Accurately reconstructing how the parts of a complex molecular are held together knowing only how the molecule distorts and breaks up—this was the challenge taken on by a research team led by SISSA’s Cristian Micheletti and recently published on Physical Review Letters. In particular, the scientists studied how a DNA double helix unzips when translocated at high velocity through a nanopore, reconstructing fundamental DNA thermodynamic properties from the sole speed of the process.
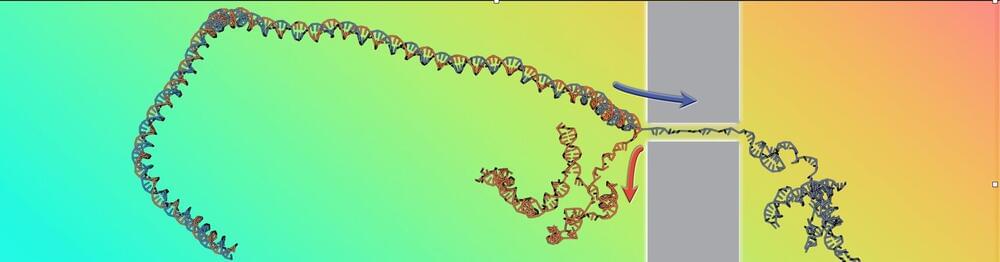
The translocation of polymers through nanopores has long studied as a fundamental theoretical problem as well as for its several practical ramifications, e.g. for genome sequencing. We recall that the latter involves driving a DNA filament through a pore so narrow that only one of the double-helical strands can pass, while the other strand is left behind. As a result, the translocated DNA double helix will necessarily split and unwind, an effect known as unzipping.
The research team, which also includes Antonio Suma from the University of Bari, first author, and Vincenzo Carnevale from Temple University, used a cluster of computers to simulate the process with different driving forces keeping track of the DNA’s unzipping speed, a type of data that has rarely been studied despite being directly accessible in experiments.