Archive for the ‘computing’ category: Page 362
Jun 12, 2022
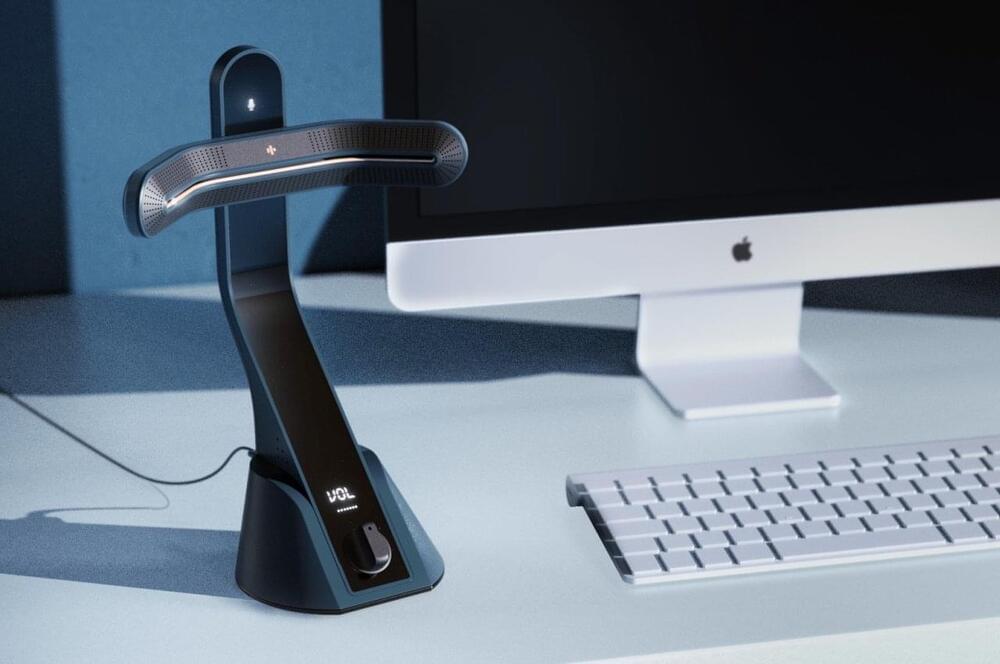
This desk microphone makes it painfully clear whether you are muted or not
Posted by Shubham Ghosh Roy in categories: computing, education
It’s amazing how simple designs can save you from hours of frustration and embarrassment, even virtually.
Work and School from Home arrangements have forced many people to get used to video meetings, virtual classrooms, and online presentations. As if those weren’t stressful enough already, the horrors of discovering that you have been speaking for the past 10 minutes to half an hour when you’re mic has been on mute all the time only adds to feelings of dread. Unfortunately, computers and software haven’t adjusted yet to these new demands on life, lacking clear indicators on the status of the mic. While there might be some sophisticated and complicated software that could try to guess whether you actually need to be muted or not, it actually takes a dead-simple idea to give that peace of mind at very little extra cost.
Designer: Yaman Gupta
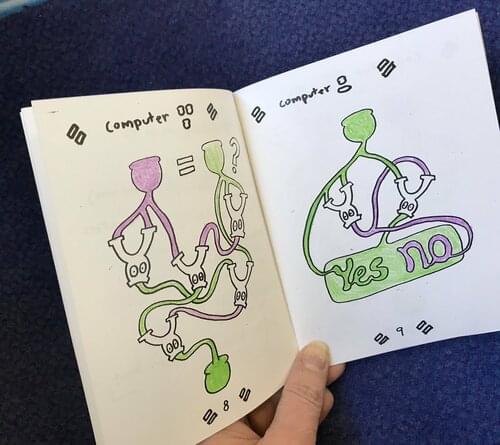
download the ready-to-print-and-cut zine (pdf). to recreate the zine: print double-sided, cut in half, fold the pages and assemble in order.
download the page-by-page zine (pdf). this one is easier to read in a browser and better if you want to extract and print individual pages in letter size.
Jun 12, 2022
Glimpses of quantum computing phase changes show researchers the tipping point
Posted by Saúl Morales Rodriguéz in categories: computing, quantum physics
Researchers at Duke University and the University of Maryland have used the frequency of measurements on a quantum computer to get a glimpse into the quantum phenomena of phase changes—something analogous to water turning to steam.
By measuring the number of operations that can be implemented on a quantum computing system without triggering the collapse of its quantum state, the researchers gained insight into how other systems—both natural and computational—meet their tipping points between phases. The results also provide guidance for computer scientists working to implement quantum error correction that will eventually enable quantum computers to achieve their full potential.
The results appeared online June 3 in the journal Nature Physics.
