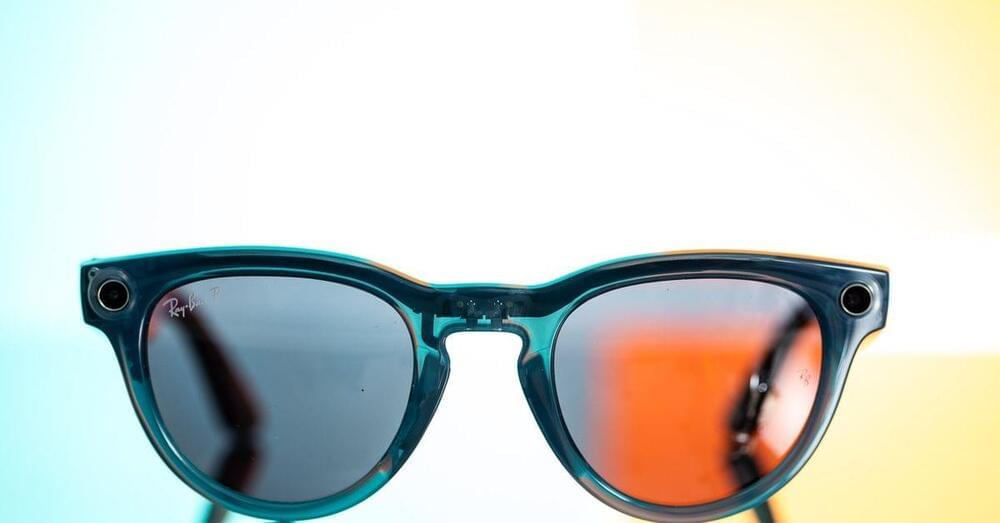
Meta’s big vision for face computers might be better than Apple’s
Posted by Shailesh Prasad in categories: computing, futurism
And it’s also about seven times the price of the Quest 3, Meta’s current answer to the Vision Pro. It’s not as flashy as the Vision Pro, but right now you can do a lot more with it. Meta CEO Mark Zuckerberg was eager to point that out in his impromptu review of Apple’s headset. Meta’s strategy is focusing on what you can do now, and doing that gives people a reason to stick around. If they stick around, they’ve inherently bought into your idea of the future.
It’s too early to say how Apple’s tried-and-true approach will pan out. But a common complaint I’ve seen from Vision Pro buyers is they don’t know what to do with it besides watch movies. It’s also too early to say whether Meta glasses users will stick around long term. (They certainly didn’t for the Ray-Ban Stories.) But we do know one thing: at the end of his Vision Pro review, Zuckerberg said the Ray-Ban Meta Smart Glasses sales have far exceeded his hopes.
Feb 17, 2024
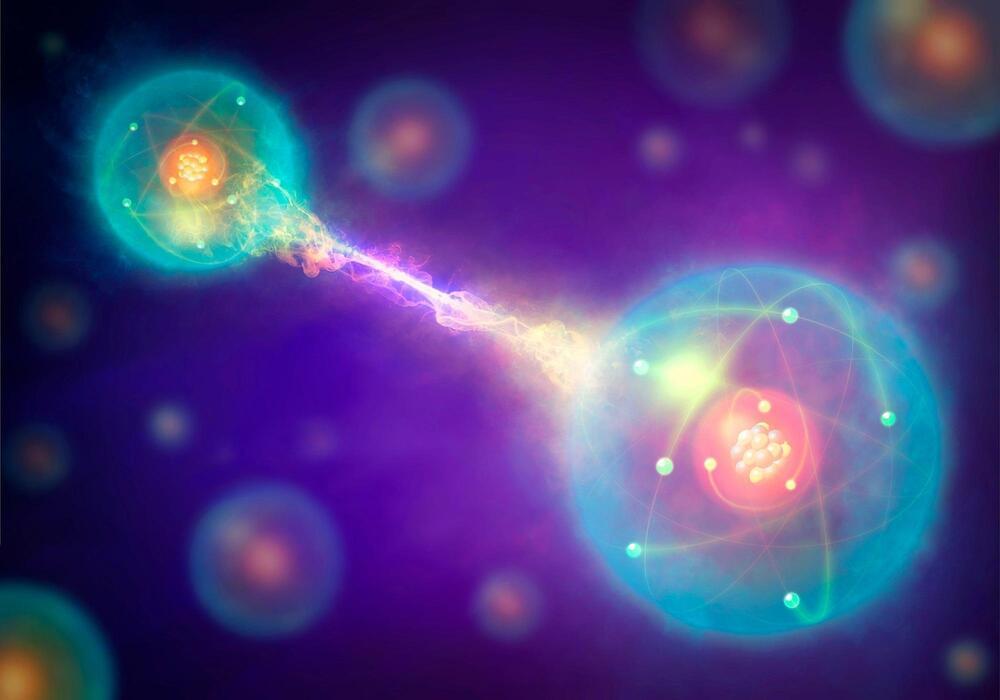
Quantum Breakthrough: New Method Preserves Information Against All Odds
Posted by Dan Breeden in categories: computing, quantum physics
Add a dash of creamer to your morning coffee, and clouds of white liquid will swirl around your cup. But give it a few seconds, and those swirls will disappear, leaving you with an ordinary mug of brown liquid.
Something similar happens in quantum computer chips—devices that tap into the strange properties of the universe at its smallest scales—where information can quickly jumble up, limiting the memory capabilities of these tools.
That doesn’t have to be the case, said Rahul Nandkishore, associate professor of physics at the University of Colorado Boulder.
Feb 17, 2024
Infleqtion Unveils Quantum Roadmap for Quantum Sensing, Software and Computing Products
Posted by Dan Breeden in categories: business, computing, engineering, particle physics, quantum physics
