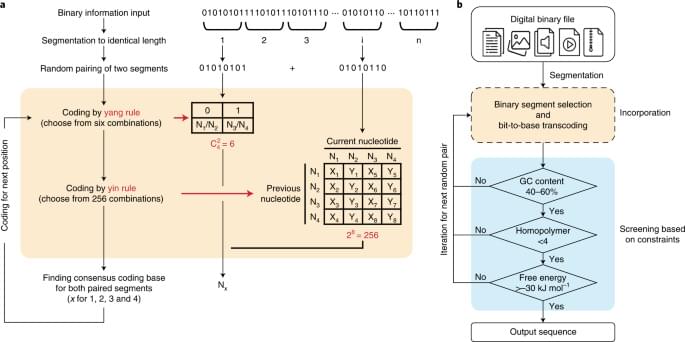
The yin-yang codec transcoding algorithm is proposed to improve the practicality and robustness of DNA data storage.
Given these results, YYC offers the opportunity to generate DNA sequences that are highly amenable to both the ‘writing’ (synthesis) and ‘reading’ (sequencing) processes while maintaining a relatively high information density. This is crucially important for improving the practicality and robustness of DNA data storage. The DNA Fountain and YYC algorithms are the only two known coding schemes that combine transcoding rules and screening into a single process to ensure that the generated DNA sequences meet the biochemical constraints. The comparison hereinafter thus focuses on the YYC and DNA Fountain algorithms because of the similarity in their coding strategies.
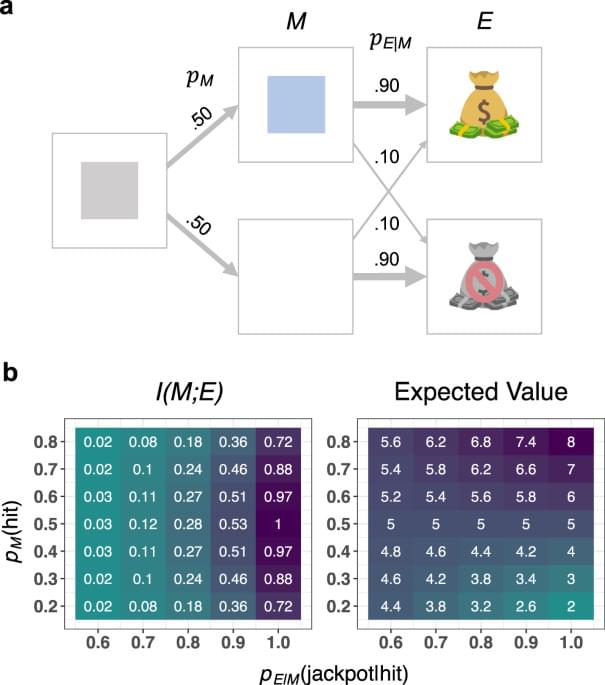
The robustness of data storage in DNA is primarily affected by errors introduced during ‘writing’ and ‘reading’. There are two main types of errors: random and systematic errors. Random errors are often introduced by synthesis or sequencing errors in a few DNA molecules and can be redressed by mutual correction using an increased sequencing depth. System atic errors refer to mutations observed in all DNA molecules, including insertions, deletions and substitutions, which are introduced during synthesis and PCR amplification (referred to as common errors), or the loss of partial DNA molecules. In contrast to substitutions (single-nucleotide variations, SNVs), insertions and deletions (indels) change the length of the DNA sequence encoding the data and thus introduce challenges regarding the decoding process. In general, it is difficult to correct systematic errors, and thus they will lead to the loss of stored binary information to varying degrees.
Continue reading “Towards practical and robust DNA-based data archiving using the yin–yang codec system” »