Jun 12, 2022
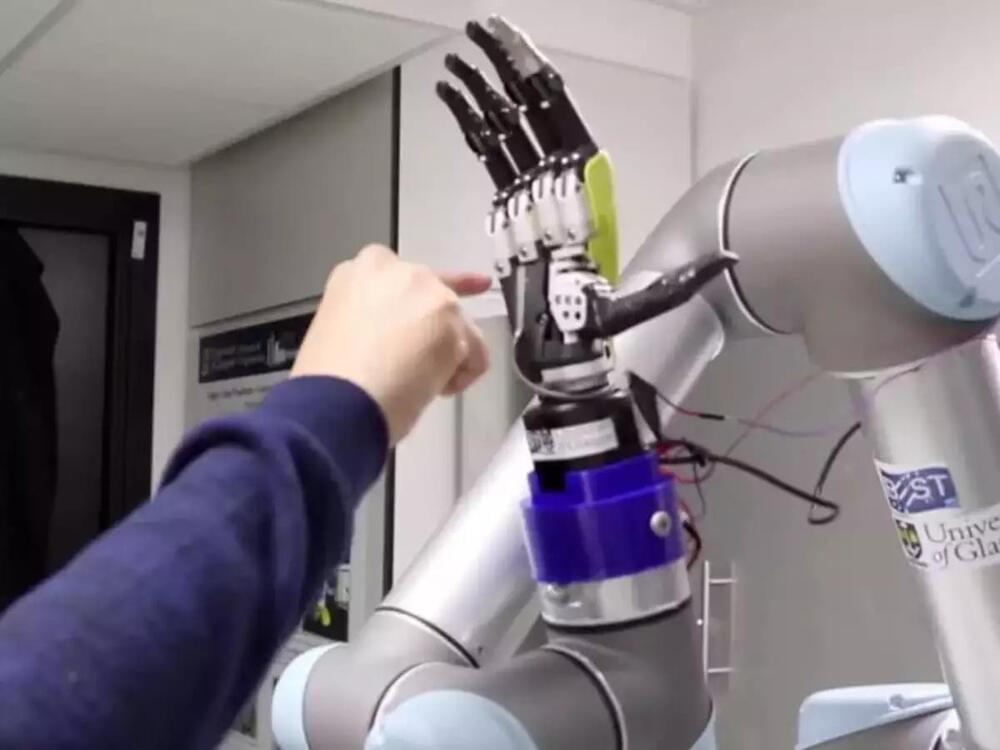
A team of researchers led by an Indian-origin engineer developed an electronic skin that feels pain
Posted by Shubham Ghosh Roy in categories: computing, cyborgs
Researchers have created an electronic skin that can feel pain. The working of artificial skin is based on synaptic transistors that eliminate the response time.
It took 157 days to calculate and required 128 vCPUs, 864GB of RAM, and 515 terabytes of storage.
Jun 11, 2022
AMD Updated EPYC Roadmap: 5th Gen EPYC “Turin” Announced, Coming
Posted by Shubham Ghosh Roy in categories: computing, finance
As part of AMD’s Financial Analysts Day 2022, AMD has provided updates to its Server CPU roadmap going into 2024. The biggest announcement is that AMD is already planning for the (next) next-gen core for its successful EPYC family, the 5th generation EPYC series, which has been assigned the codenamed Turin. Some key announcements include various segmentations of its expected EPYC 7,004 portfolio, including Genoa, Bergamo, Genoa-X, and Siena.
Jun 10, 2022
Decoding a key part of the cell, atom
Posted by Shubham Ghosh Roy in categories: computing, genetics, nanotechnology, nuclear energy, particle physics
Whatever you are doing, whether it is driving a car, going for a jog, or even at your laziest, eating chips and watching TV on the couch, there is an entire suite of molecular machinery inside each of your cells hard at work. That machinery, far too small to see with the naked eye or even with many microscopes, creates energy for the cell, manufactures its proteins, makes copies of its DNA, and much more.
Among those pieces of machinery, and one of the most complex, is something known as the nuclear pore complex (NPC). The NPC, which is made of more than 1,000 individual proteins, is an incredibly discriminating gatekeeper for the cell’s nucleus, the membrane-bound region inside a cell that holds that cell’s genetic material. Anything going in or out of the nucleus has to pass through the NPC on its way.
Nuclear pores stud the surface of the cell’s nucleus, controlling what flows in and out of it. (Image: Valerie Altounian)
Jun 10, 2022
Whole human genome sequencing for $100
Posted by Future Timeline in categories: biotech/medical, chemistry, computing, genetics, health
“When the Human Genome Project began in 1990, it had a projected budget of $3 billion. […] Now, one company claims to have achieved the major milestone of whole genome sequencing for just $100.”
Ultima Genomics, a biotech company based in California, has emerged from stealth mode with a new high-throughput, low-cost sequencing platform that it claims can deliver a $100 genome.
When the Human Genome Project began in 1990, it had a projected budget of $3 billion. Some researchers believed it would take centuries to map all 20,000+ genes and to determine the sequence of chemical base pairs making up DNA, though in the end it took 13 years. Since then, genome sequencing has undergone technology and cost improvements at a rate faster than Moore’s Law (a long-term trend in the computer industry that involves a doubling of performance every two years). What used to require billions of dollars and many years of work is now several orders of magnitude cheaper and possible in a matter of hours.
Jun 10, 2022
Room-temperature molecular switch discovery paves the way for faster computers, longer-lasting batteries
Posted by Jose Ruben Rodriguez Fuentes in categories: computing, mathematics, quantum physics
University of Queensland scientists have cracked a problem that’s frustrated chemists and physicists for years, potentially leading to a new age of powerful, efficient, and environmentally friendly technologies.
Using quantum mechanics, Professor Ben Powell from UQ’s School of Mathematics and Physics has discovered a “recipe” which allows molecular switches to work at room temperature.
“Switches are materials that can shift between two or more states, such as on and off or 0 and 1, and are the basis of all digital technologies,” Professor Powell said. “This discovery paves the way for smaller and more powerful and energy efficient technologies. You can expect batteries will last longer and computers to run faster.”