Infleqtion is unique amongst quantum companies due its participation in so many different segments of the quantum computing industry including quantum components, quantum computers, quantum software, and quantum sensors. This strategy of a broad product portfolio provides both advantages and disadvantages for a company. The potential advantages include achieving synergy between different product areas with the neutral atom, atomic prism, photonic, software, and other technologies they have developed over the years. It also brings some diversity in the revenue streams because some products will provide early revenue while others might take a few years of development before they can make a revenue contribution. The potential disadvantages could include execution risks if the engineering resources are spread too thin. Also, there may be different sets of customers and sales channels for the different product lines which can increase the complexities of managing a sales force, calling on customers, and generating new business.
Nonetheless, Infleqtion has made some interesting announcements in the past few months. In 2023 alone, the Quantum Computing Report by GQI ran 17 different stories that included Infleqtion. This week they hosted a webinar to discuss their product roadmaps for sensors, software, and computing. The highlight of the webinar was the announcement of their quantum computing roadmap. In this article, we will cover their plans for quantum computing, but first we will start with the progress they talked about in quantum sensors and quantum software and then discuss quantum computing afterwards.
Infleqtion’s discussion of sensor products included ones named Tiqker, Sqywire, and eXaqt. Tiqker is a small form factor ultra-accurate clock intended for use in navigation, data centers, and communication networks. The company asserts that this clock is 100X more accurate than cesium beam atomic clocks and 100,000X more accurate than a crystal oscillator. In navigation applications it can be used in GPS-denied environments and in communication networks it can help increase bandwidth and reduce latencies due to the more precise clocking of the data signals. The company mentioned that they are partnering with a large company for use of Tiqker in data center applications and that Tiqker is now available for pre-order. Sqywire is an ultra-sensitive radio frequency (RF) receiver that senses RF signals with Rydberg state atom-based sensing. It can be used installed of a classical antenna and provides high sensitivity, lower power, and ultra-wide bandwidth in a form factor.
