Nov 29, 2023
Dark matter could help solve the final parsec problem of black holes
Posted by Dan Breeden in categories: computing, cosmology, information science, physics
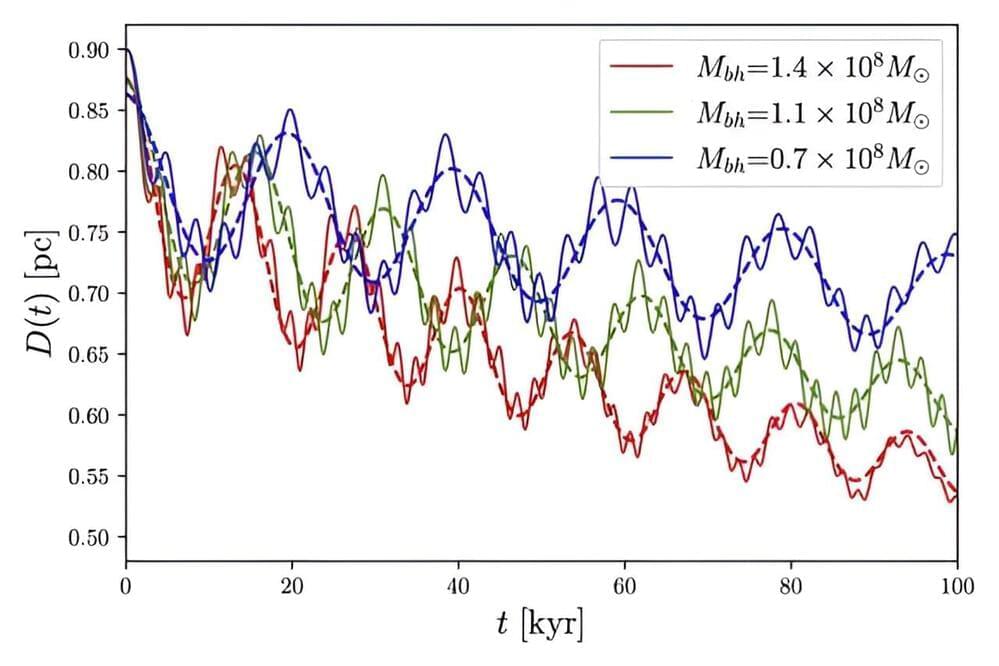
When galaxies collide, their supermassive black holes enter into a gravitational dance, gradually orbiting each other ever closer until eventually merging. We know they merge because we see the gravitational beasts that result, and we have detected the gravitational waves they emit as they inspiral. But the details of their final consummation remain a mystery. Now a new paper published on the pre-print server arXiv suggests part of that mystery can be solved with a bit of dark matter.
Just as the famous three-body problem has no general analytical solution for Newtonian gravity, the two-body problem has no general solution in general relativity. So, we have to resort to computer simulations to model how black holes orbit each other and eventually merge.
For binary black holes that are relatively widely separated, our simulations work really well, but when black holes are close to each other things get complicated. Einstein’s equations are very nonlinear, and modeling the dynamics of strongly interacting black holes is difficult.