Feb 16, 2024
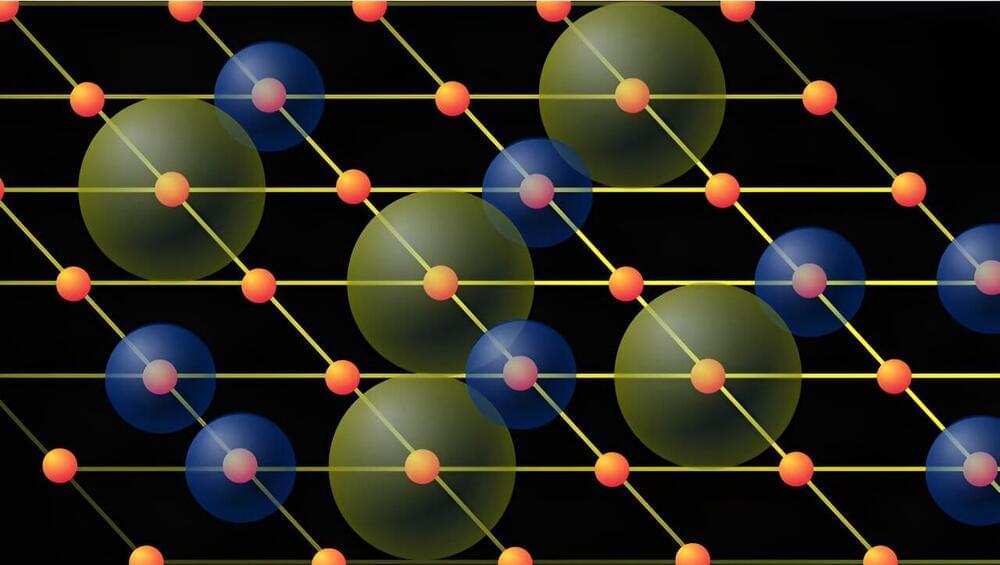
Voltage Control over Magnons
Posted by Saúl Morales Rodriguéz in categories: computing, materials
Researchers have demonstrated that magnetic spin waves called magnons can be controlled by voltage and thus could operate more efficiently as information carriers in future devices.
Magnonic devices are being developed to transmit signals, not with electrons, but with magnons—traveling waves in the magnetic ordering of a material. New work provides one of the missing elements of the magnonics toolbox: a voltage-controlled magnon transistor [1]. The device is made up of a magnetic insulator sandwiched between two metal plates. The researchers show that they can control the flow of magnons in the insulator through voltages applied to the plates. The results could lead to more-efficient magnonic devices.
A magnon can be imagined as a row of fixed magnetic elements, or “spins,” that tilt and rotate their orientations in a coordinated pattern. This “spin wave” can carry information through a material without involving the movement of charges, which can cause undesirable heating in a circuit. Magnonics—though still in its infancy—is a potentially energy-efficient alternative to traditional electronics, says Xiu-Feng Han from the Chinese Academy of Sciences. The challenge right now for the magnonics field, he says, is developing practical versions of the four basic components of a magnonic circuit: a generator, a detector, a switch, and a transistor.
Feb 16, 2024
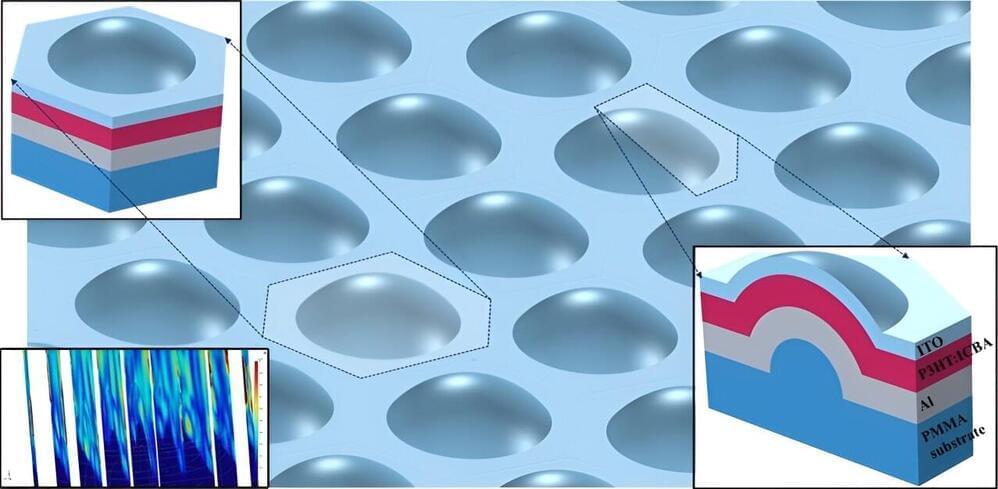
Harnessing light with hemispherical shells for improved photovoltaics
Posted by Saúl Morales Rodriguéz in categories: computing, solar power, sustainability
In the pursuit of sustainable energy solutions, the quest for more efficient solar cells is paramount. Organic photovoltaic cells have emerged as a promising alternative to traditional silicon-based counterparts due to their flexibility and cost-effectiveness. However, optimizing their performance remains a significant challenge.
In a pioneering move, new research from Abdullah Gül University (Türkiye) reimagines the structure of organic photovoltaic cells, opting for a hemispherical shell shape to unlock unprecedented potential in light absorption and angular coverage.
As reported in the Journal of Photonics for Energy, this innovative configuration aims to maximize light absorption and angular coverage, promising to redefine the landscape of renewable energy technologies. The study presents advanced computational analysis and comparative benchmarks to spotlight the remarkable capabilities of this new design.
Feb 16, 2024
Fermi Paradox: The Impossible Earth hypothesis
Posted by Dan Breeden in categories: computing, existential risks, life extension

The aliens haven’t contacted us because they have uploaded themselves into digital information where they live forever anf create simulated universes that they live in or they upload themselves into femto tech level computational substrates and they could surround us.
Is Earth impossible? An exploration of the impossible earth hypothesis and its implications on science and existence.
Continue reading “Fermi Paradox: The Impossible Earth hypothesis” »
Feb 16, 2024
Scientists Create World’s First “Quantum Semiconductor”
Posted by Dan Breeden in categories: biotech/medical, computing, mobile phones, quantum physics
Semiconductor devices are small components that manage the movement of electrons in contemporary electronic gadgets. They are essential for powering a wide range of high-tech products, including cell phones, laptops, and vehicle sensors, as well as cutting-edge medical devices. However, the presence of material impurities or variations in temperature can interfere with electron flow, causing instability.
But now, theoretical and experimental physicists from the Würzburg-Dresden Cluster of Excellence ct.qmat—Complexity and Topology in Quantum Matter have developed a semiconductor device from aluminum-gallium-arsenide (AlGaAs). This device’s electron flow, usually susceptible to interference, is safeguarded by a topological quantum phenomenon. This groundbreaking research was recently detailed in the esteemed journal Nature Physics.
“Thanks to the topological skin effect, all of the currents between the different contacts on the quantum semiconductor are unaffected by impurities or other external perturbations. This makes topological devices increasingly appealing for the semiconductor industry. They eliminate the need for the extremely high levels of material purity that currently drive up the costs of electronics manufacturing,” explains Professor Jeroen van den Brink, director of the Institute for Theoretical Solid State Physics at the Leibniz Institute for Solid State and Materials Research in Dresden (IFW) and a principal investigator of ct.qmat.
Feb 16, 2024
A new design for quantum computers
Posted by Dan Breeden in categories: computing, encryption, finance, quantum physics
Creating a quantum computer powerful enough to tackle problems we cannot solve with current computers remains a big challenge for quantum physicists. A well-functioning quantum simulator—a specific type of quantum computer—could lead to new discoveries about how the world works at the smallest scales.
Quantum scientist Natalia Chepiga from Delft University of Technology has developed a guide on how to upgrade these machines so that they can simulate even more complex quantum systems. The study is now published in Physical Review Letters.
“Creating useful quantum computers and quantum simulators is one of the most important and debated topics in quantum science today, with the potential to revolutionize society,” says researcher Natalia Chepiga. Quantum simulators are a type of quantum computer. Chepiga explains, “Quantum simulators are meant to address open problems of quantum physics to push our understanding of nature further. Quantum computers will have wide applications in various areas of social life, for example, in finances, encryption, and data storage.”